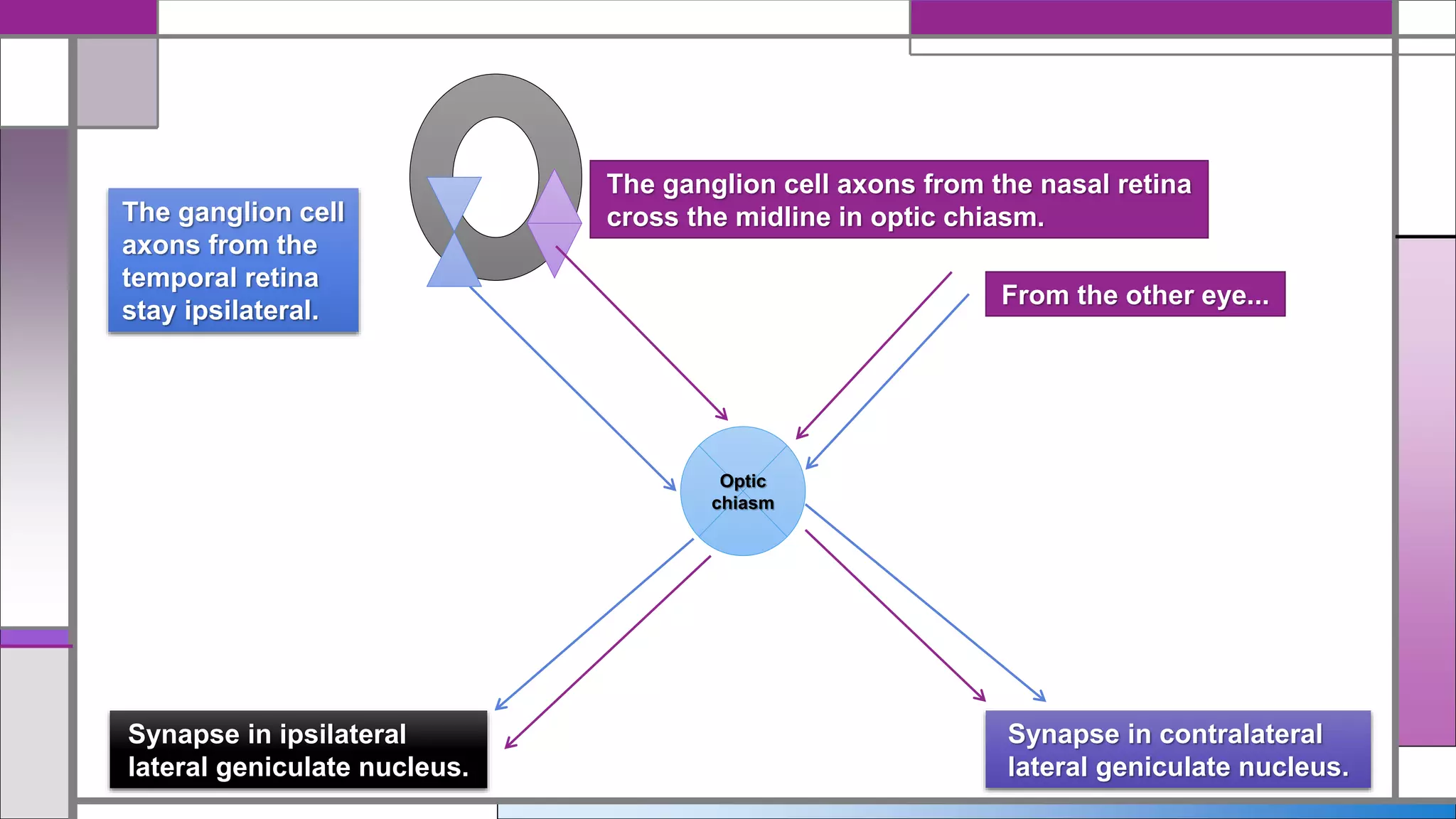
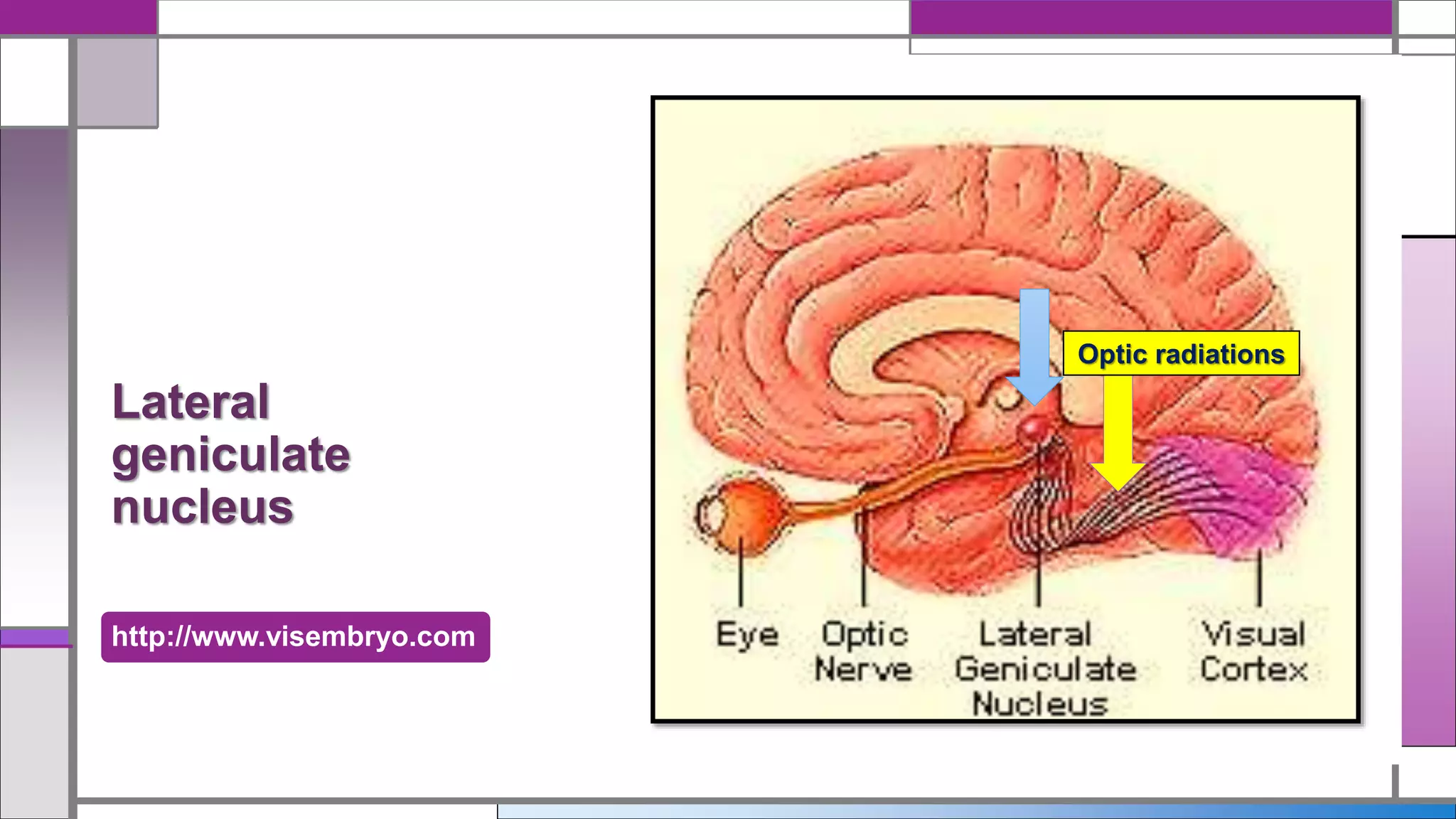
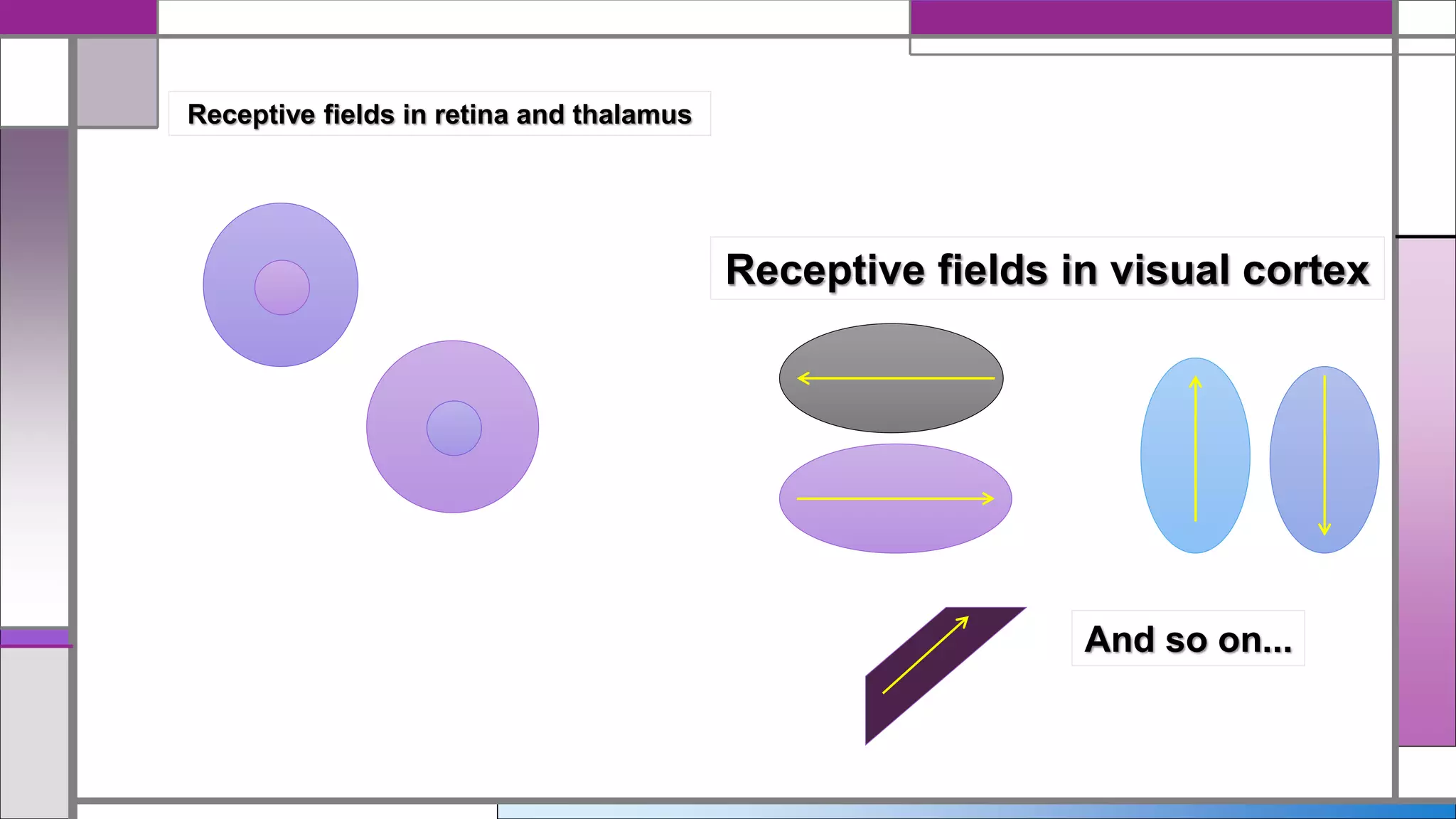
