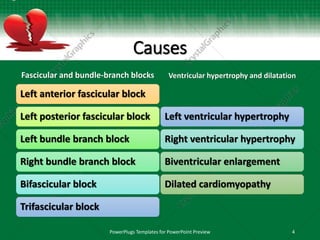
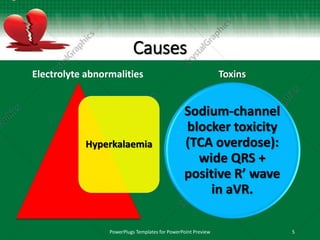
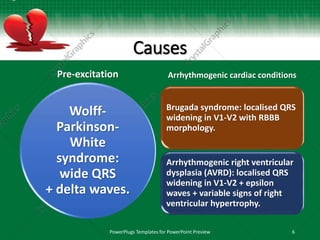
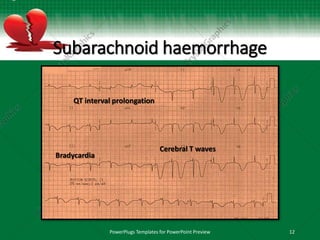
This document discusses interventricular conduction delay and raised intracranial pressure as seen on electrocardiograms (ECGs). It defines interventricular conduction delay and lists various causes including fascicular blocks, bundle branch blocks, ventricular hypertrophy, dilatation, electrolyte abnormalities, toxins, pre-excitation, and arrhythmogenic cardiac conditions. It then discusses raised intracranial pressure and the associated ECG findings of widespread T-wave inversions, QT prolongation, and bradycardia as part of the Cushing reflex, indicating imminent brainstem herniation. Massive intracranial hemorrhages such as subarachnoid hemorrhage are the most common causes