Cerebral palsy can be classified in several ways:
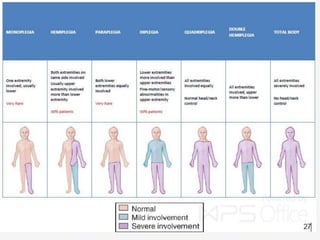
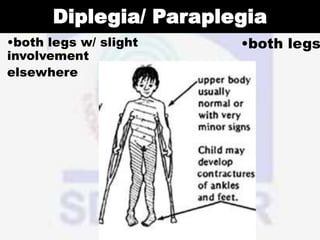
(1) By the region of the body affected, such as hemiplegia which affects one side of the body, diplegia which primarily affects both legs, and quadriplegia which affects all four limbs.
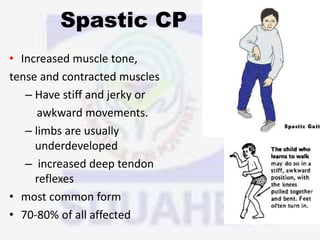
(2) By the type of motor impairment, with spastic cerebral palsy being the most common type and affecting muscle tone, and other types including athetoid, choreiform, ataxic, and rigid.
(3) Temporally based on when the brain injury occurred such as prenatal, perinatal, or postnatal causes. Cerebral palsy results from a non-progressive