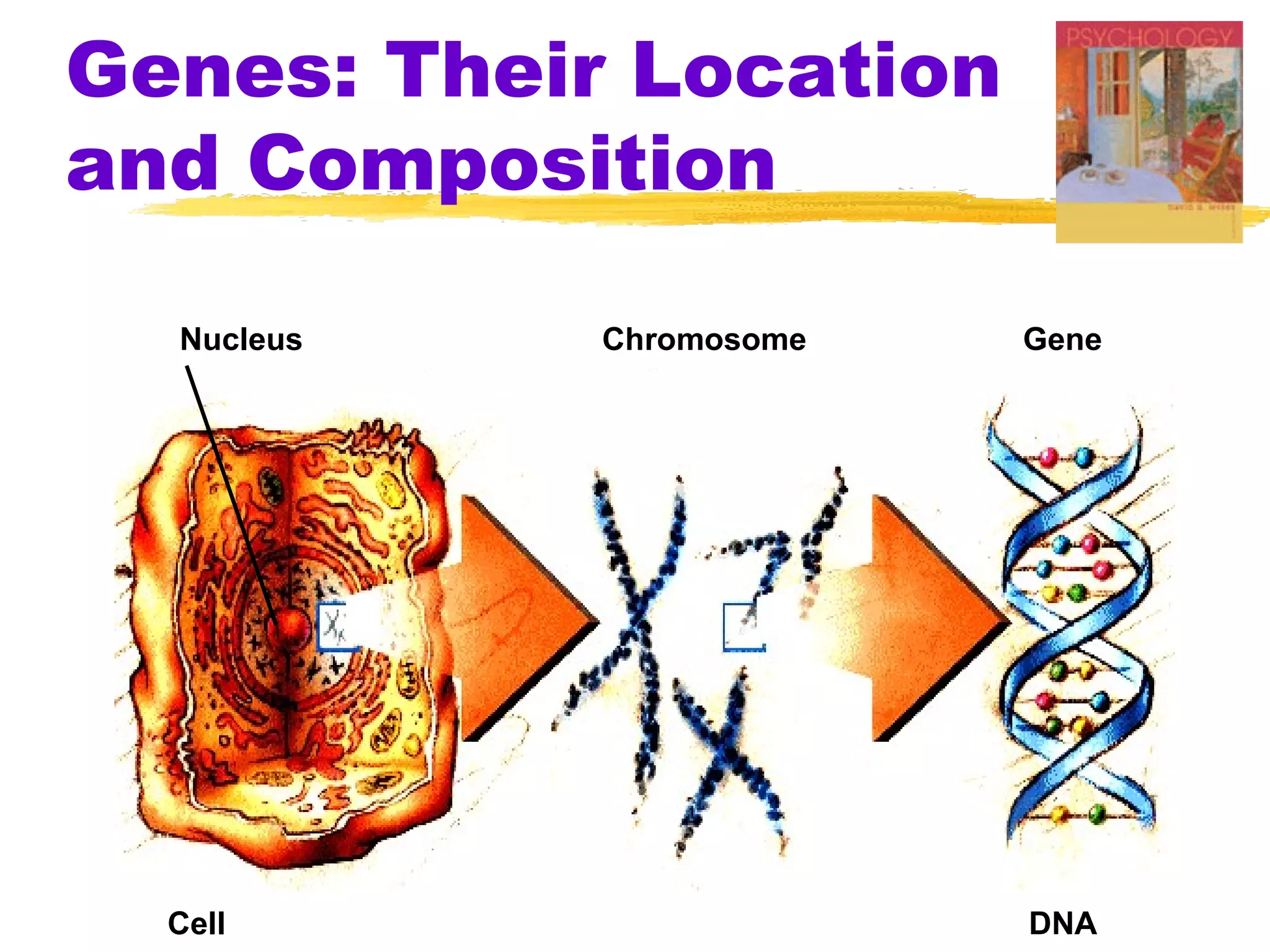
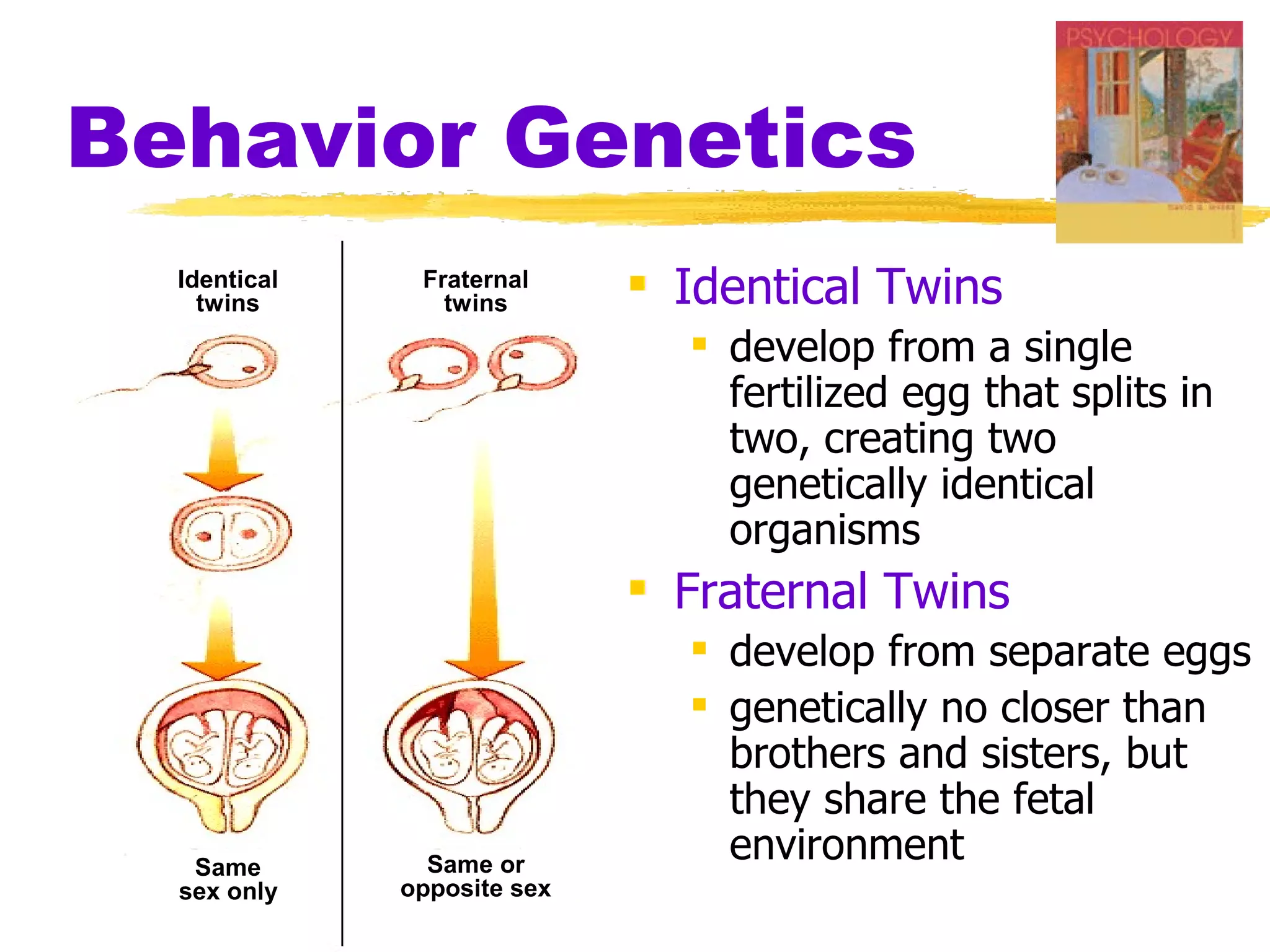
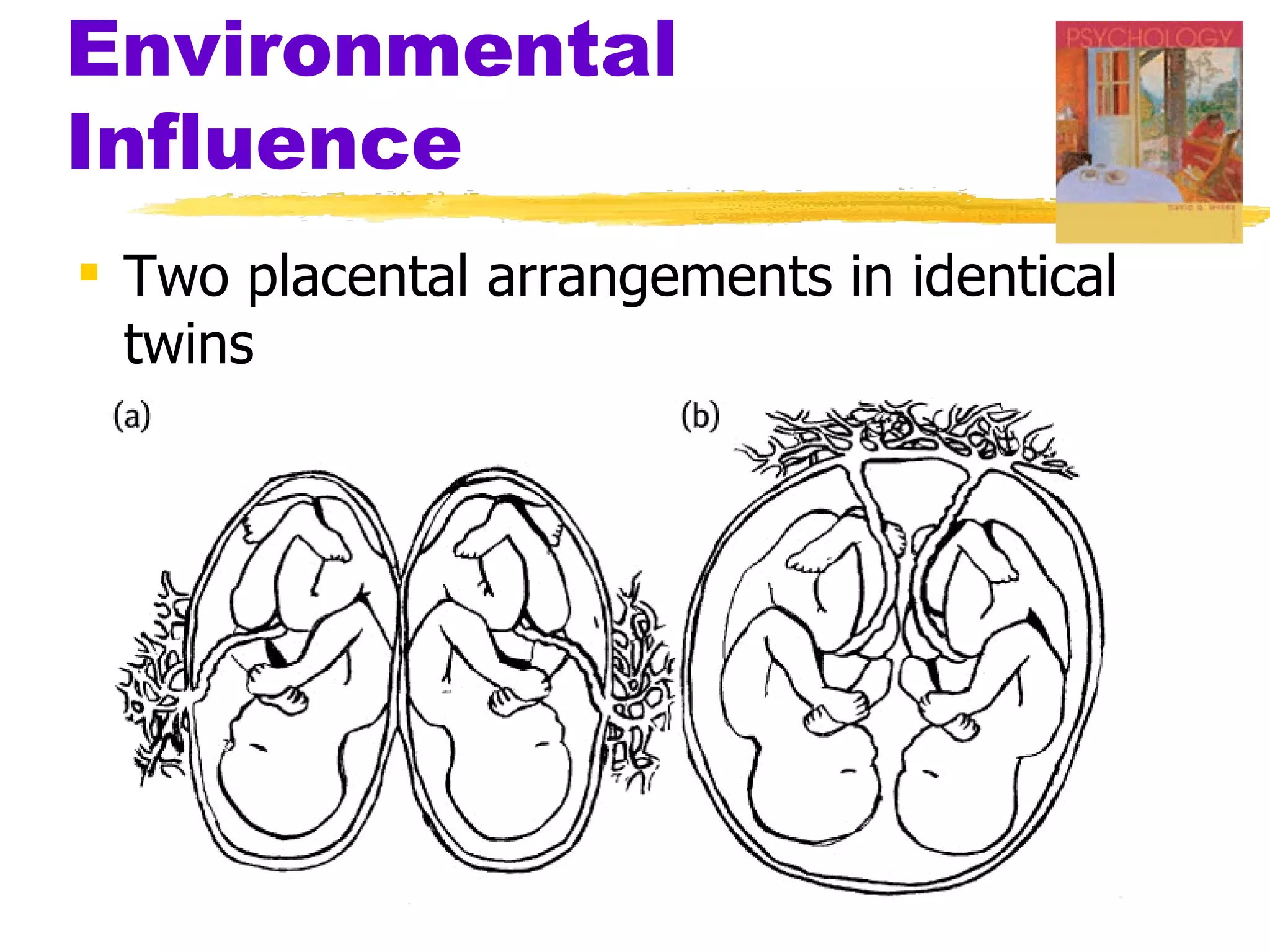
