Embed presentation
Downloaded 204 times


![Equation of Vibrating String OR 1D Wave Equation The boundary conditions to be satisfied by the Equation are : y=0 ,when x=0 Y=0 , when x =1 [ These should be satisfied by every value of ‘t’ ] MRCE, B.Tech ECE 1st year](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/partial-110414232601-phpapp02/75/Partial-5-2048.jpg)
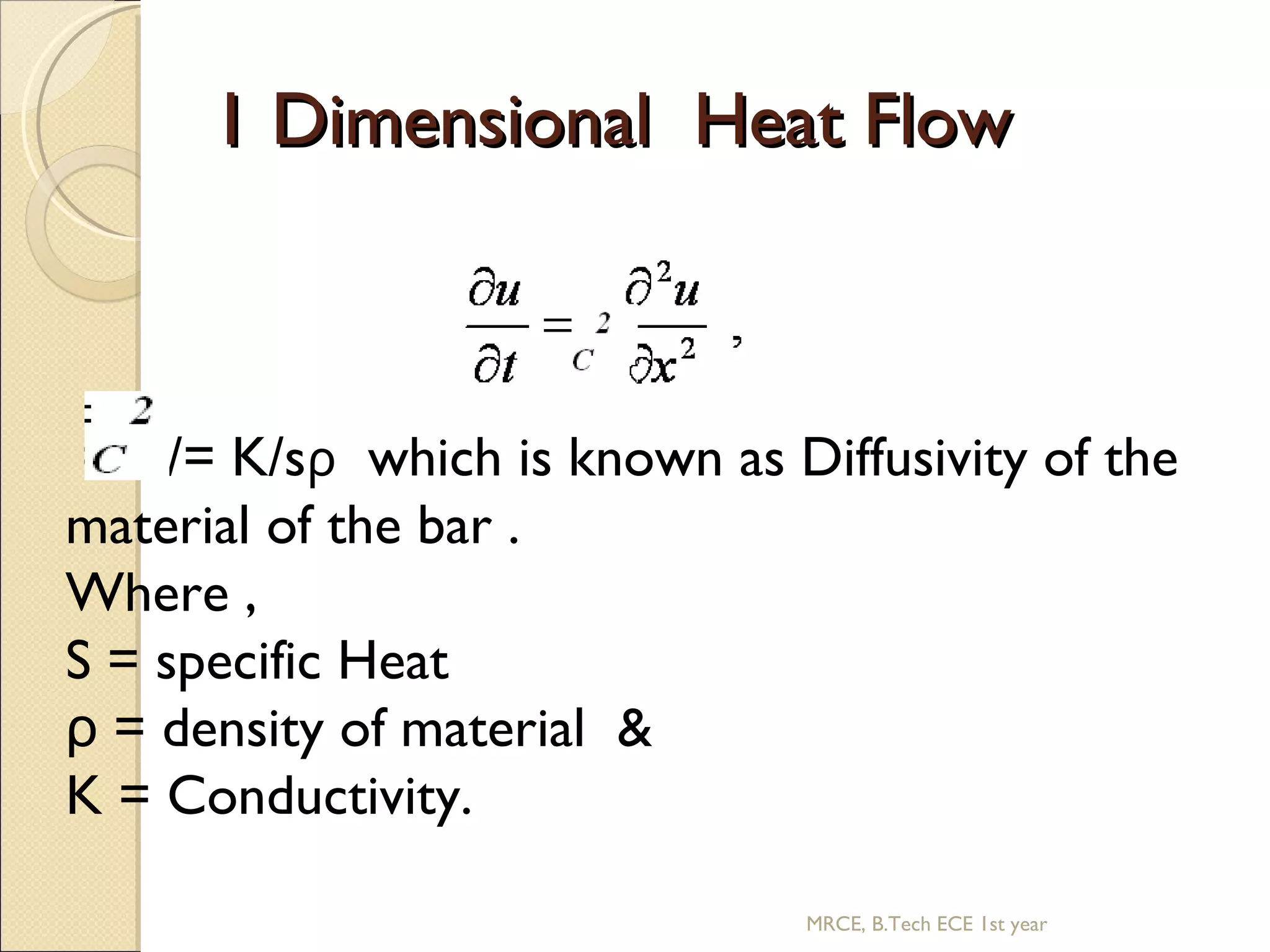


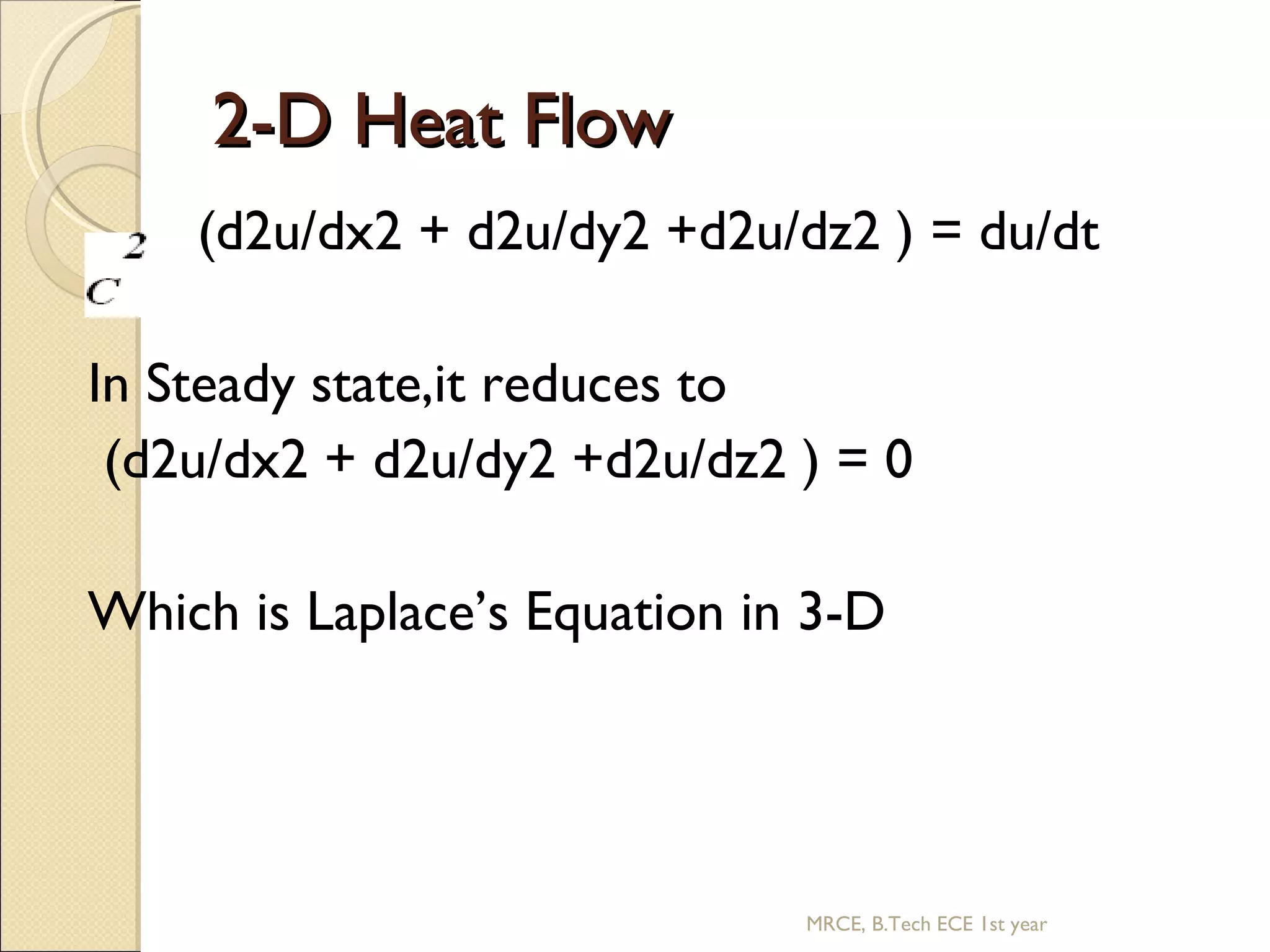


