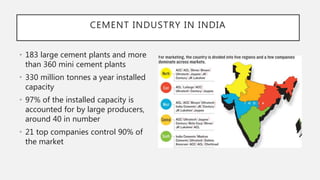
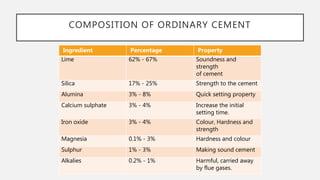
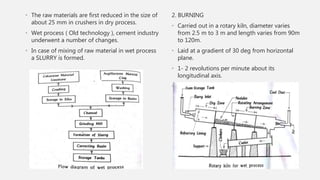
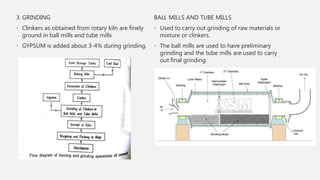
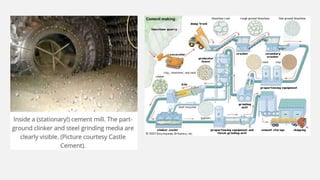
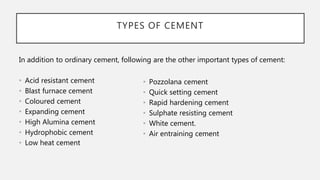
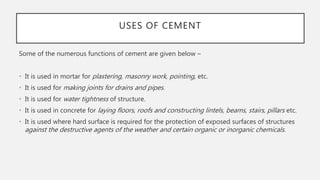
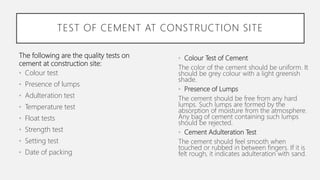
The document provides an overview of cement, highlighting its composition, manufacturing processes, types, and applications, emphasizing Portland cement as the most common variety. It details hydration, setting stages, and quality tests for cement, along with a description of various types such as acid-resistant, blast furnace, and white cement, among others. Additionally, it outlines the numerous functions of cement in construction and describes essential properties that characterize good-quality cement.