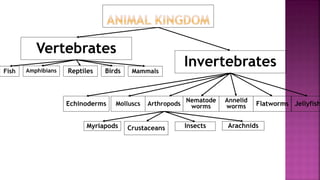
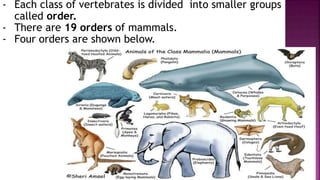
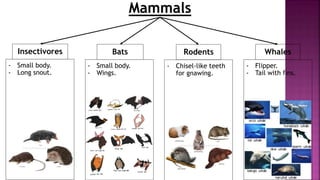
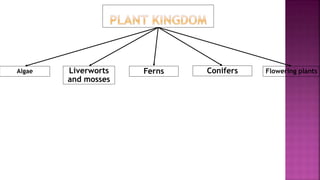
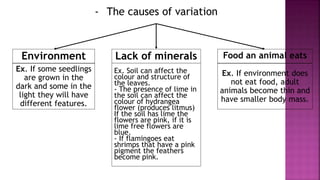
This document summarizes different types of organisms including vertebrates like mammals, fish, birds, reptiles and amphibians as well as invertebrates like jellyfish, flatworms, annelid worms, nematode worms, arthropods, molluscs and echinoderms. It also discusses simple plants like algae, liverworts and mosses, as well as ferns, conifers and flowering plants. The document notes there is variation both between and within species due to environmental factors and availability of food and minerals.