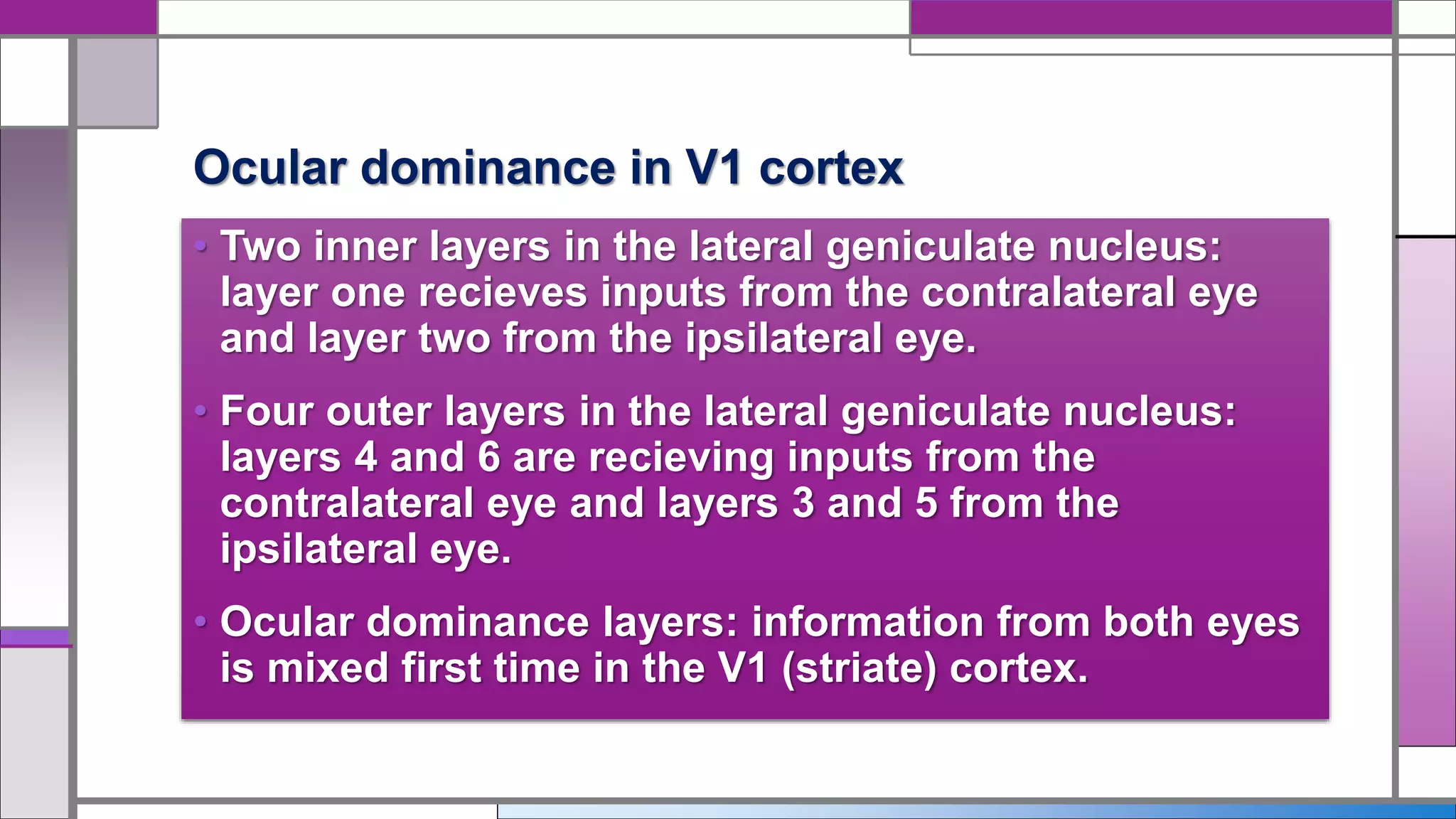
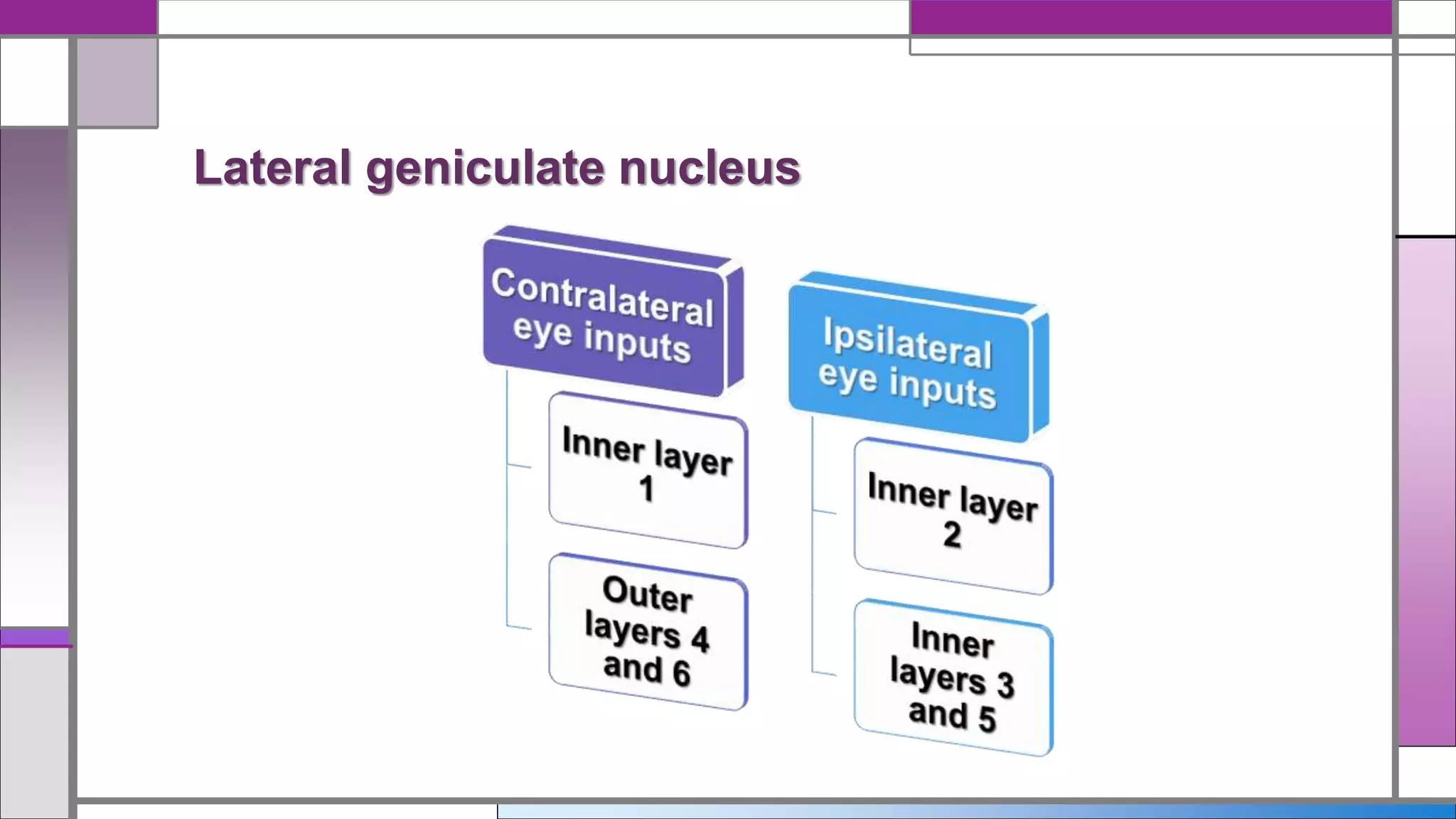
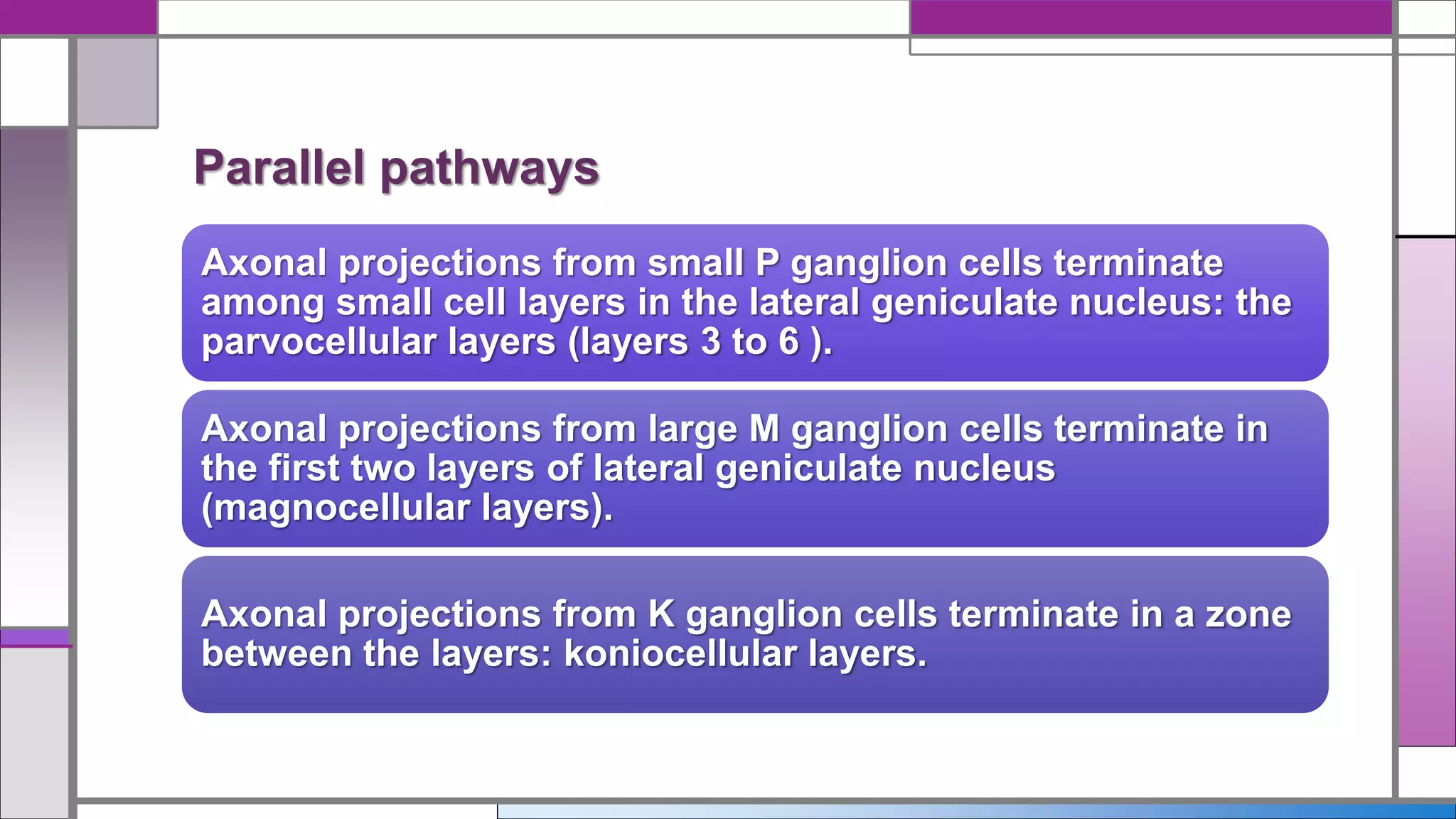
