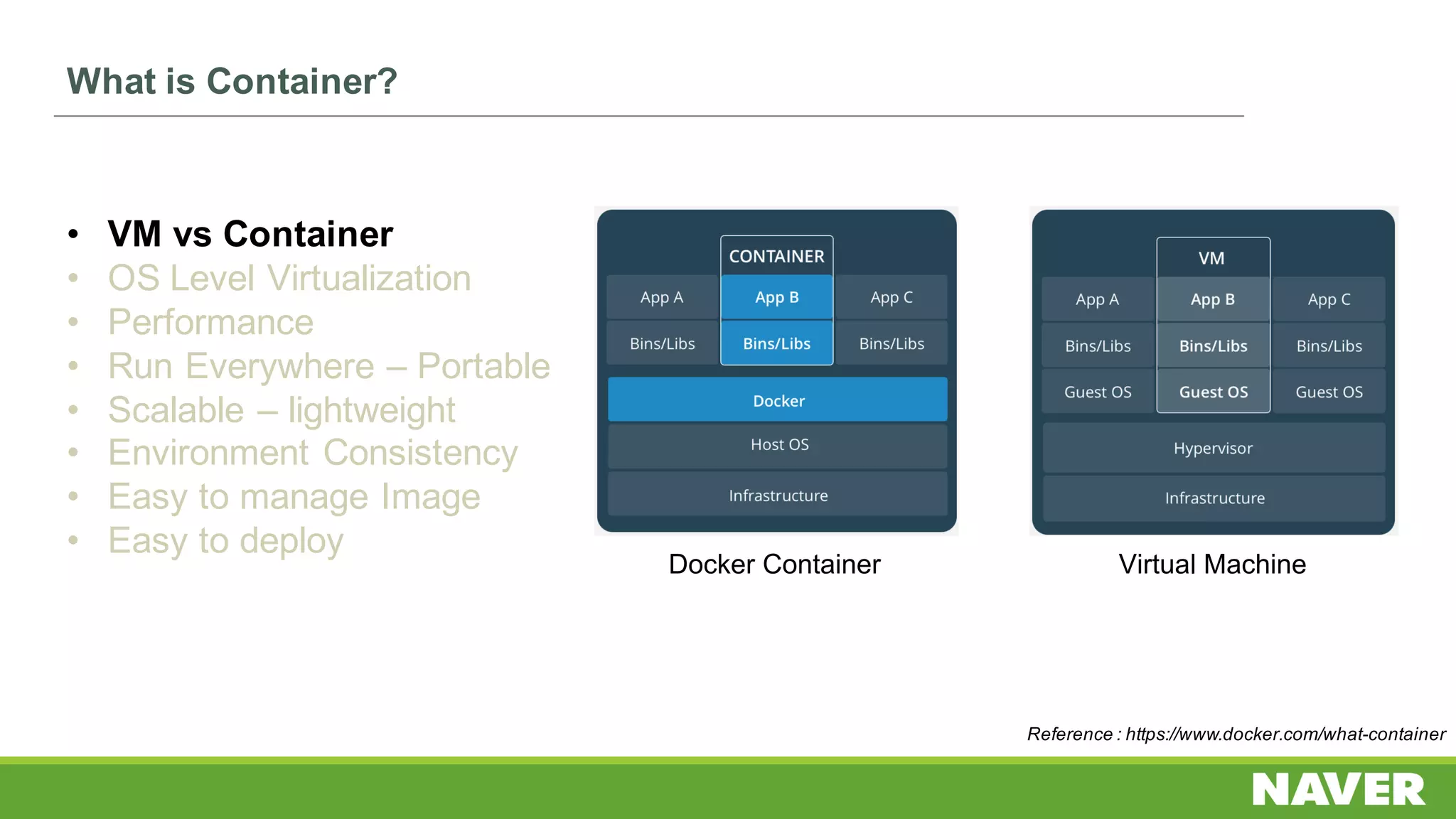
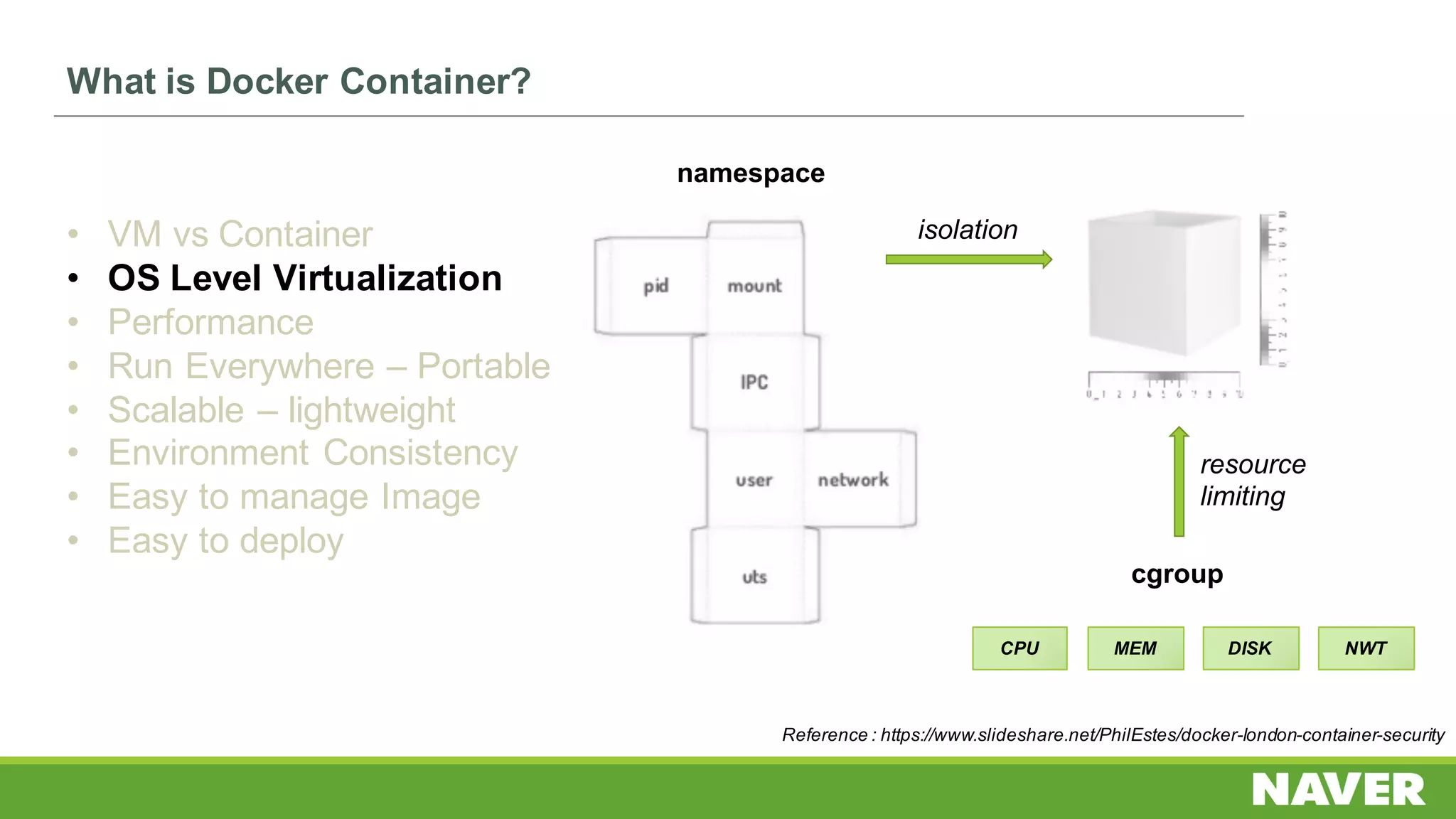
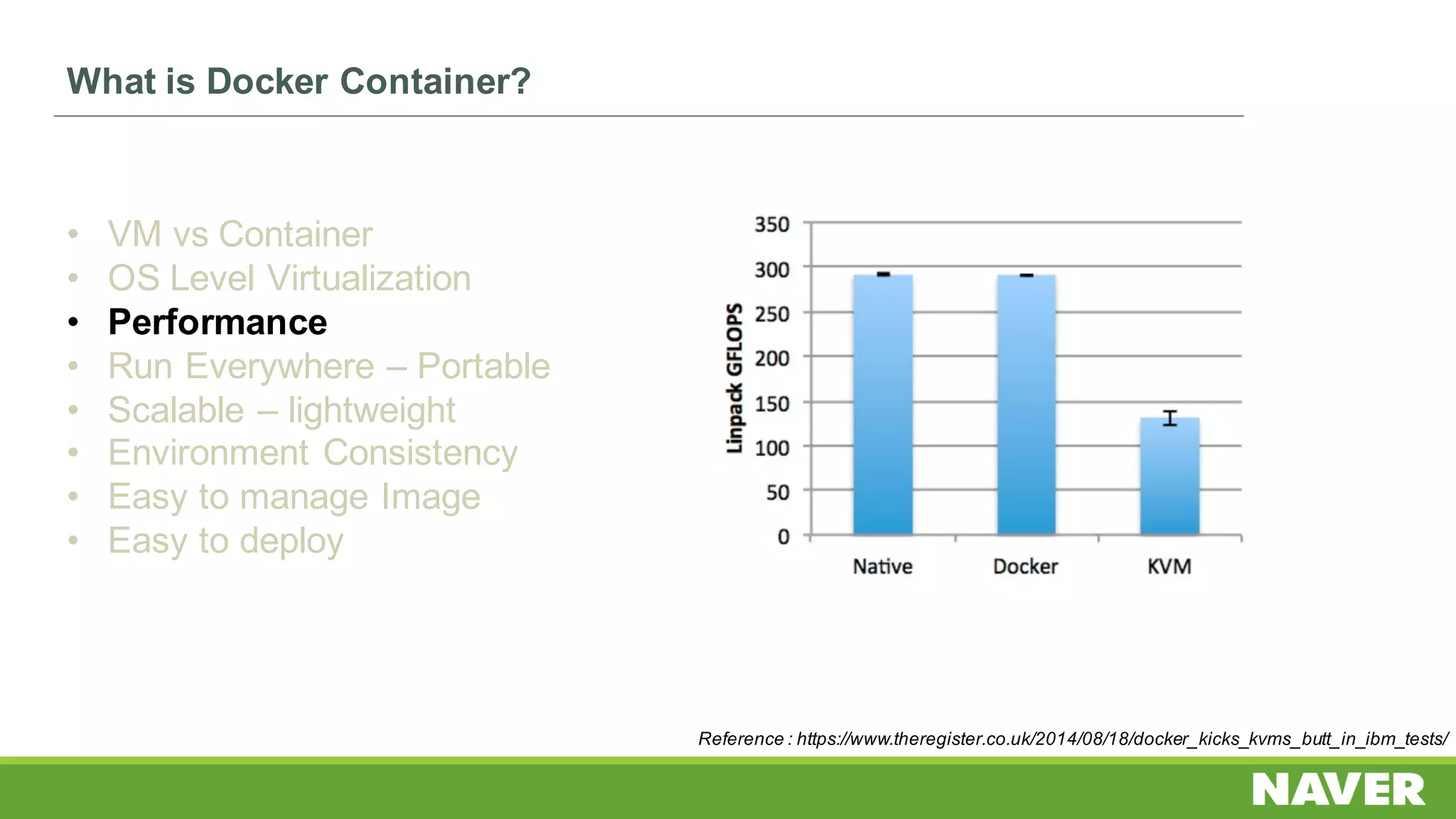
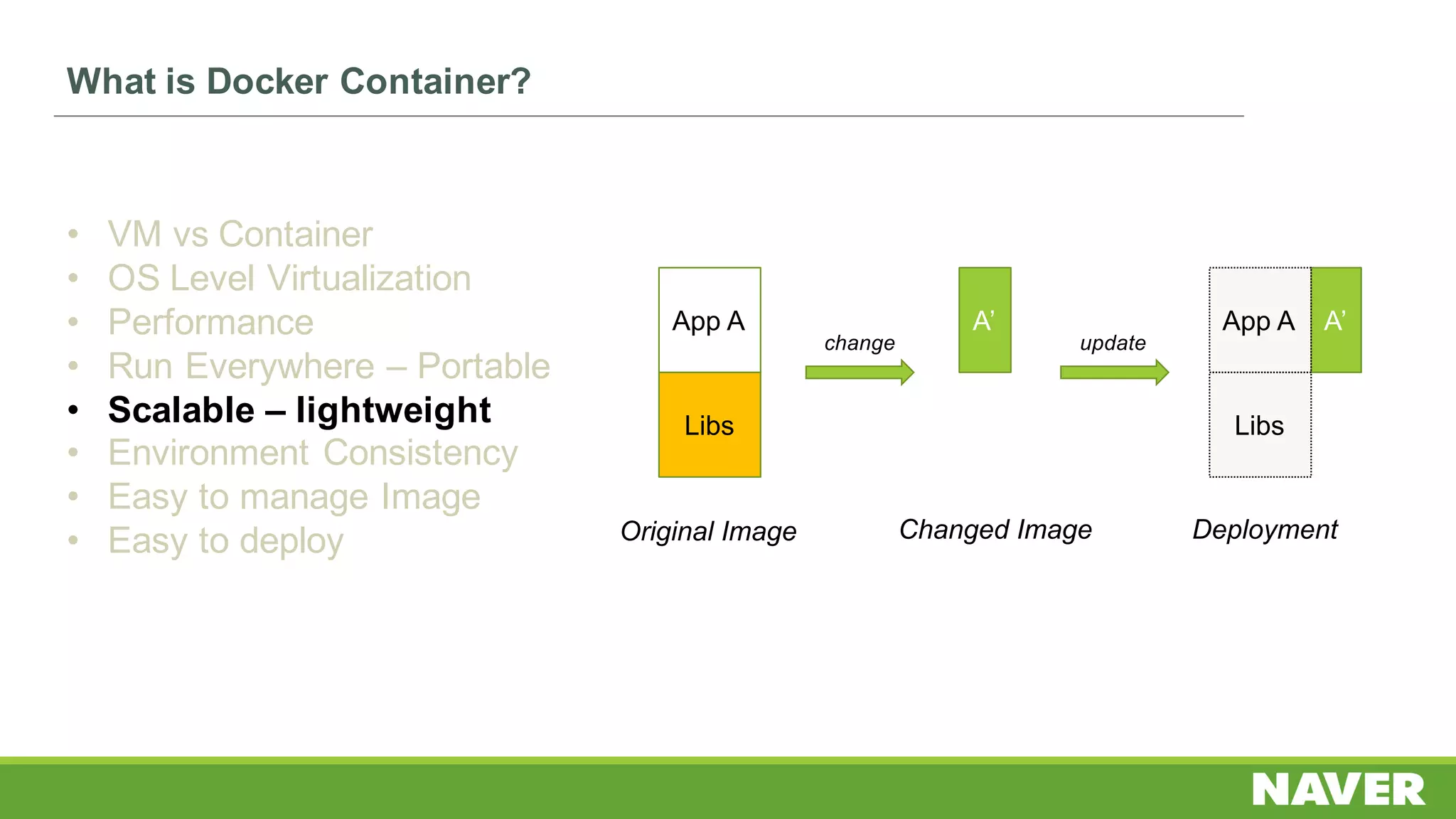
