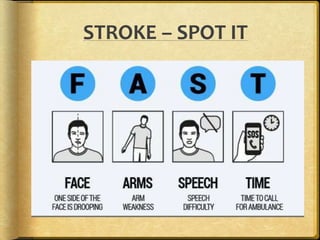
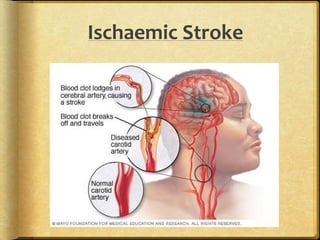
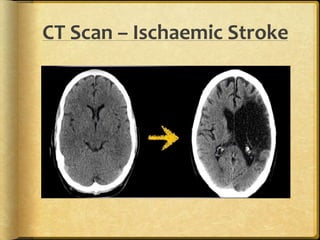
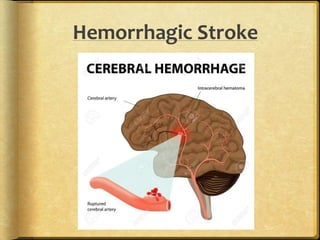
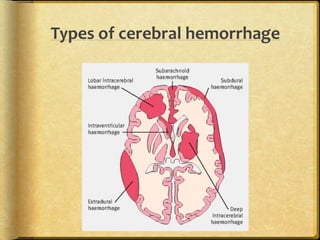
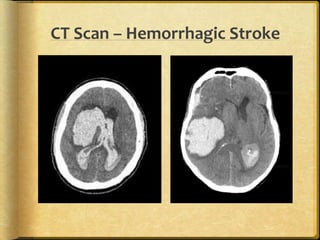
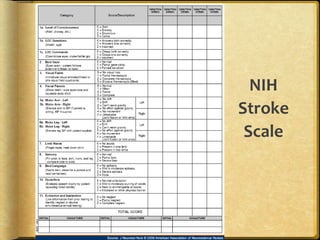
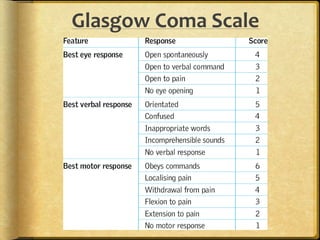
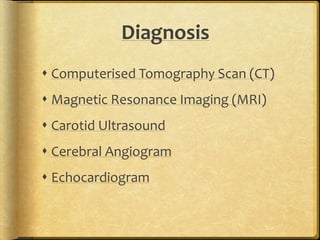
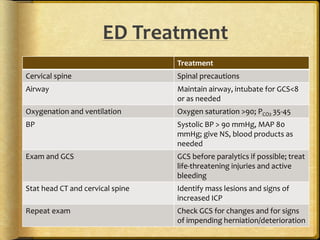
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted, depriving brain tissue of oxygen. It is a medical emergency. Globally, there are over 13 million new strokes per year resulting in over 5.5 million deaths annually. Common symptoms include trouble speaking, paralysis, trouble seeing, and trouble walking. Risk factors include hypertension, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, and age over 55. Treatment depends on whether the stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic and may include clot-busting drugs, surgery, or other procedures. Nursing care focuses on monitoring the patient's condition, preventing complications, and facilitating recovery and rehabilitation with a team-based approach.