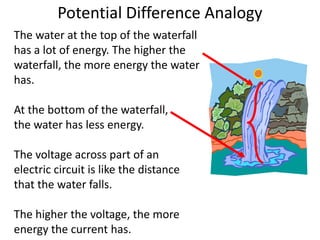
This document summarizes key concepts about quantifying electricity including electric potential energy, electric potential difference (voltage), and how to calculate energy using voltage and charge. It defines electric potential energy as the amount of energy stored in each coulomb, measured in joules. It explains that voltage is the difference in electric potential energy on either side of a source or load, measured in volts. It provides an analogy that voltage is like the height of a waterfall, with higher voltage meaning more energy. Finally, it gives the formula that potential difference equals energy divided by charge, and provides an example calculation of energy used by a hair dryer.