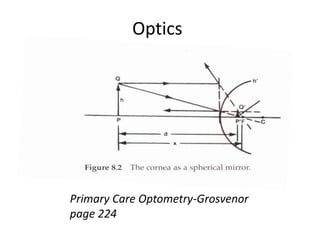
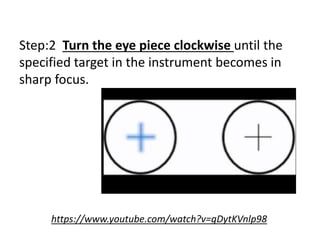
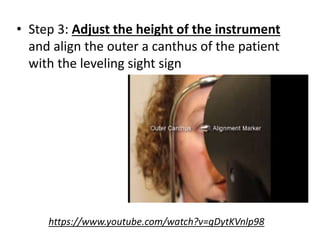
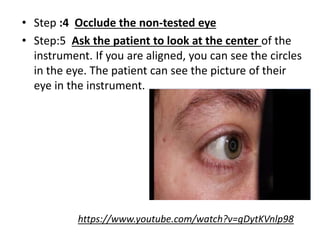
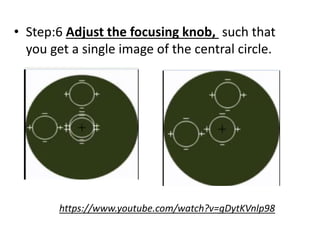
The document discusses the keratometer, an instrument used to measure the curvature of the cornea. It describes the keratometer's parts including the focusing knob, rotating grip, and measuring drums. The optical principle is that the cornea acts as a convex refracting surface and the keratometer uses the doubling principle to measure the corneal curvature. The document outlines the procedure for taking keratometry measurements, which involves adjusting the instrument height, focusing on the patient's eye, and reading the values from the measuring scales to determine the corneal curvature and astigmatism. Keratometry is important for contact lens fitting, evaluating keratoconus, and determining intraocular lens power for cataract surgery.