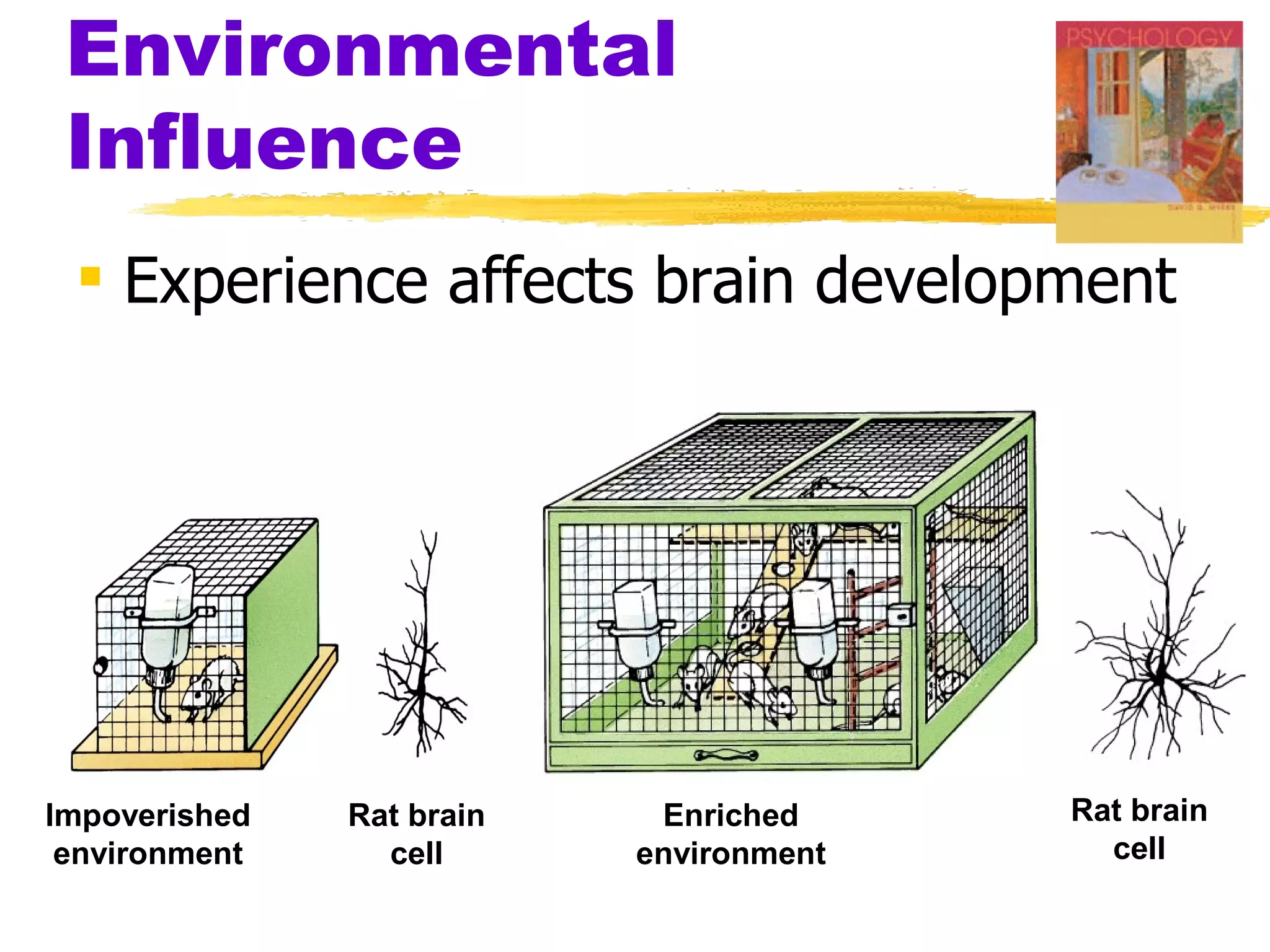
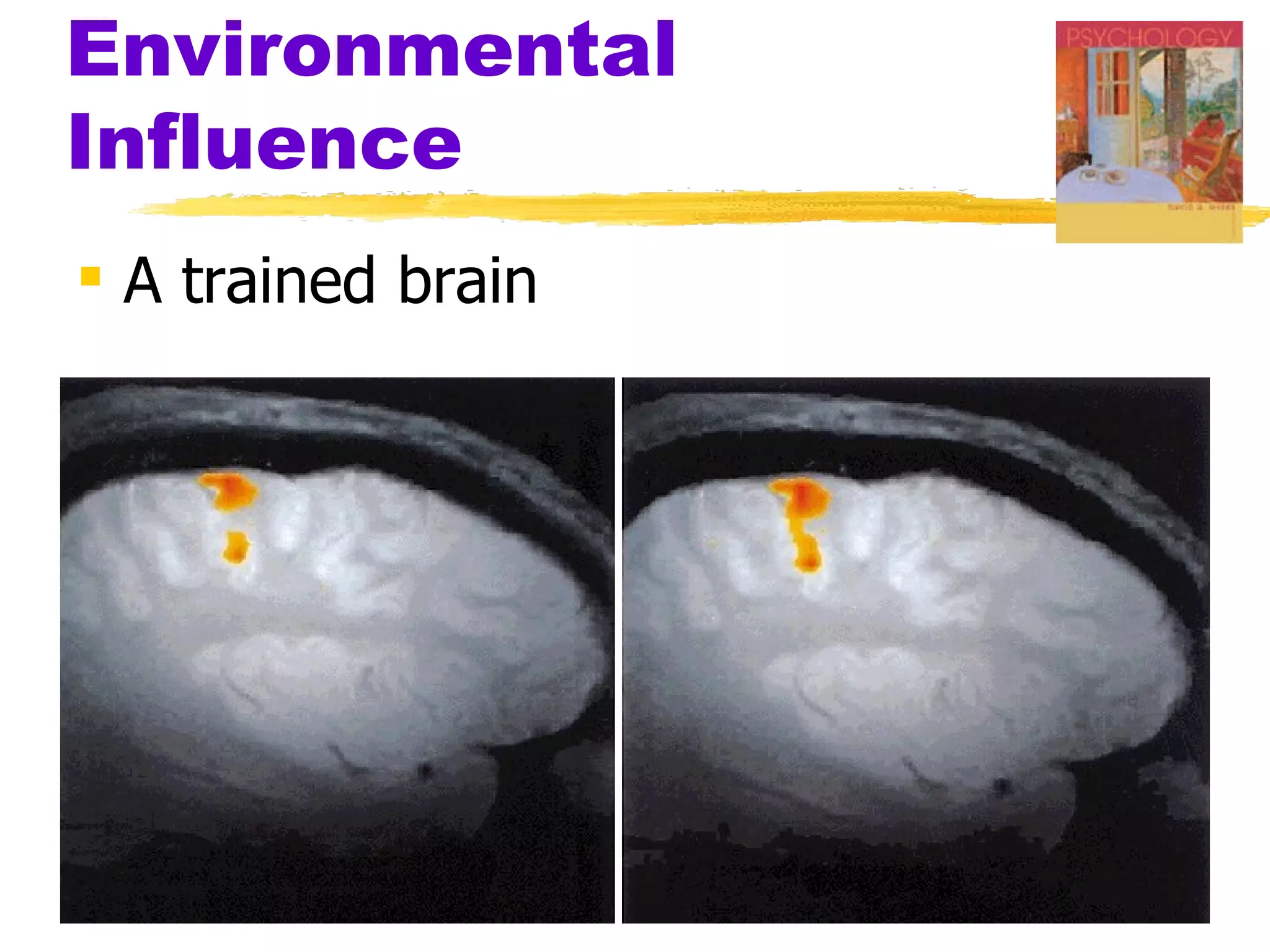
