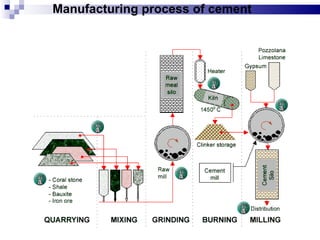
This document discusses cement, including its composition, manufacturing process, types, storage, field and laboratory tests. Cement is produced by burning and crushing limestone and clay. The main steps are mixing raw materials, burning at high temperatures, and grinding the resulting clinker along with gypsum. Common cement types include ordinary Portland cement, Portland pozzolana cement, and colored cement. Proper storage and testing ensures the quality and performance of cement.