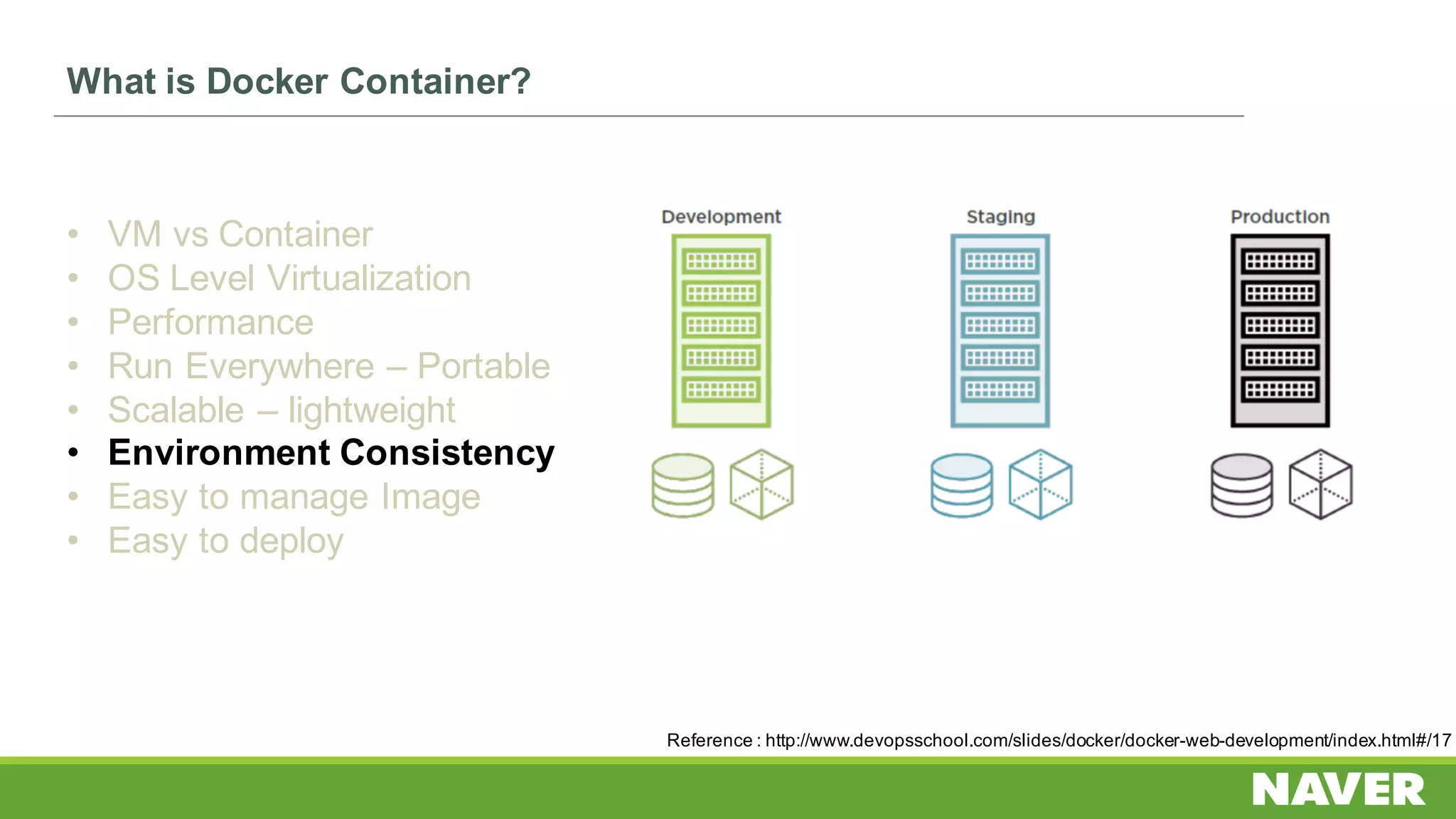
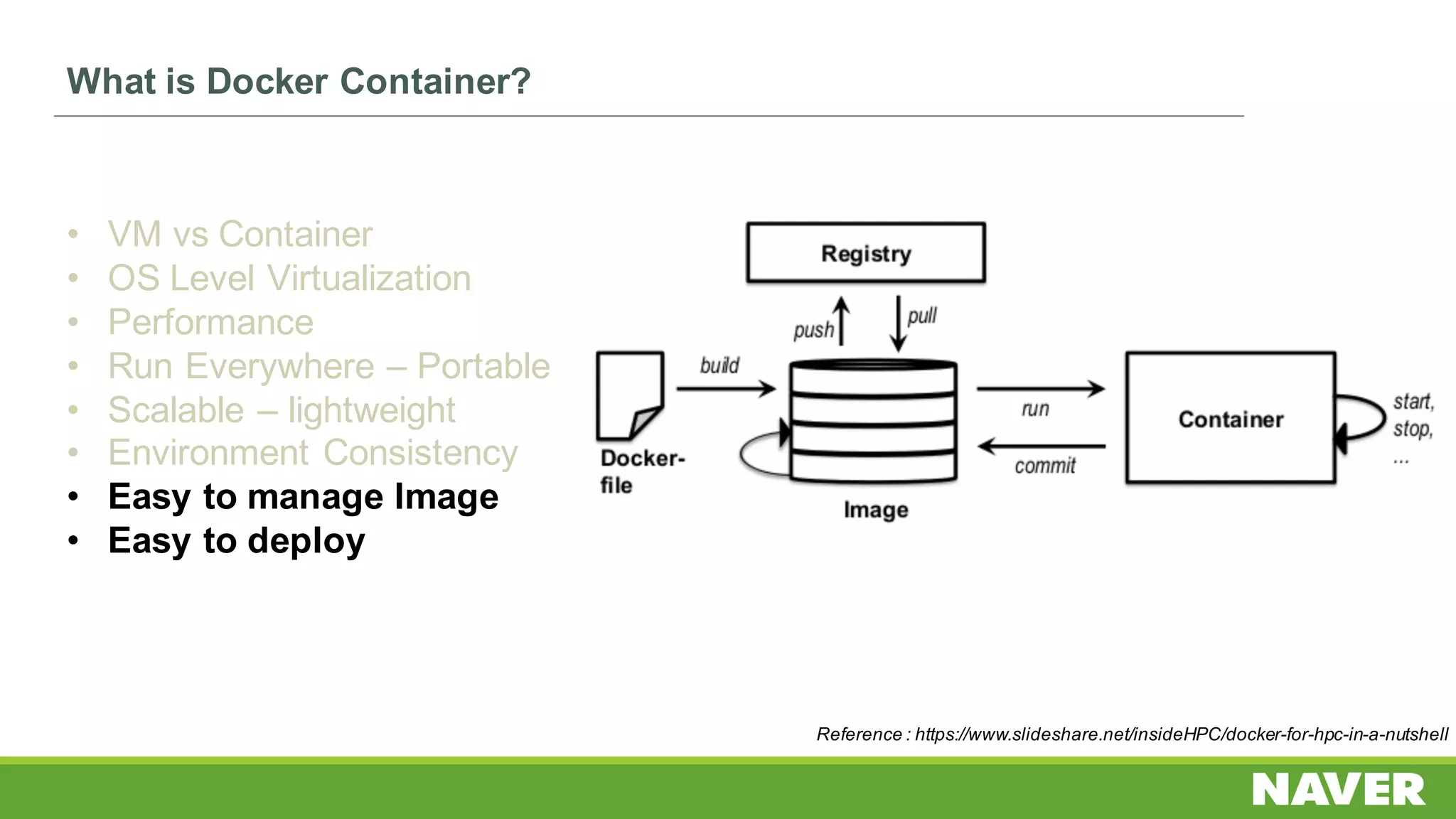
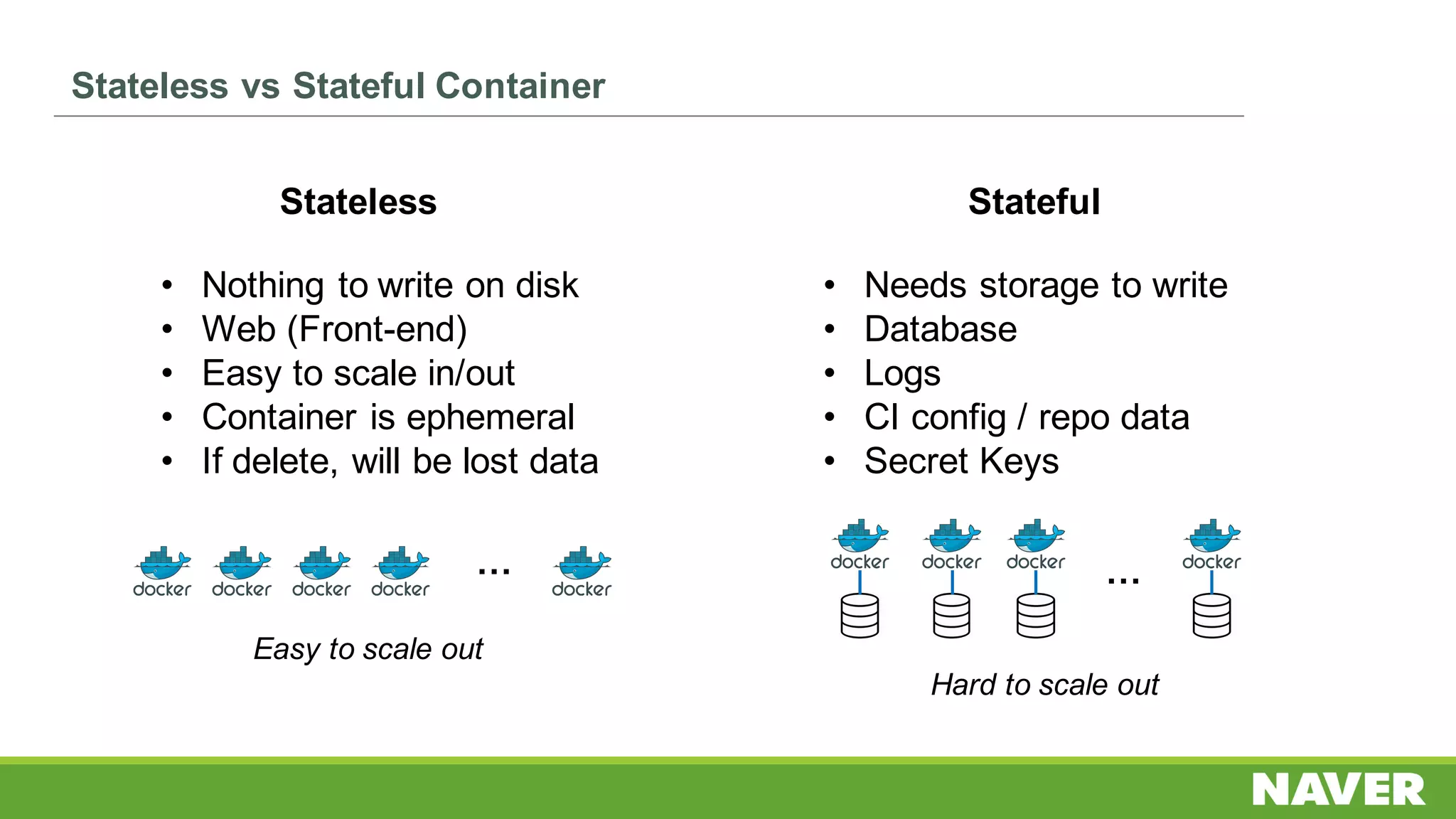
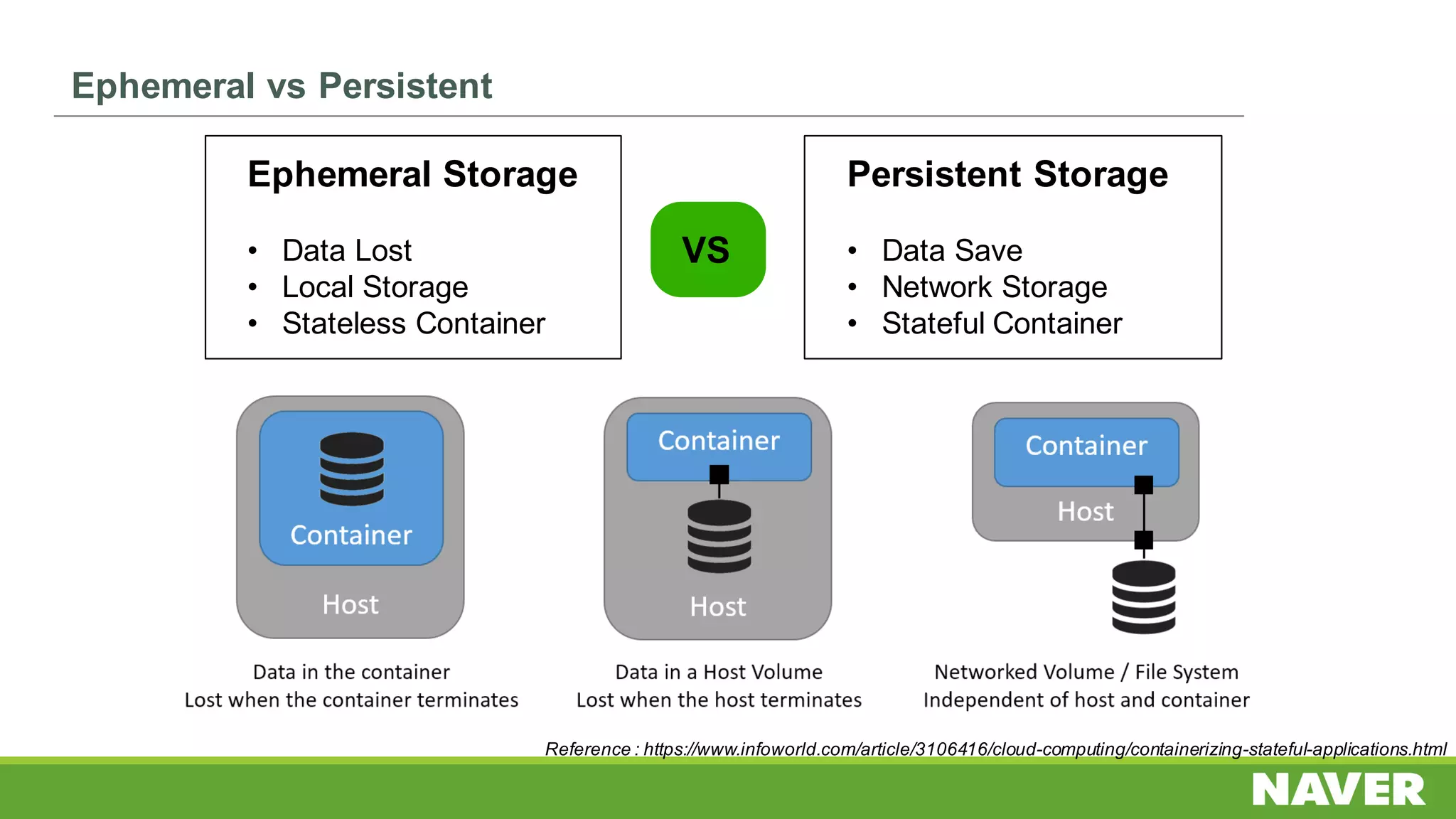
