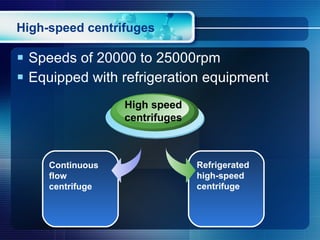
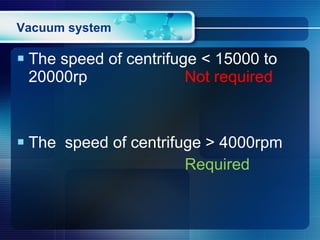
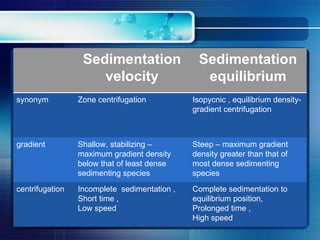
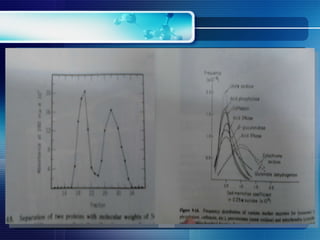
Centrifugation is a process that uses centrifugal force to separate mixtures based on density. There are different types of centrifuges that vary in maximum speed and application. Desktop centrifuges have the lowest maximum speed below 3000rpm, while ultracentrifuges can reach speeds over 75,000rpm. Centrifuges consist of major components including a drive system, temperature control, vacuum system, and rotors. Common applications include sedimentation velocity, which separates based on size, shape, and density over short times, and sedimentation equilibrium, which separates based on density differences after prolonged high-speed centrifugation.































![SUN WEI Pharmacy of woosuk university [email_address] Thank You !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/centrifugationsunwei2011-3-17-110317020648-phpapp01/85/Centrifugation-sunwei-2011-3-17-36-320.jpg)