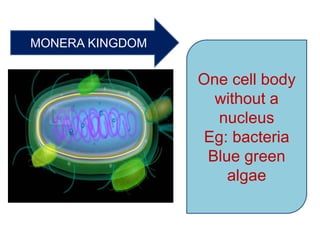
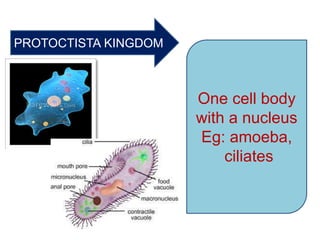
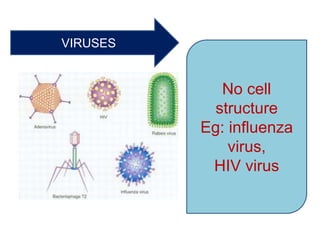
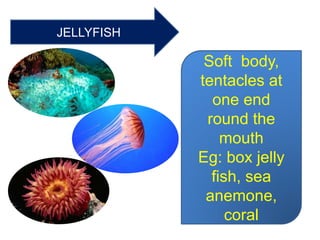
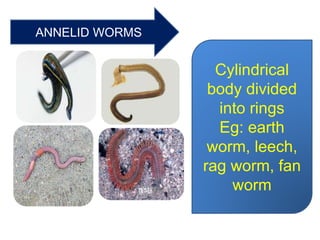
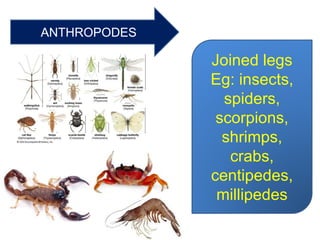
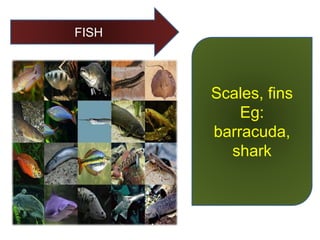
This document provides a classification of the main kingdoms of living things: microorganisms, plant, and animal kingdoms. Microorganisms are divided into four groups - fungi, monera, protoctista, and viruses. The plant kingdom is divided into five groups - algae, liverworts and mosses, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants. The animal kingdom is divided into two main groups - invertebrates and vertebrates. Examples are given for major subgroups under each kingdom.