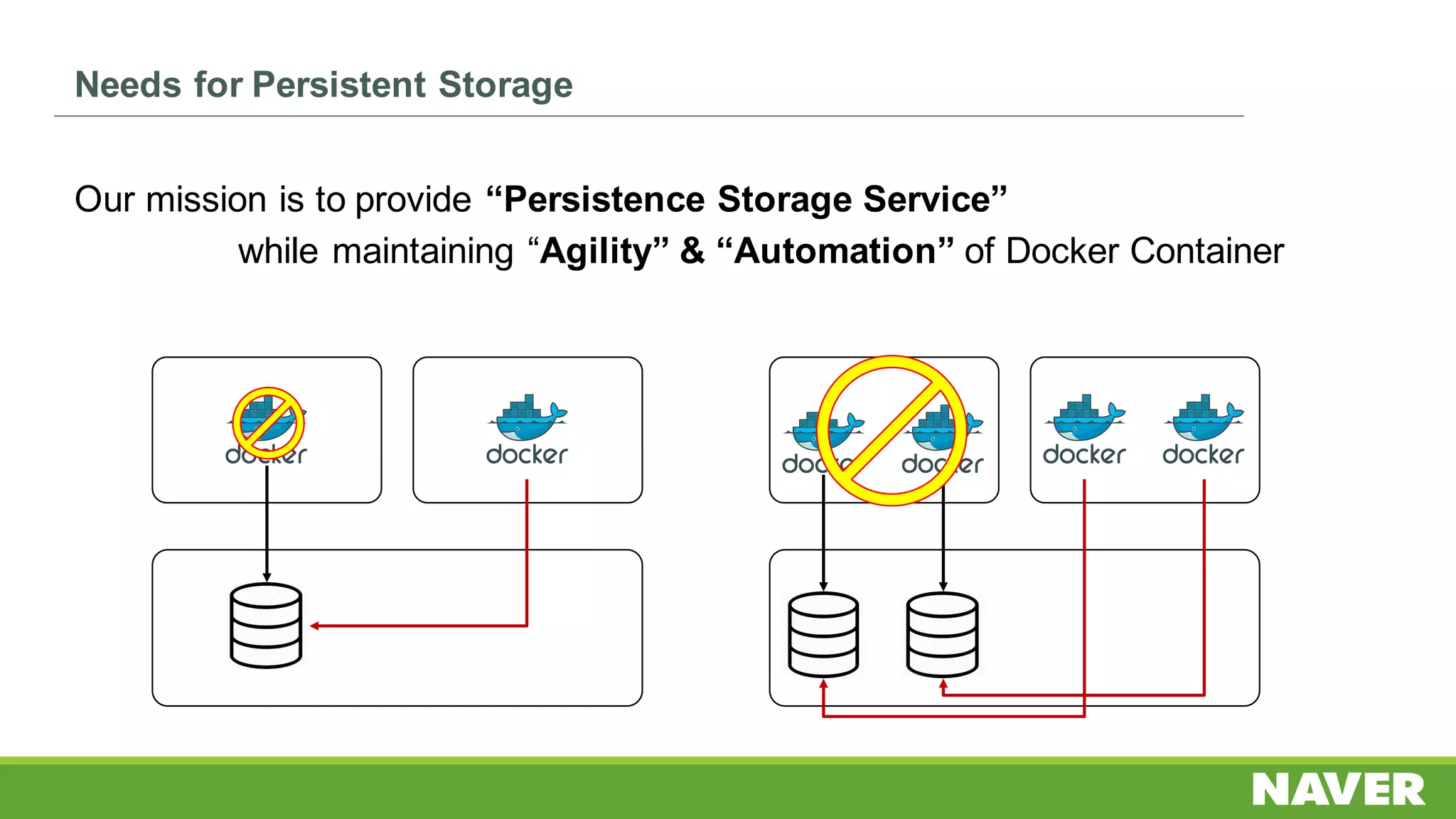
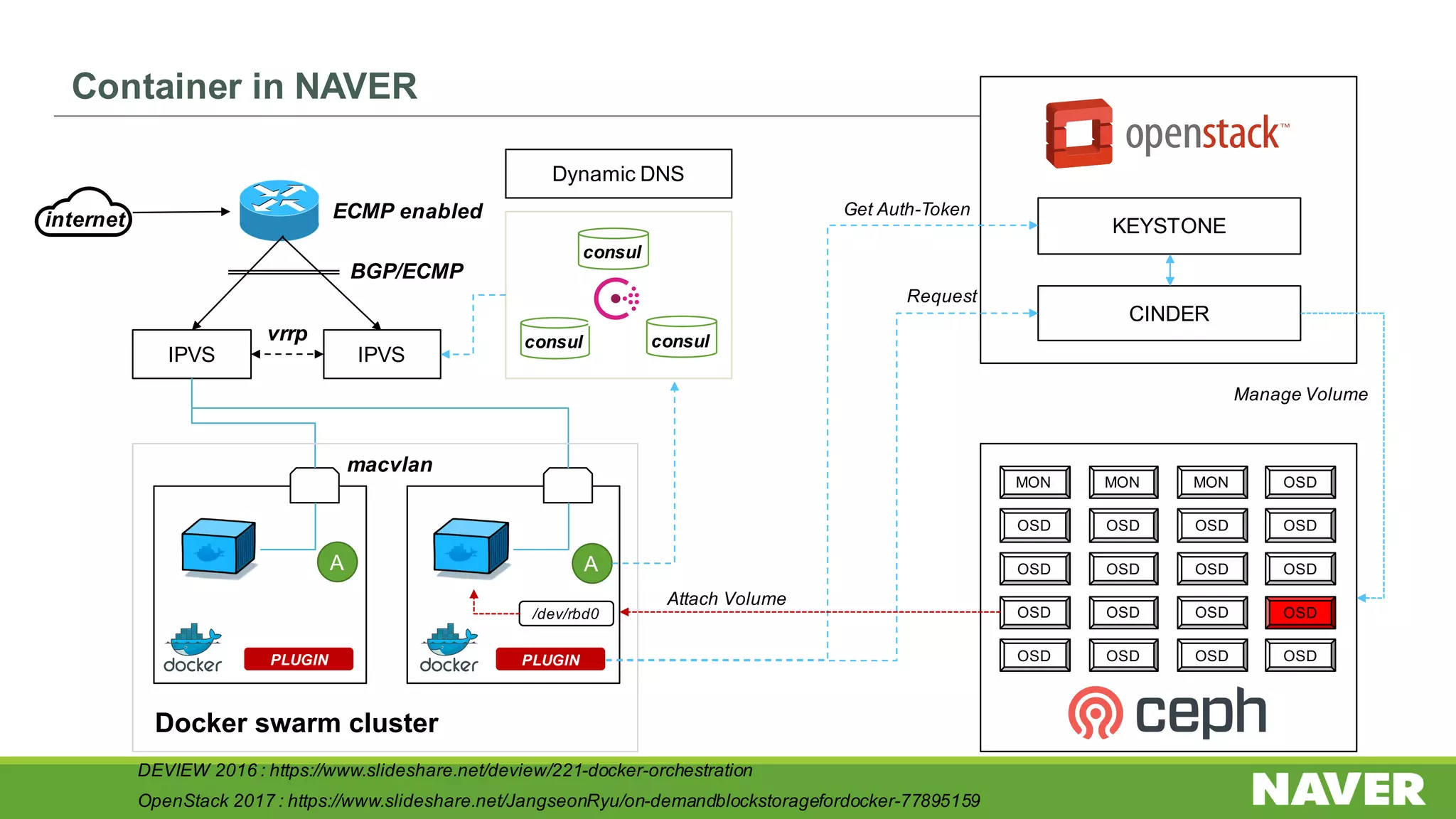
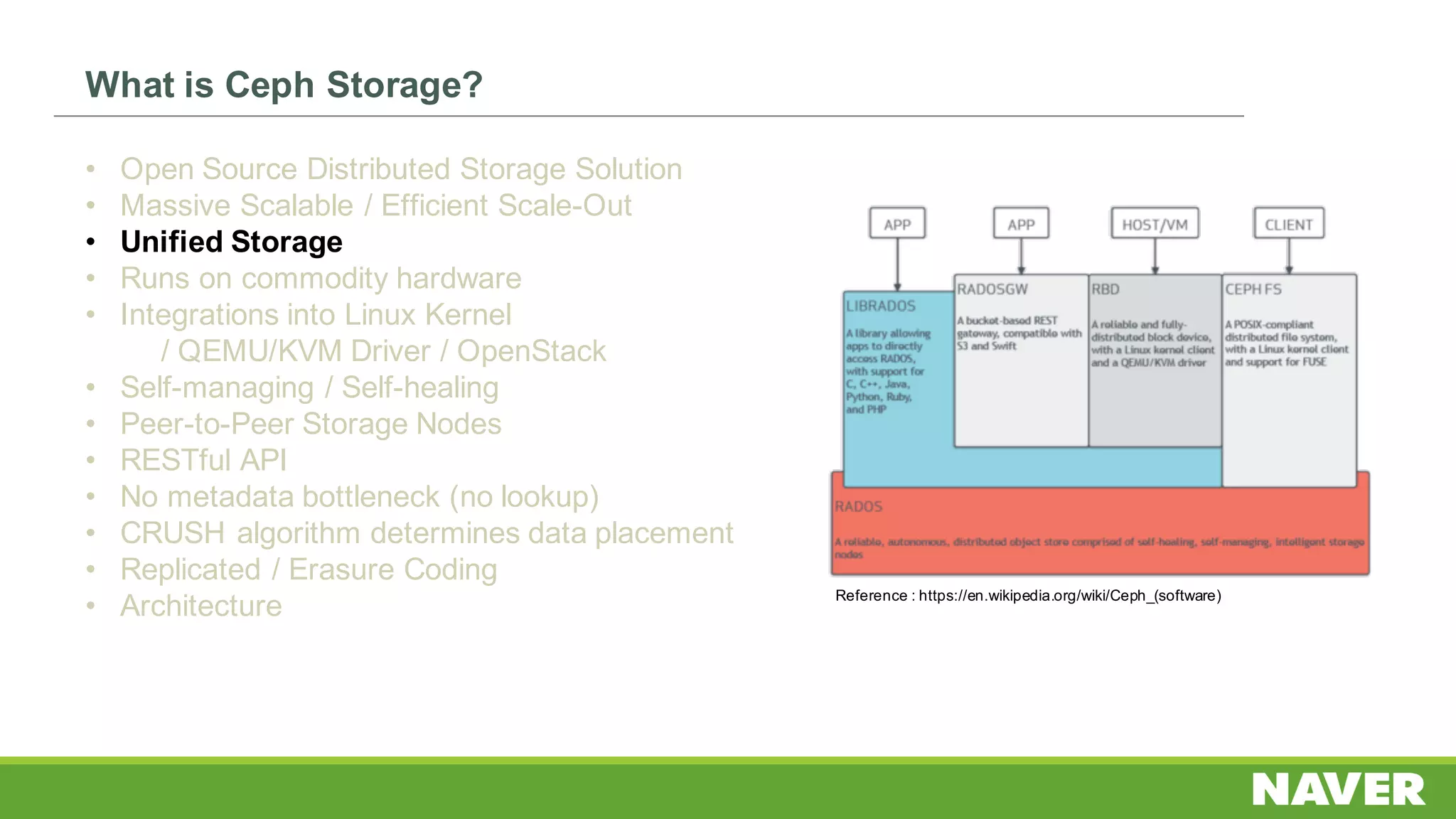
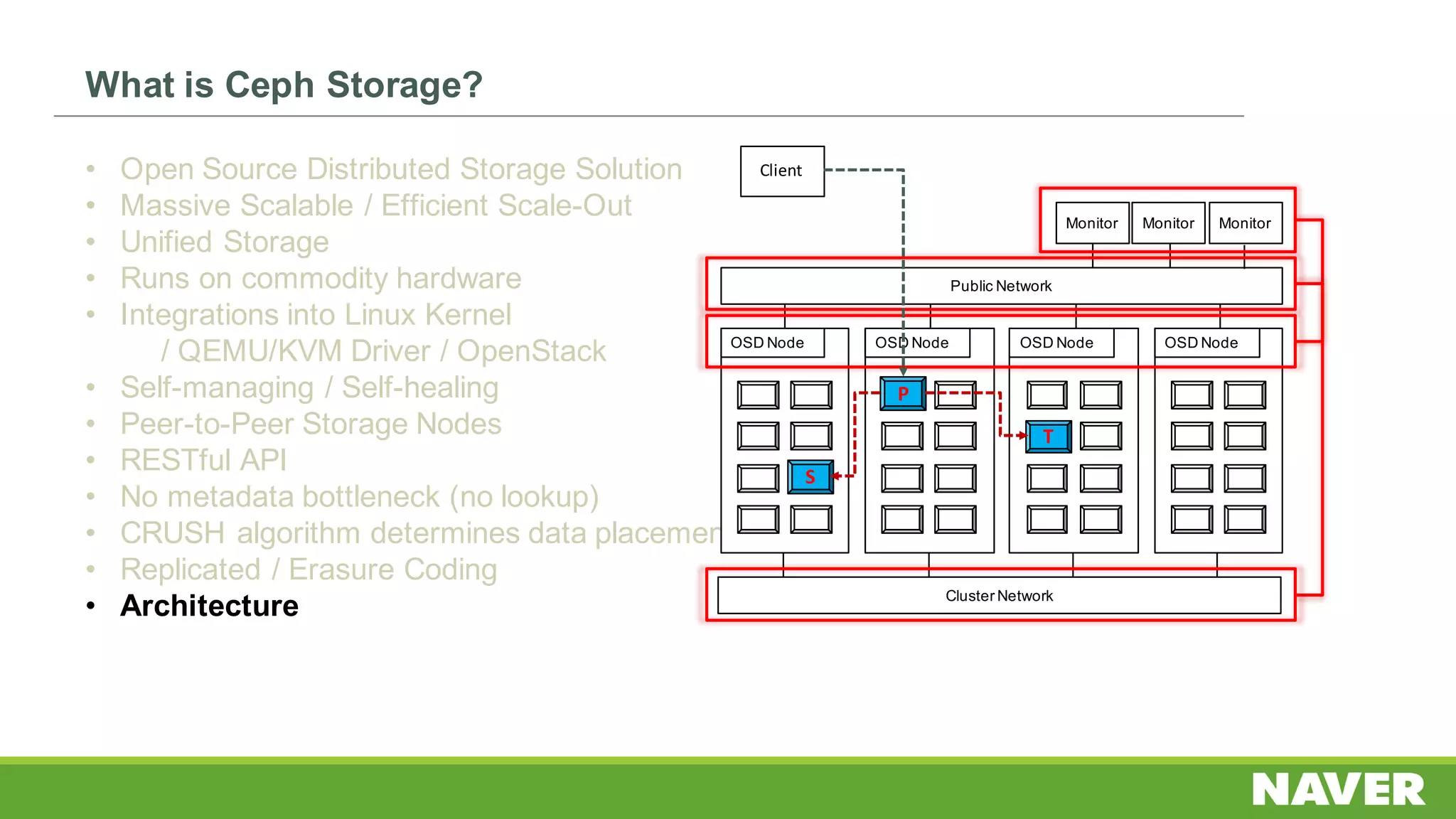
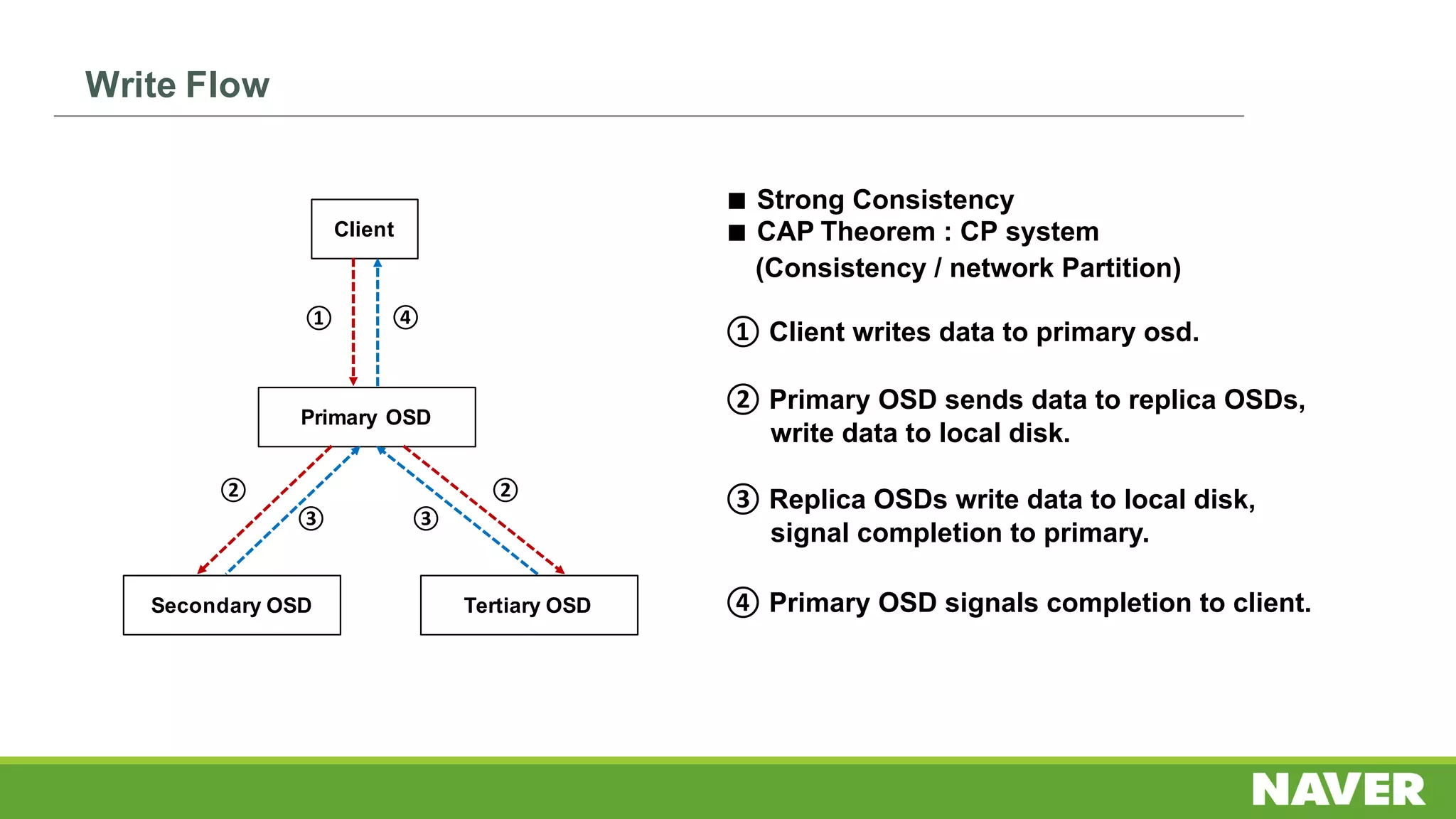