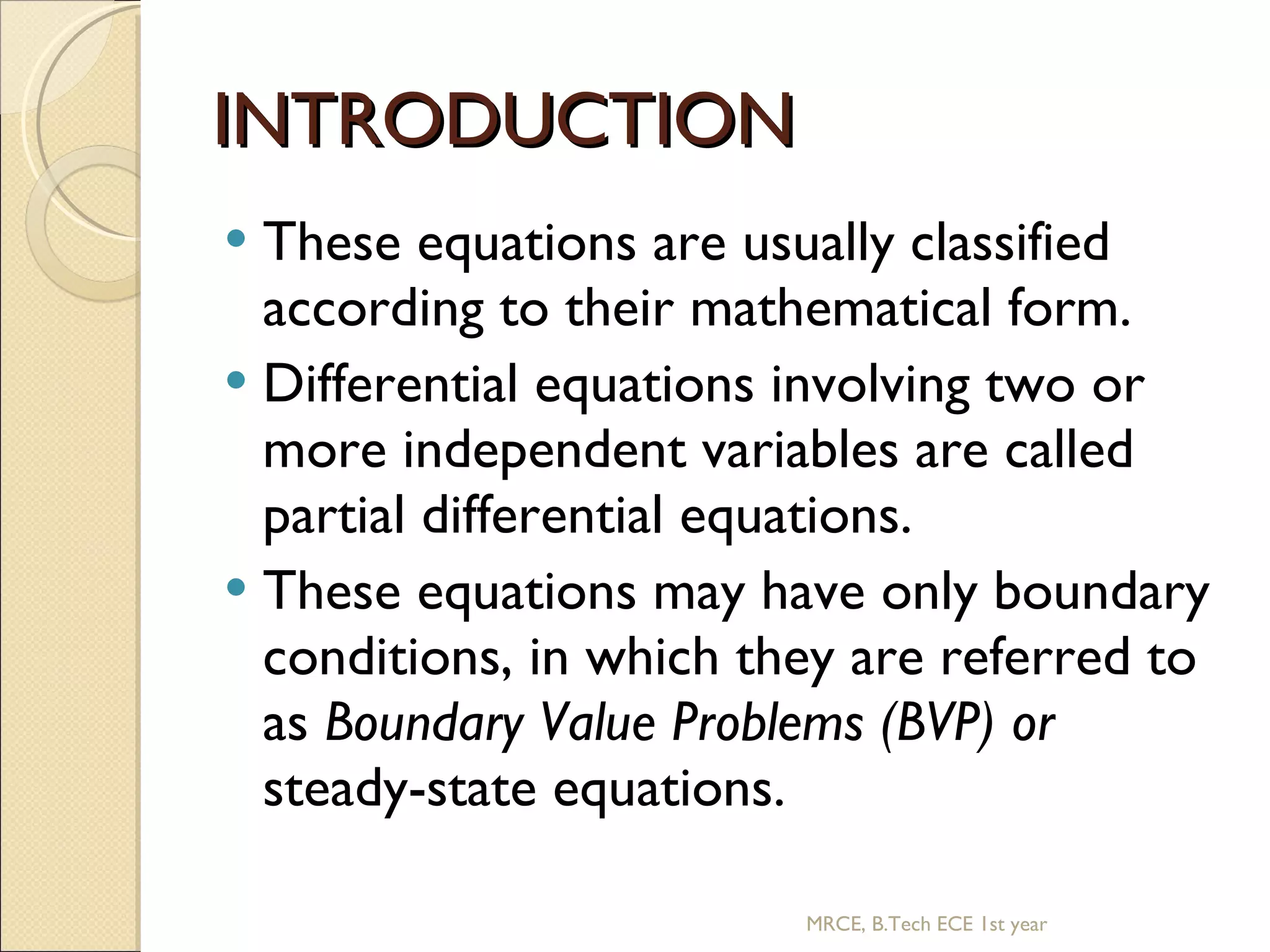
This document discusses the application of partial differential equations. It begins by classifying partial differential equations according to their mathematical form as either boundary value problems or steady-state equations. Some common partial differential equations are then presented, including the wave equation, heat equations, and Laplace's equation. Solution methods like separation of variables are introduced. Specific examples of the 1D wave equation and 1D heat equation are then covered. Finally, the document discusses the Laplace equation in 2D and 3D.




![Equation of Vibrating String OR 1D Wave Equation The boundary conditions to be satisfied by the Equation are : y=0 ,when x=0 Y=0 , when x =1 [ These should be satisfied by every value of ‘t’ ] MRCE, B.Tech ECE 1st year](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/partial-110414232601-phpapp02/75/Partial-5-2048.jpg)





