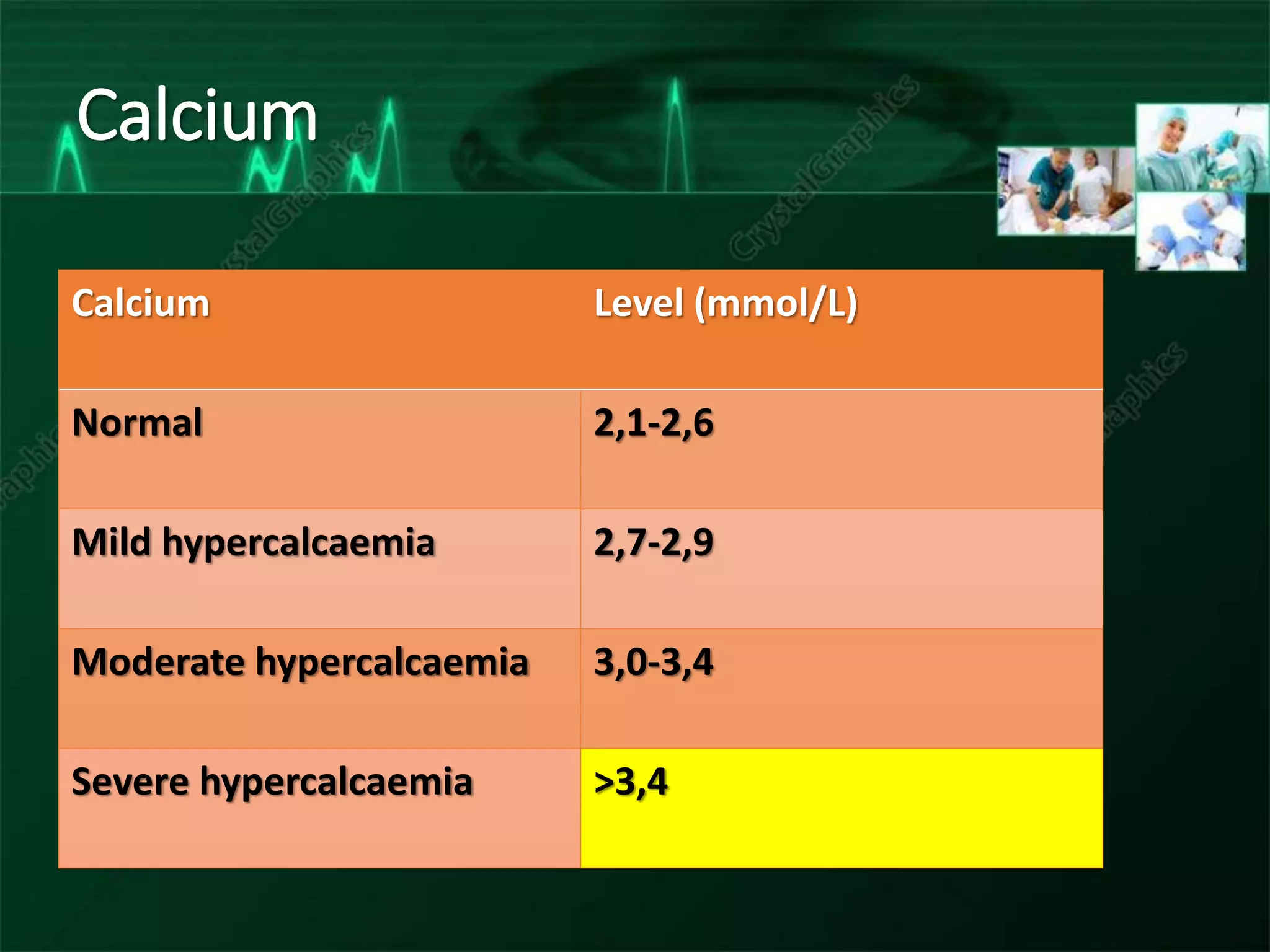
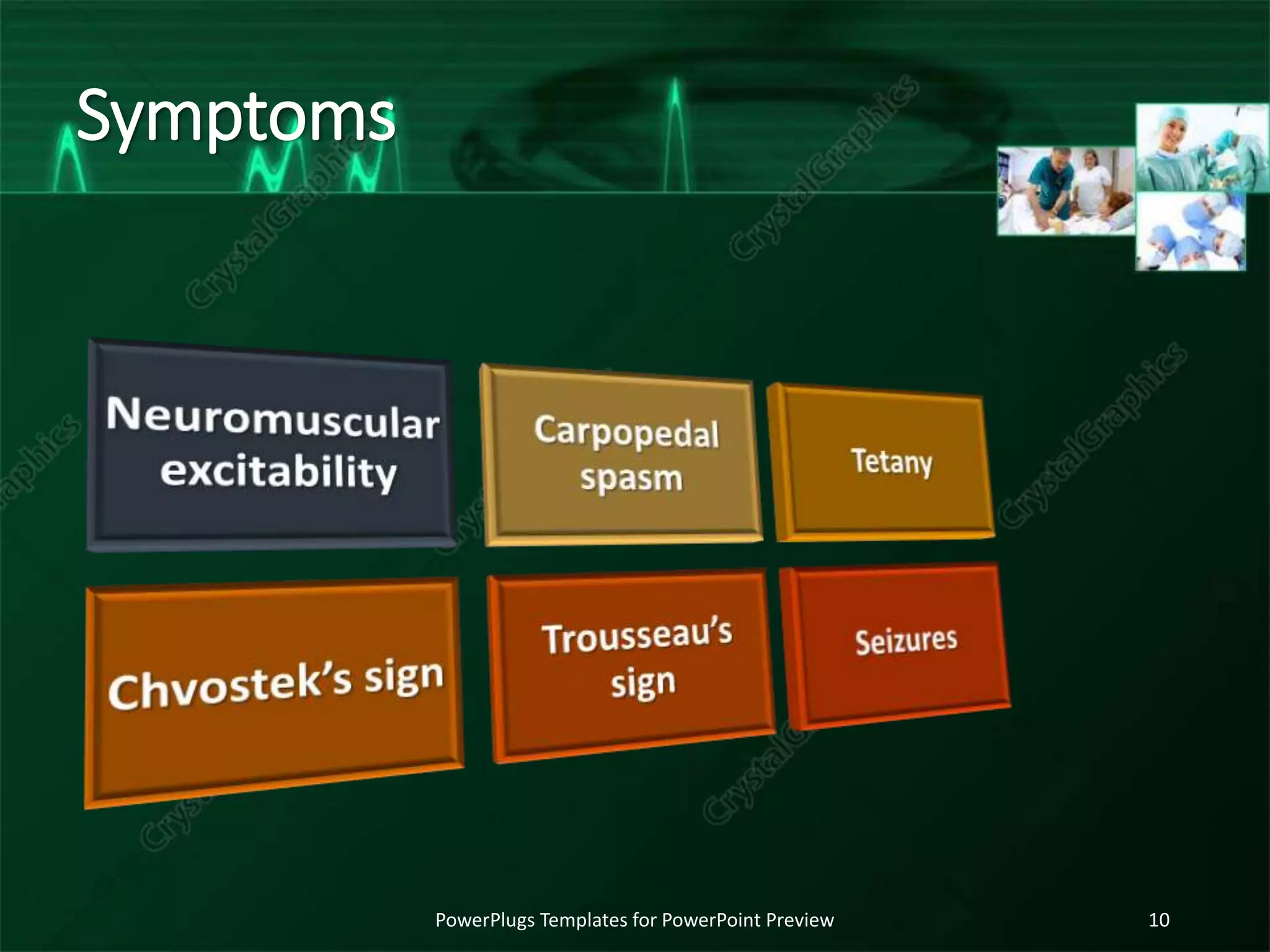
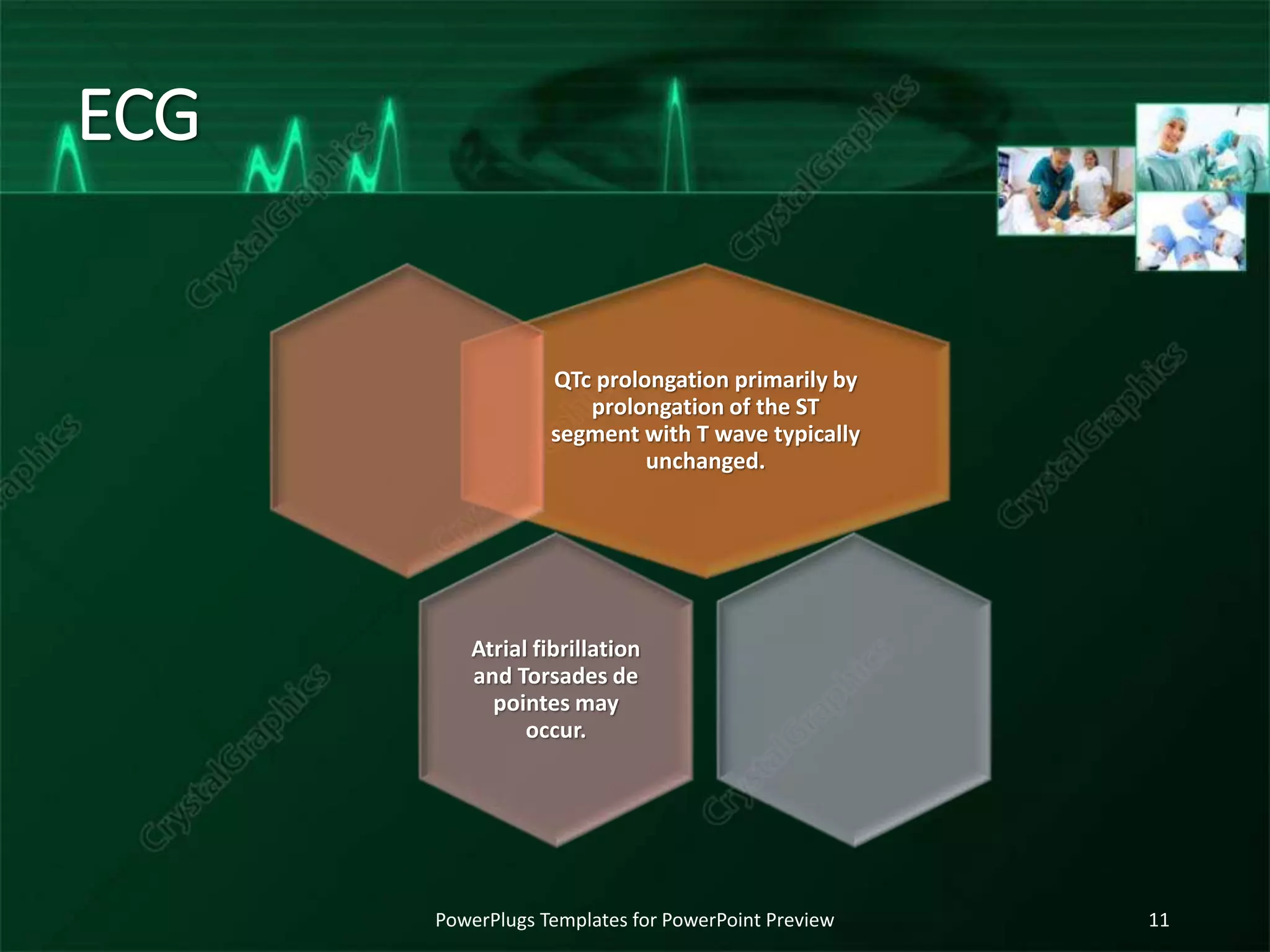
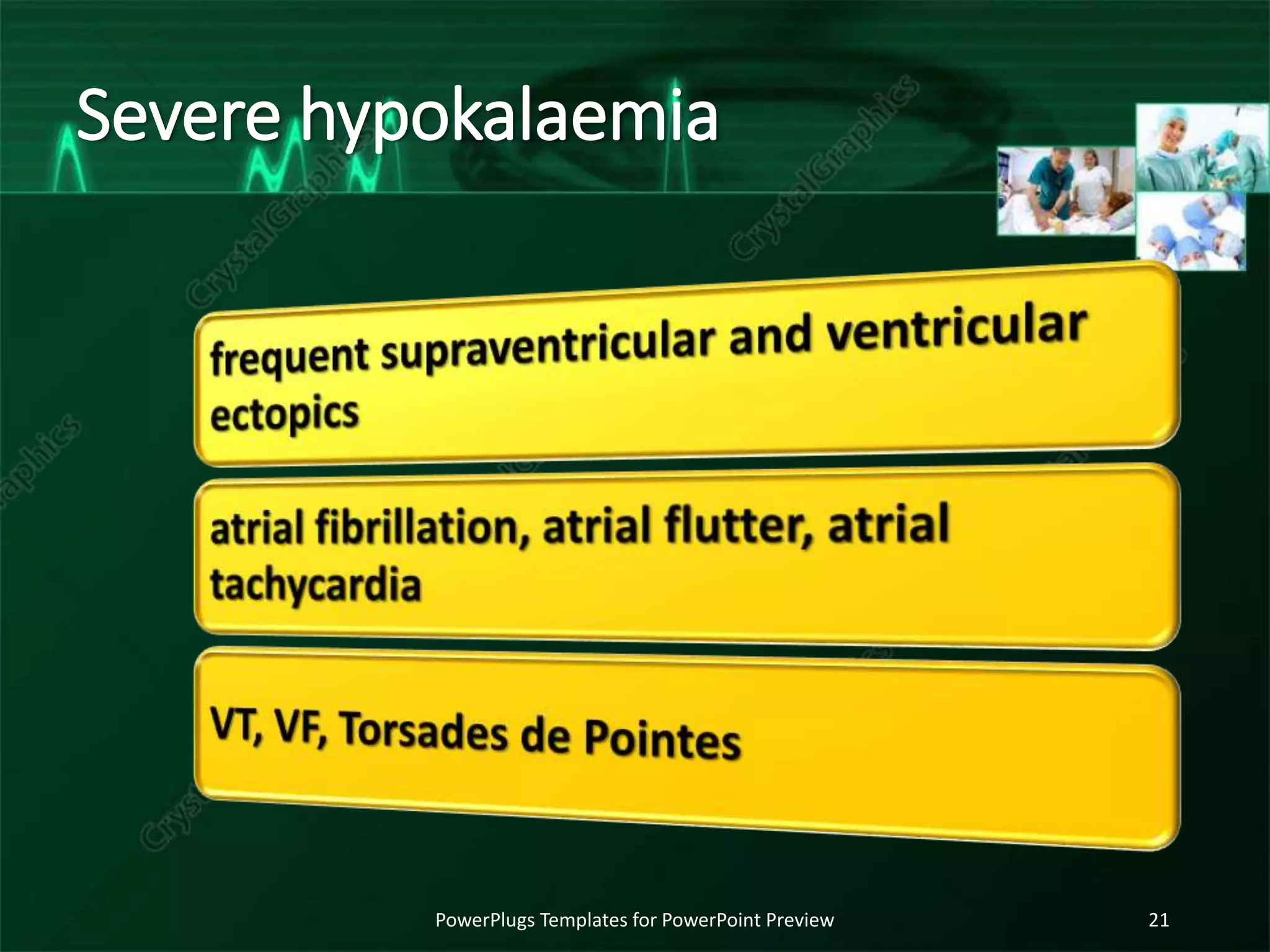
The document discusses various electrolyte abnormalities and their ECG manifestations, including hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesia, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and hypothermia. For each condition, it provides the normal and abnormal ranges for the electrolyte levels and describes the associated ECG changes such as peaked T waves, QT prolongation, low QRS voltage, bradycardia, and arrhythmias. The document serves as a reference for clinicians to recognize ECG patterns caused by electrolyte and endocrine abnormalities.