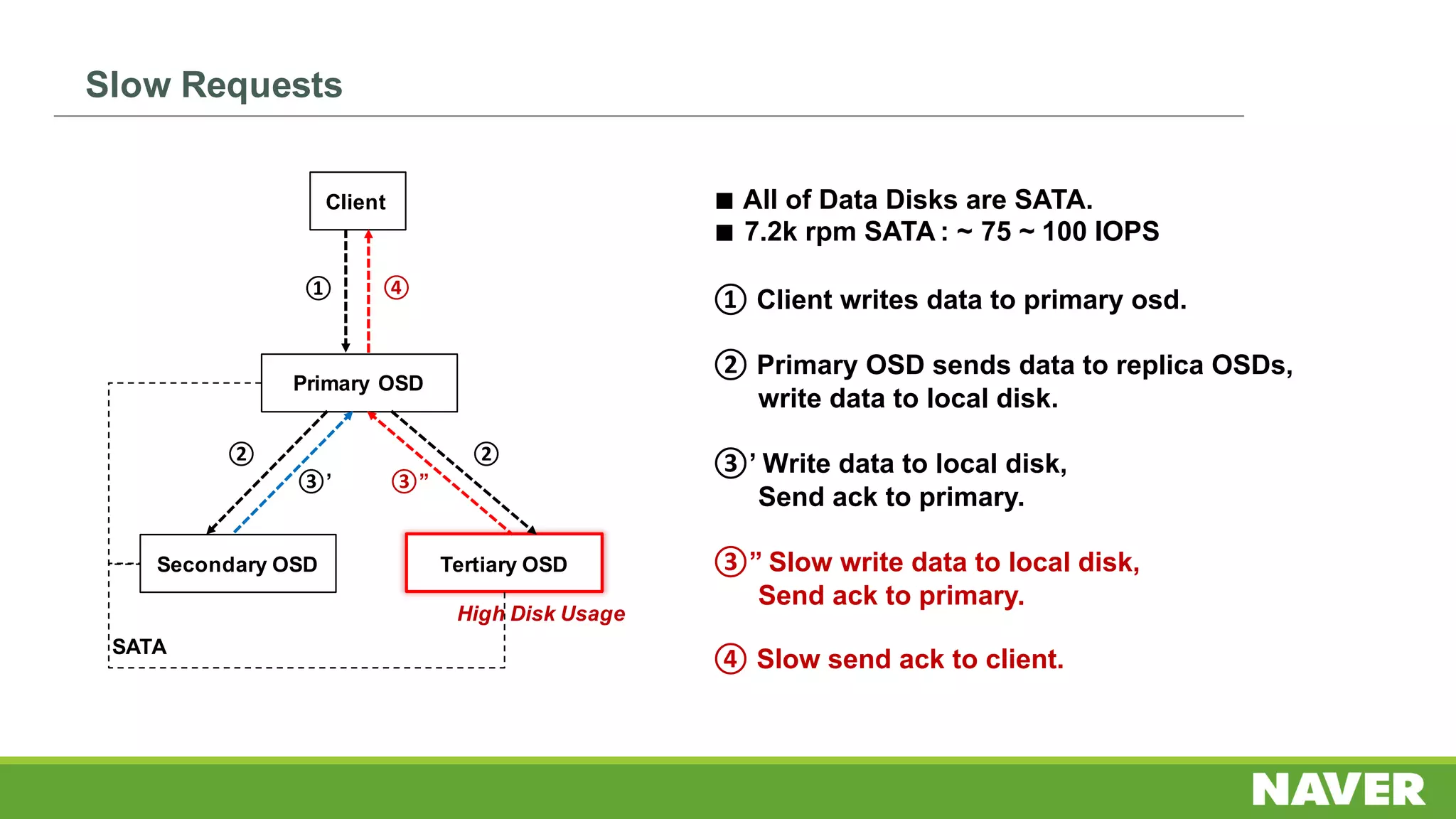
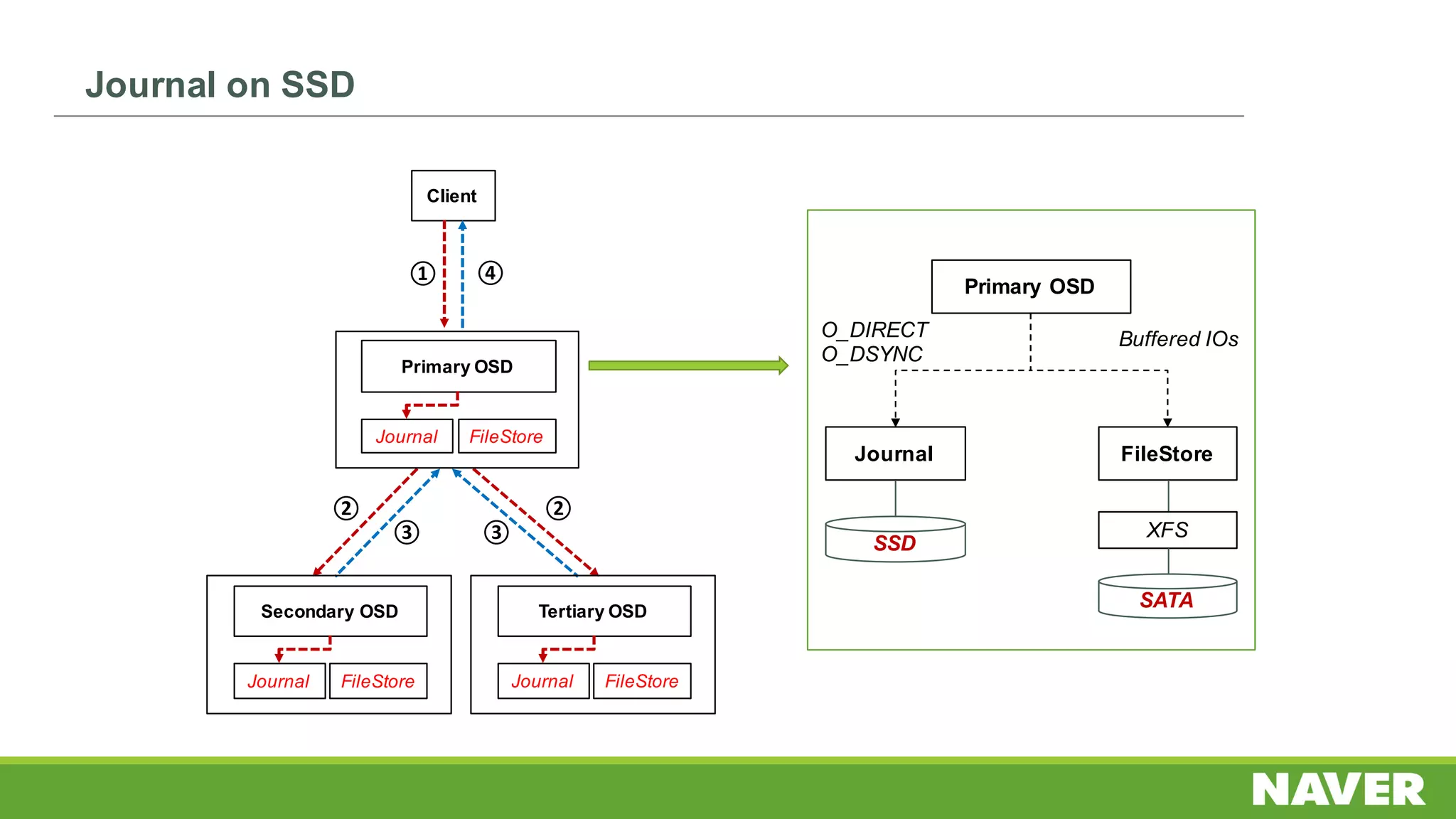
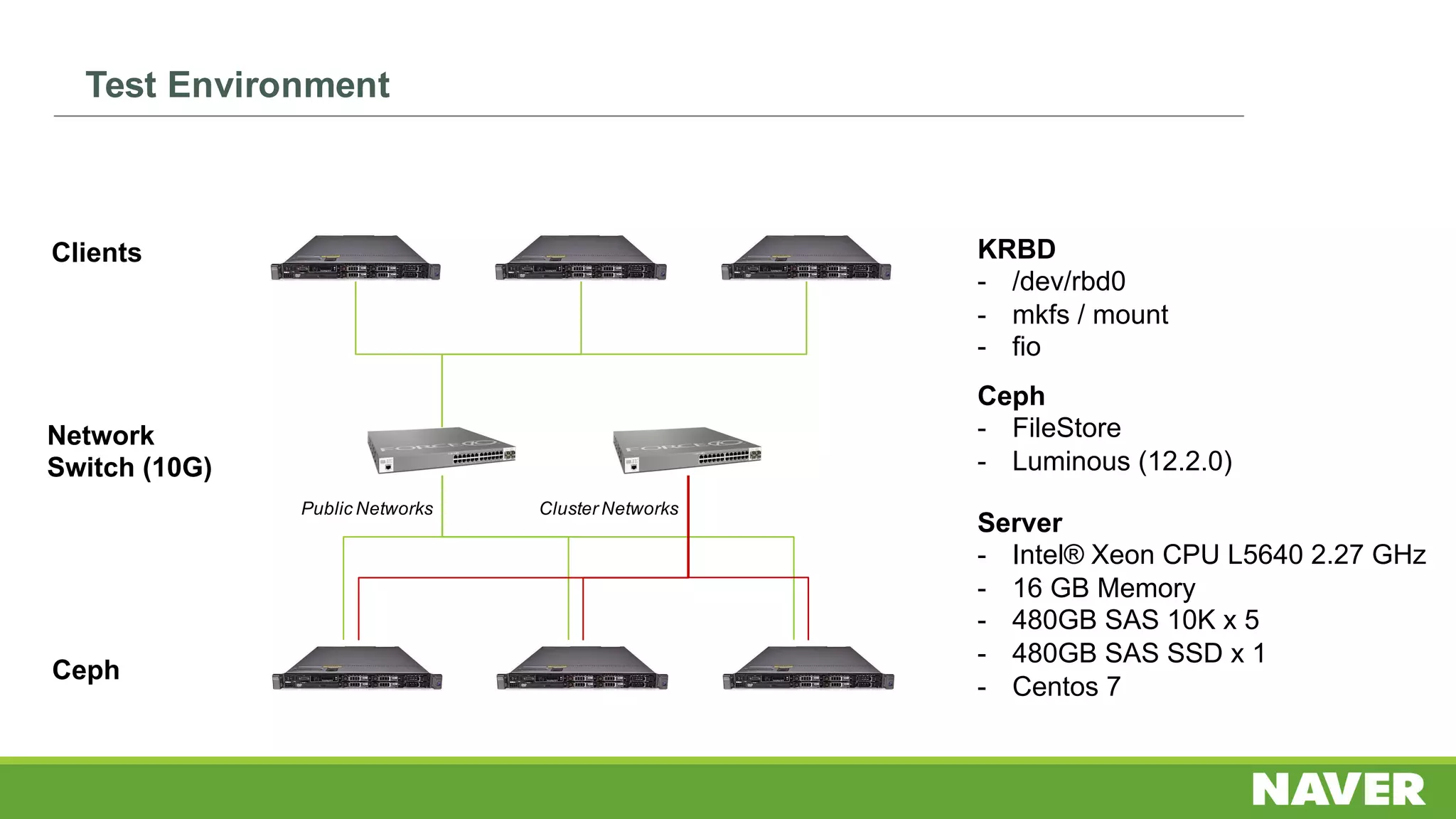
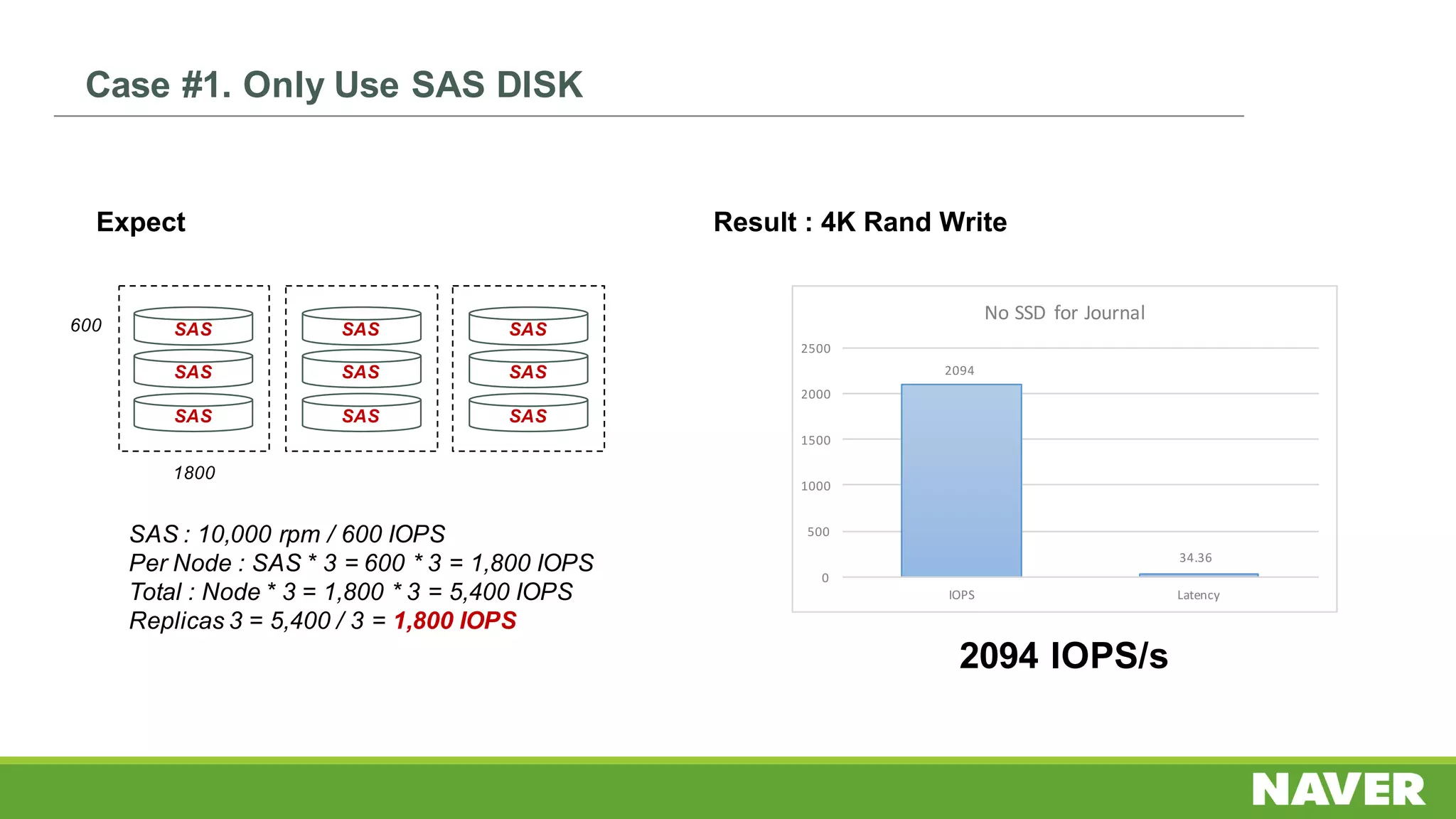
