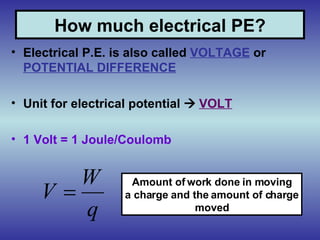
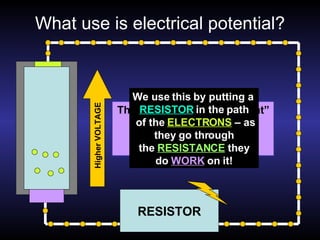
1) Electrical potential energy, also called voltage or potential difference, is a measure of the work required to move a charge in an electric field.
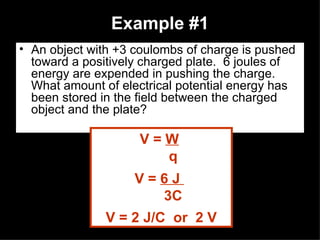
2) Voltage is calculated by dividing the work done (in Joules) by the charge moved (in Coulombs).
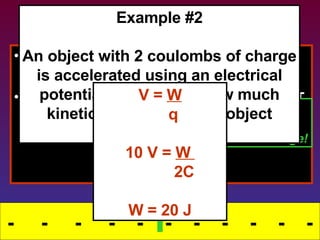
3) Stored electrical potential energy can be released as kinetic energy when charges are accelerated by a voltage and moved in an electric field.