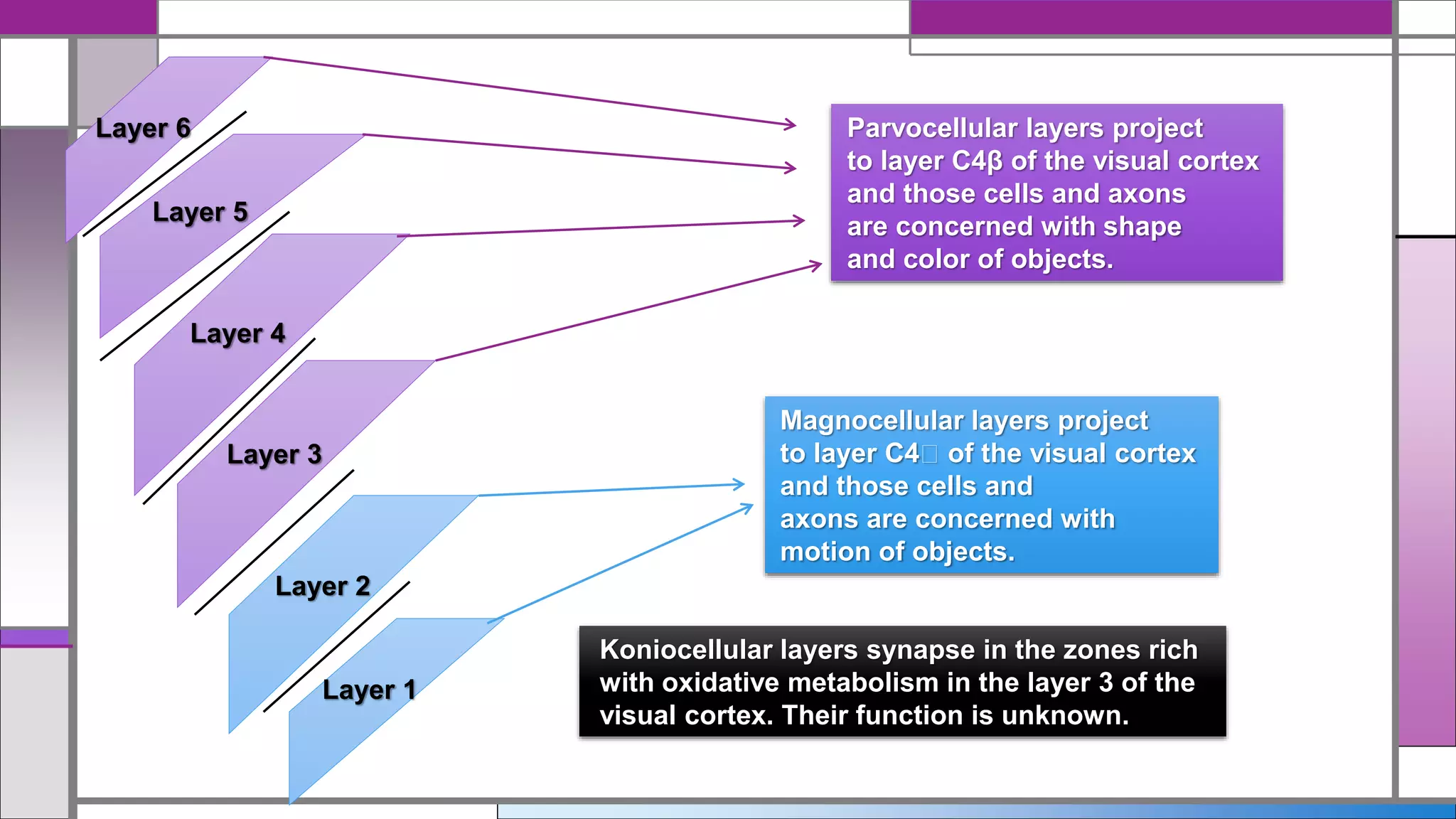
This document discusses central visual processing and the pathways from the retina to the primary visual cortex. It notes that ganglion cell axons from the nasal retina cross the midline while those from the temporal retina remain ipsilateral. These axons synapse in the lateral geniculate nucleus and then travel via the optic radiations to the primary visual cortex. There are parallel magnocellular and parvocellular pathways that are involved in motion detection and shape/color processing respectively. Damage to the fusiform gyrus can cause prosopagnosia or the inability to recognize faces.