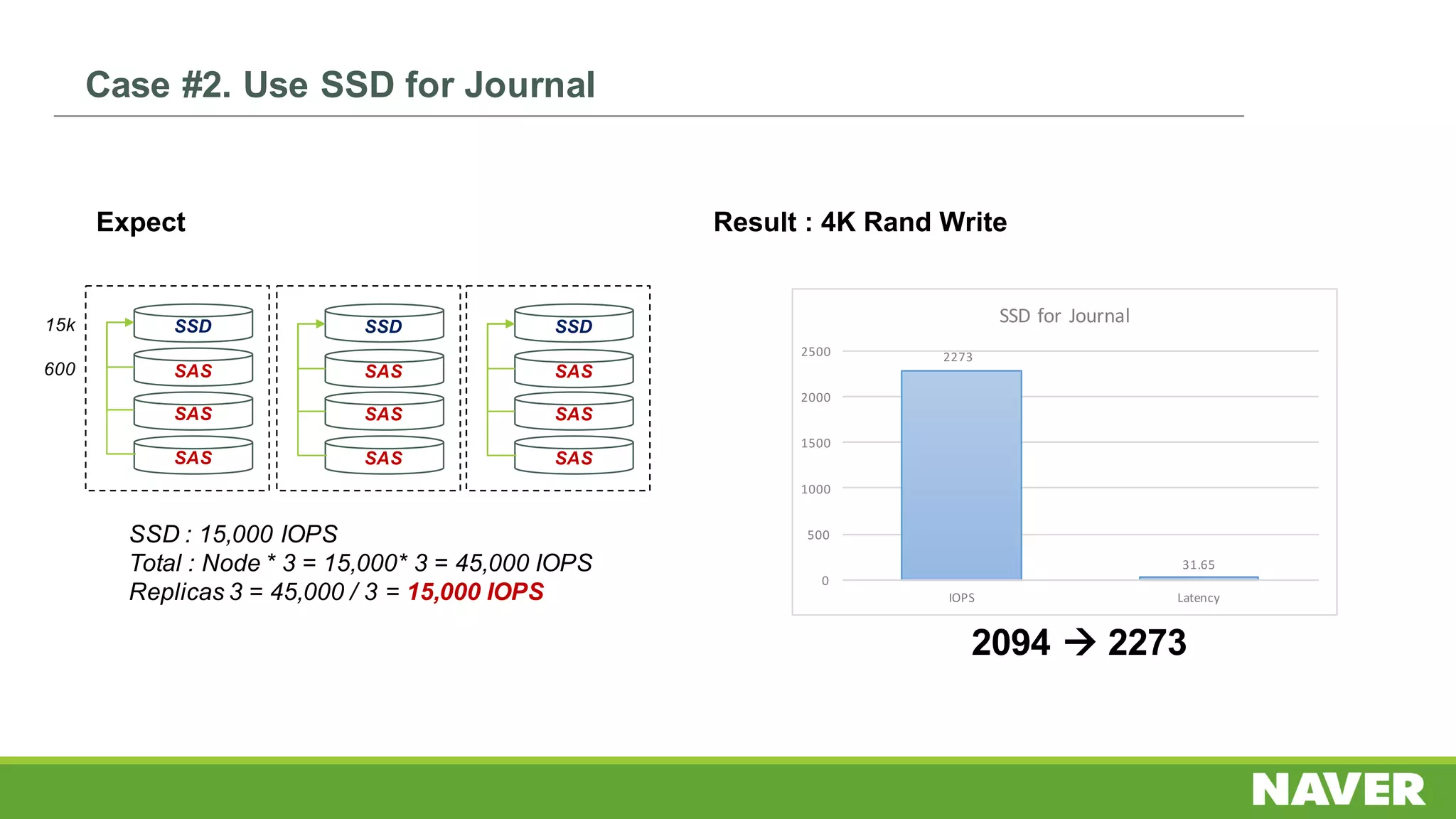
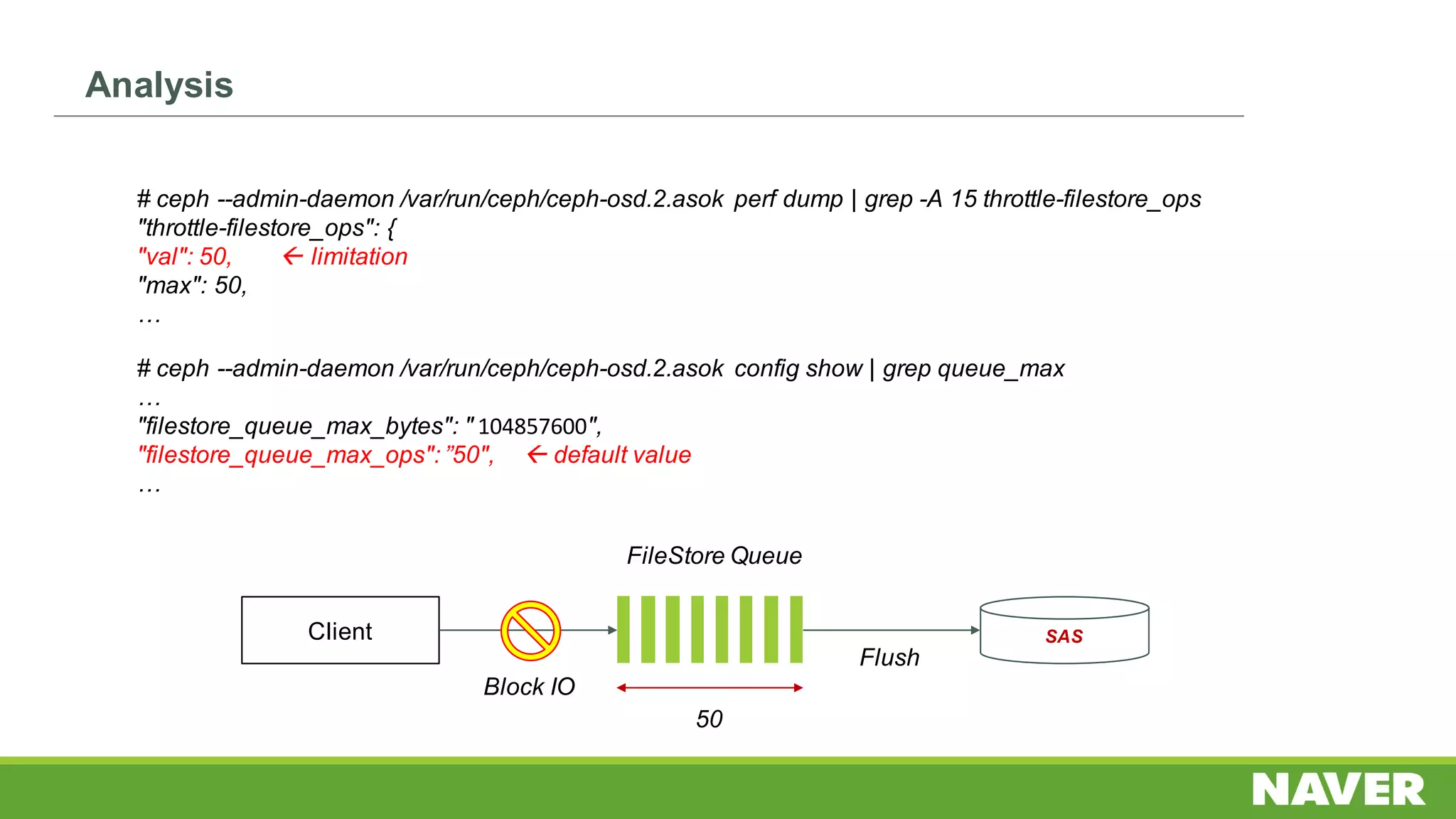
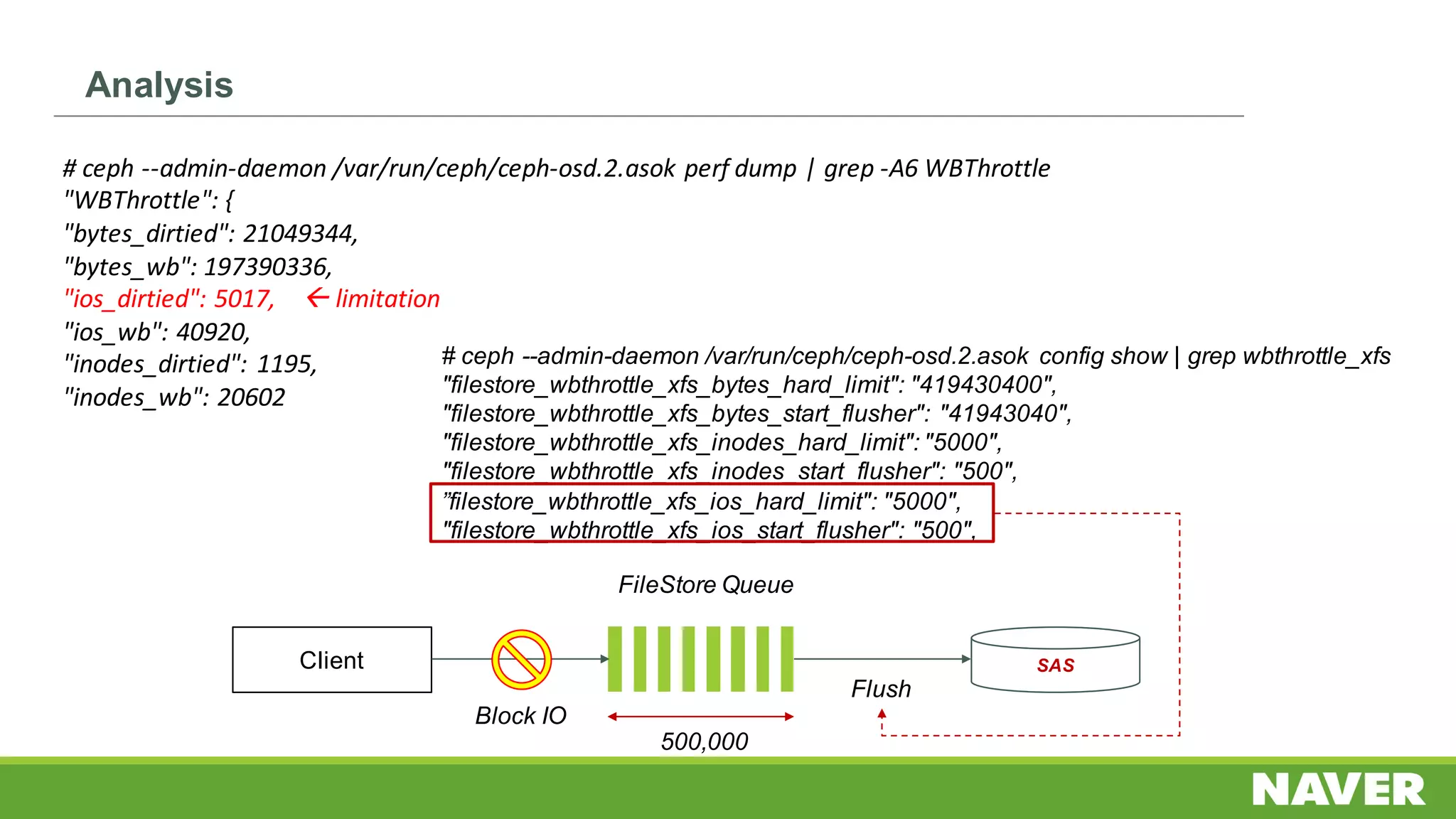
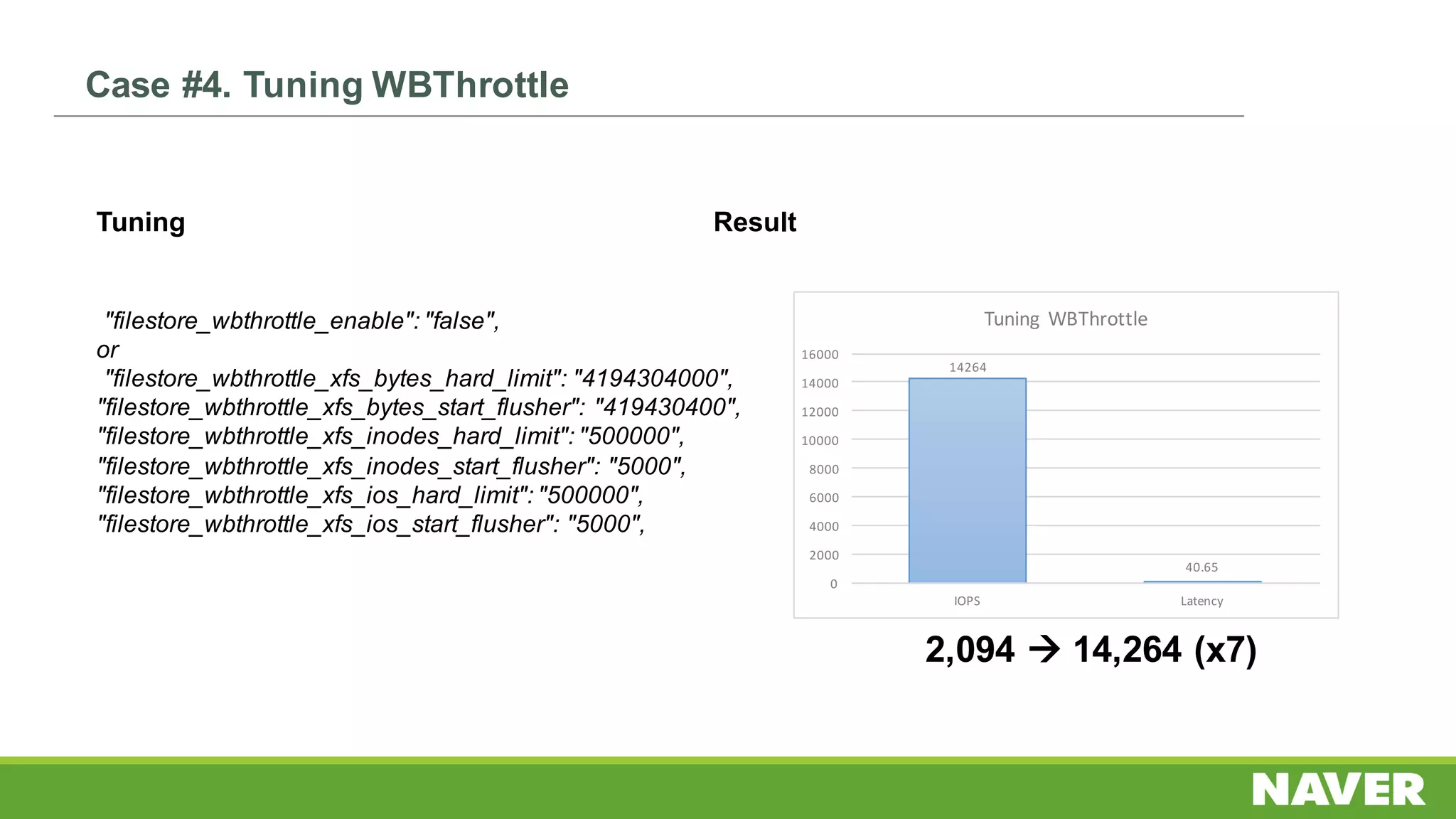