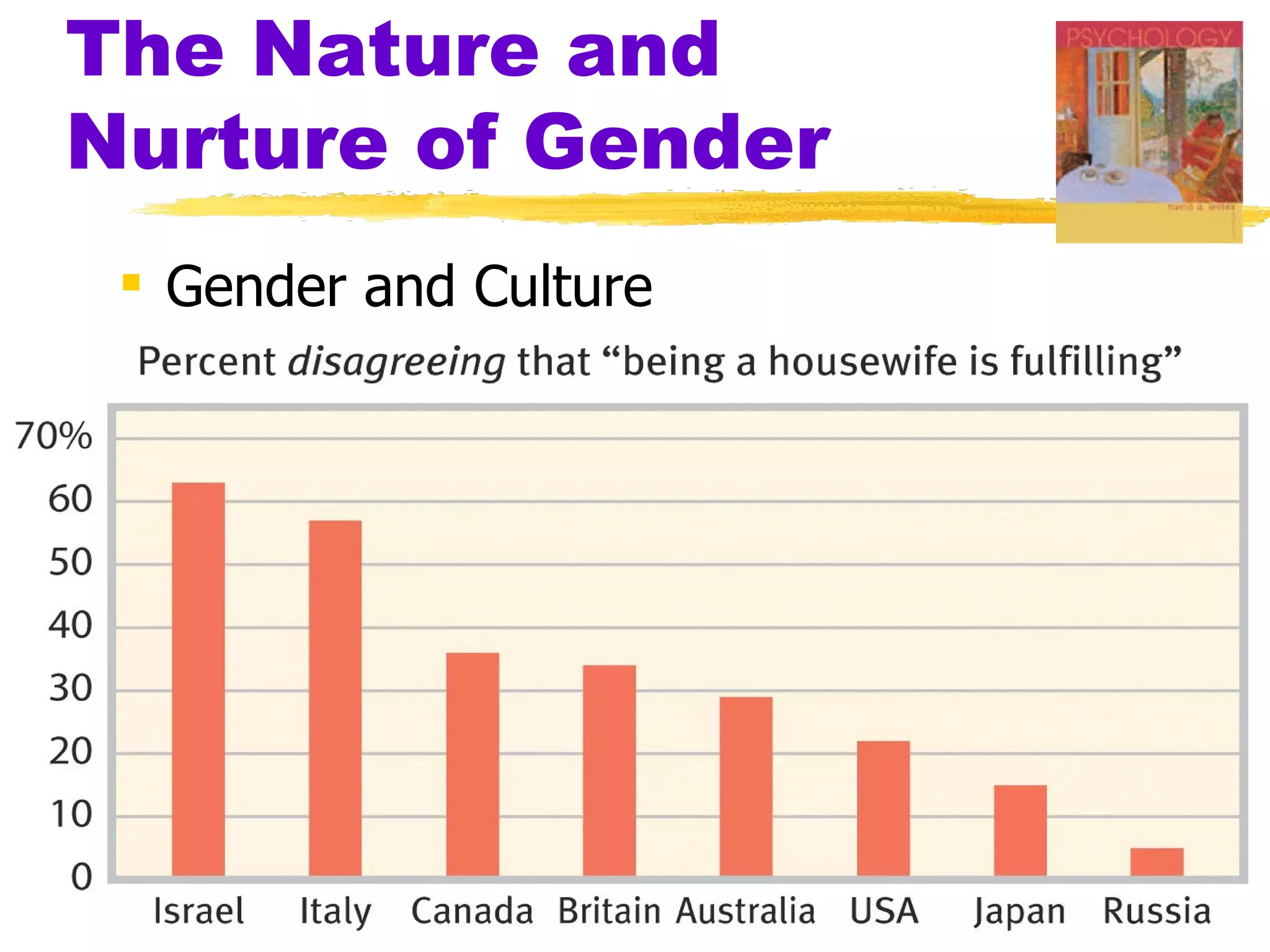
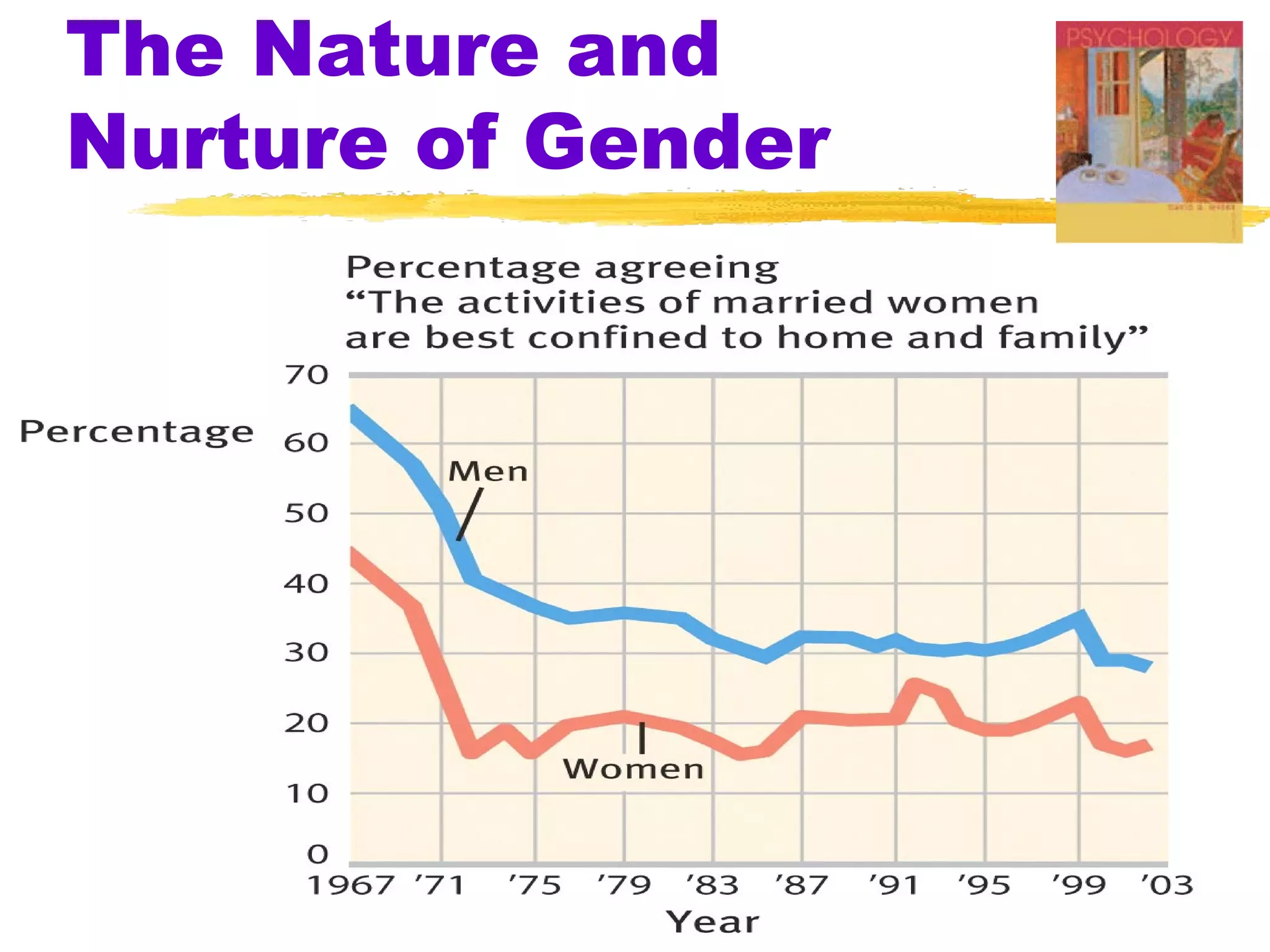
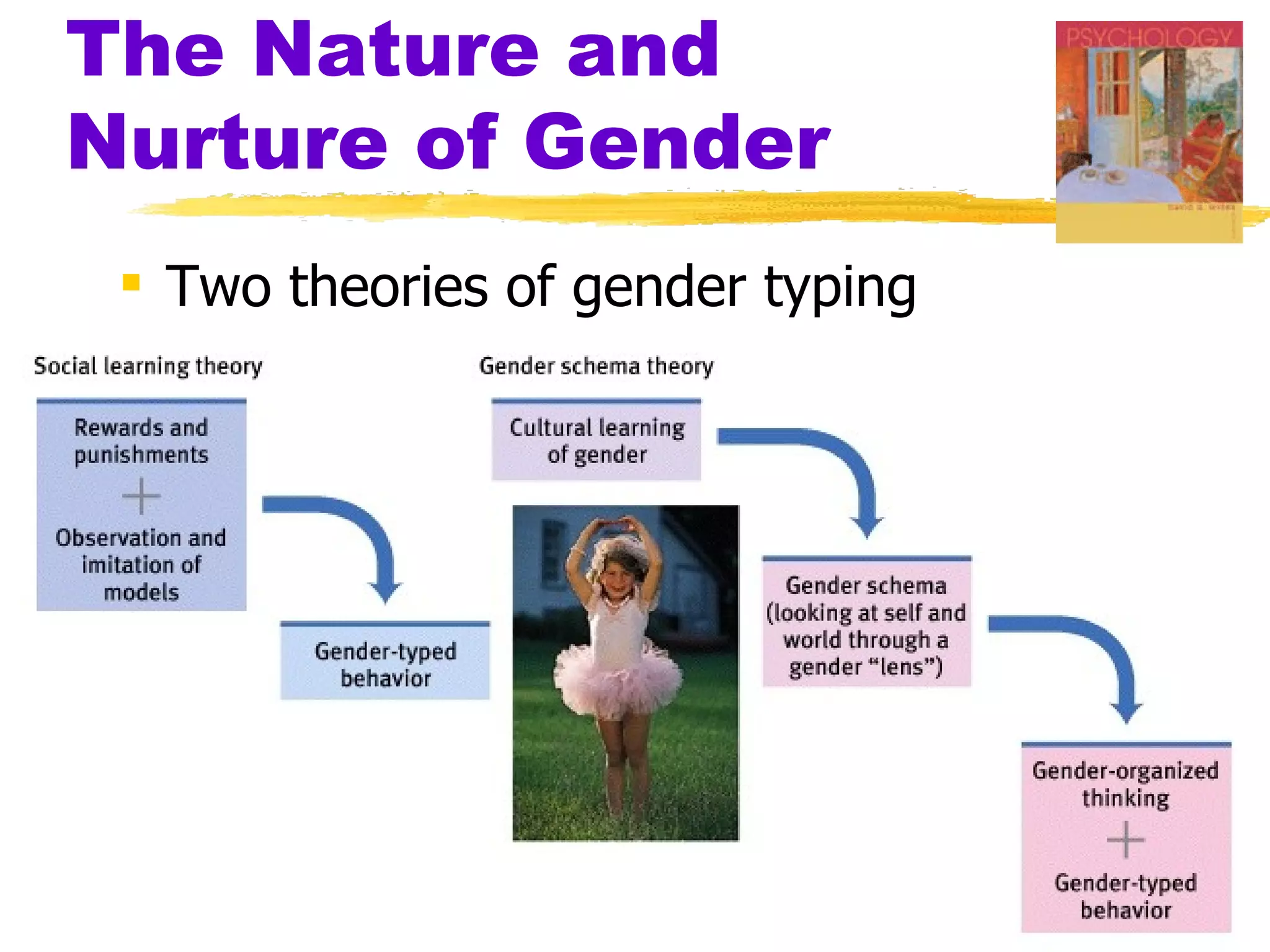
The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of Myers' Psychology textbook regarding the nature and nurture of behavior and gender. It discusses how genes contain the biological blueprint in DNA and chromosomes, and how evolutionary psychology studies the evolution of behavior. Behavior genetics examines the influence of heredity and environment on behaviors and traits. While genes and hormones influence gender, culture and social learning also strongly impact the formation of gender roles, identity, and expression.