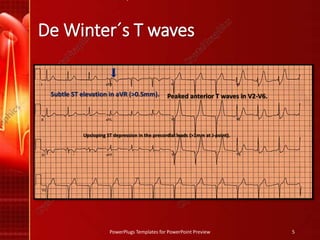
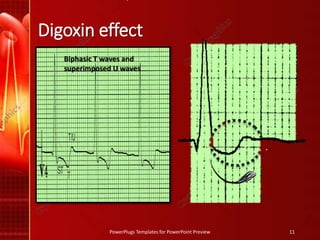
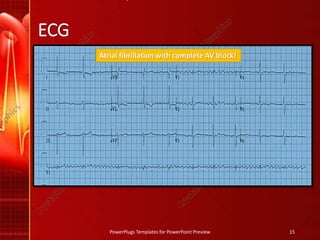
The document discusses De Winter's T waves, which are characterized by three key findings on ECG: upsloping ST depression in precordial leads, tall symmetric T waves in precordial leads, and ST elevation in aVR. It also summarizes the ECG patterns seen in dextrocardia, including right axis deviation, positive complexes in aVR, and dominant S waves in precordial leads. Finally, it outlines the ECG features of digoxin effect and toxicity, such as biphasic T waves, shortened QT, and the dysrhythmia of supraventricular tachycardia with a slow ventricular response seen in digoxin toxicity.