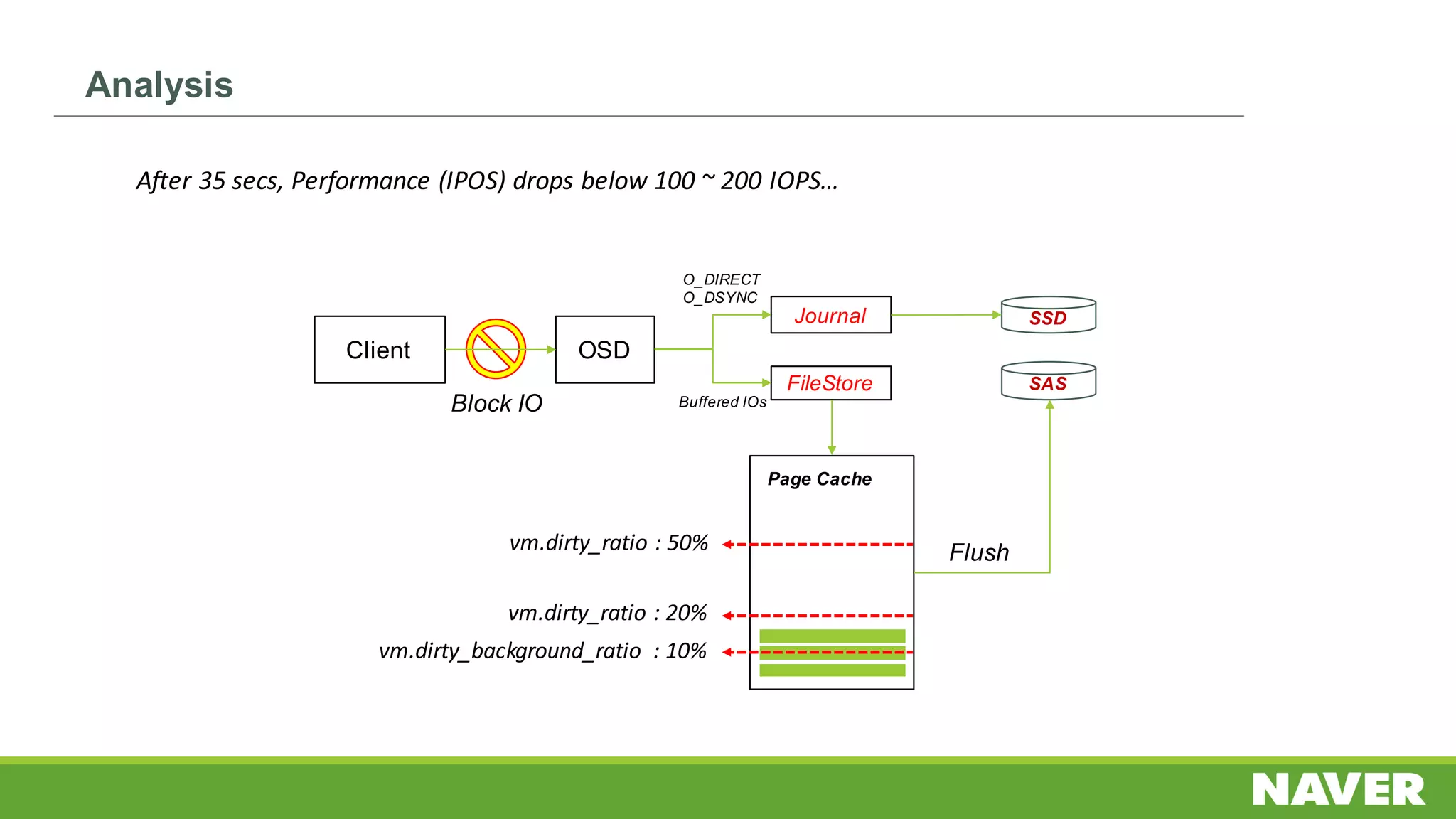
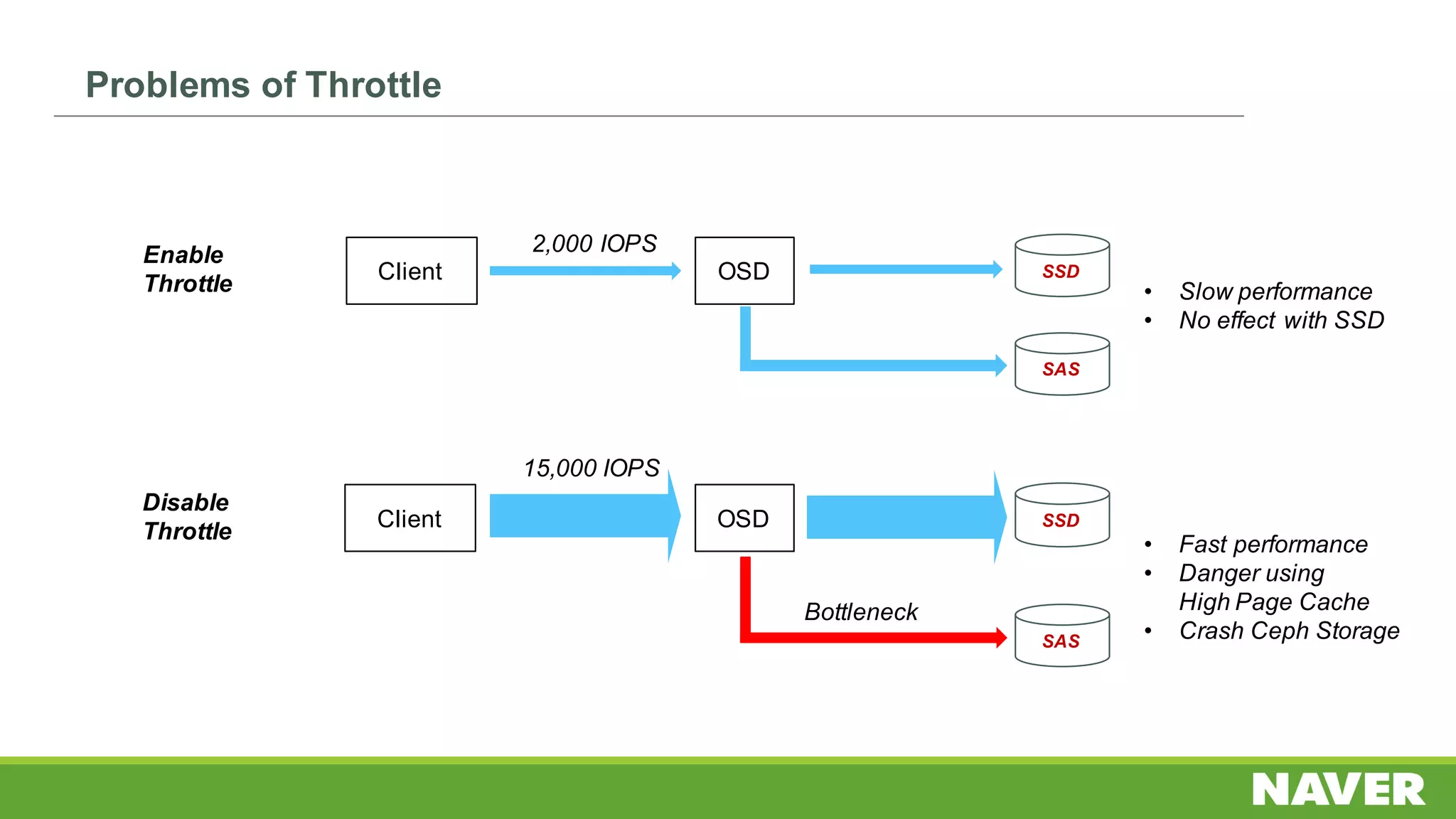
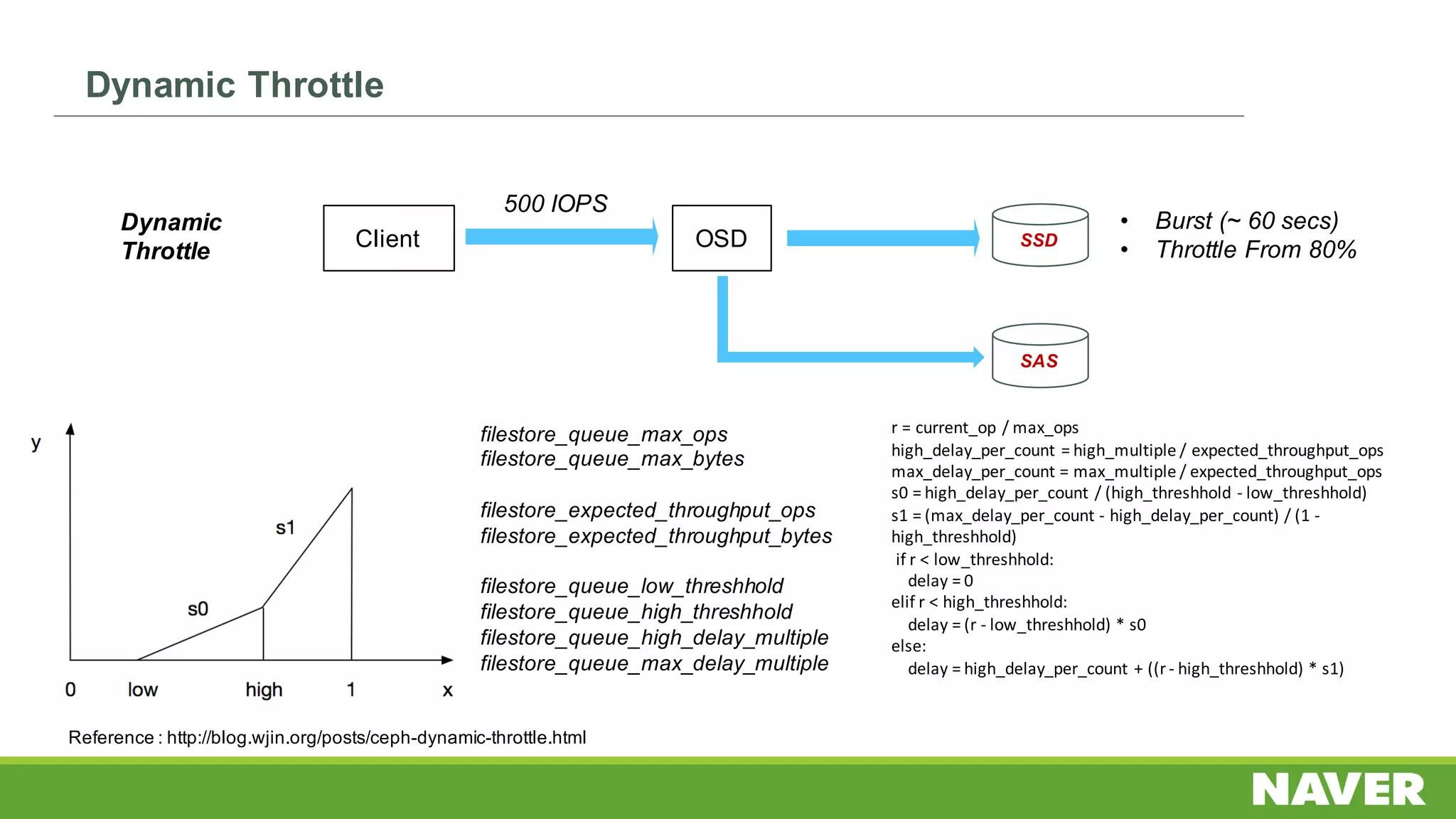
The document discusses Ceph storage on SSD for containers, covering concepts like containerization, persistent storage, and the Ceph architecture. It highlights Ceph's scalability, efficiency, and integration capabilities while detailing the write process and performance testing results. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of throttling and tuning for optimal storage performance.