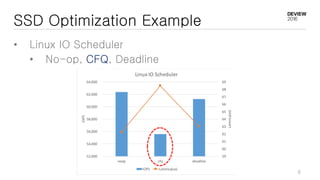
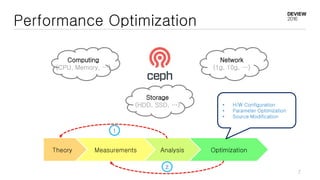
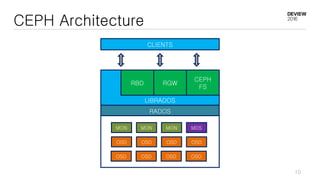
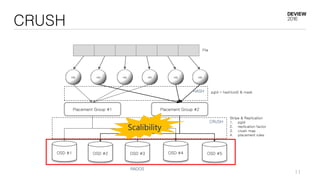
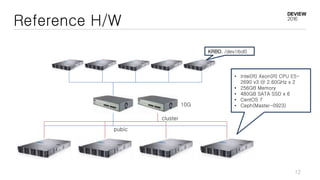
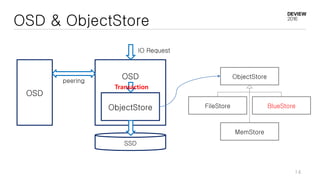
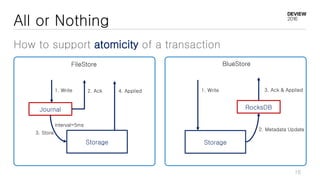
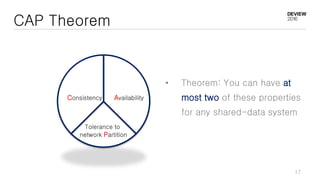
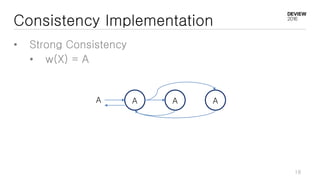
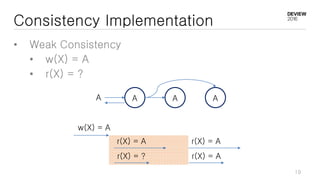
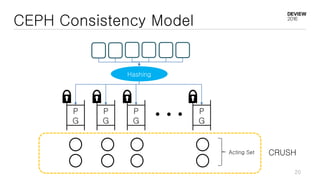
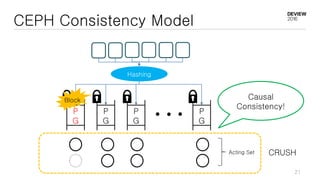
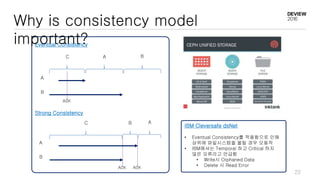
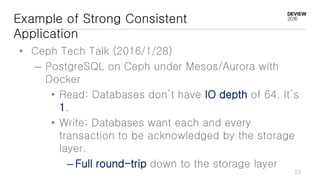
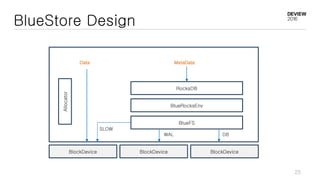
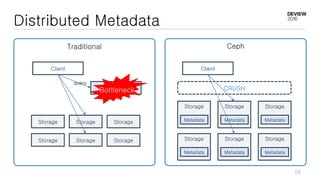
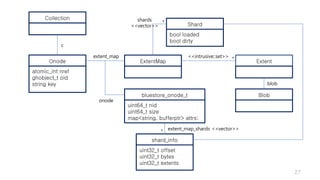
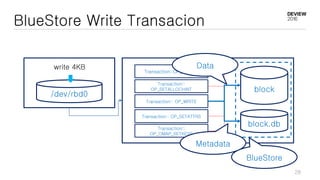
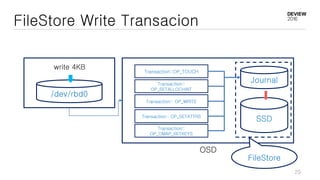
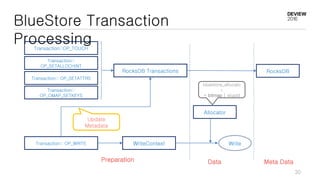
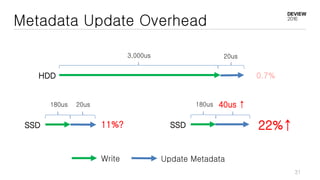
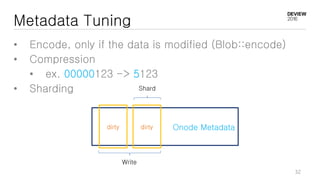
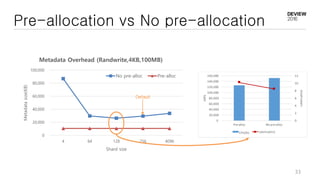
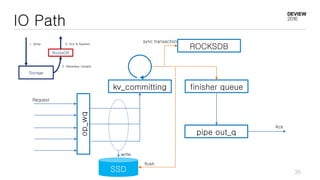
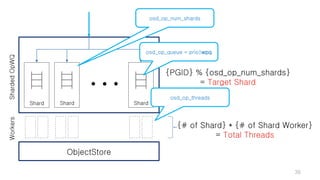
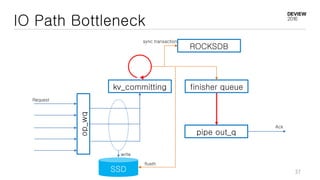
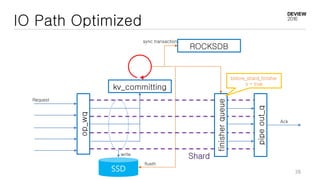
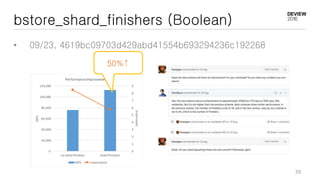
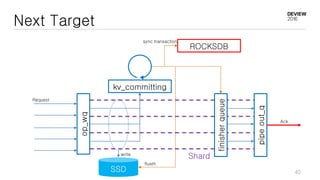
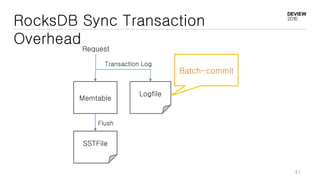
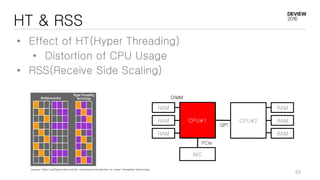
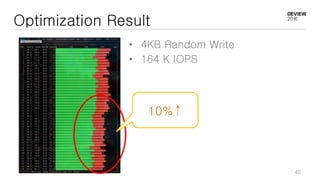
This document discusses optimizations for CEPH storage on SSDs. It begins with an introduction to NIC tech lab and software defined storage. It then explains why SSDs provide higher performance than HDDs due to lower latency and higher parallelism. The document provides examples of optimizing the Linux IO scheduler and discusses principles of performance tuning. It describes the CEPH architecture including RADOS, CRUSH, and consistency models. It focuses on optimizations for metadata processing in BlueStore including sharding, pre-allocation, and reducing acknowledgment overhead. Overall optimizations included reducing metadata overhead, improving IO paths, using shard finishers, and optimizing the operating system.