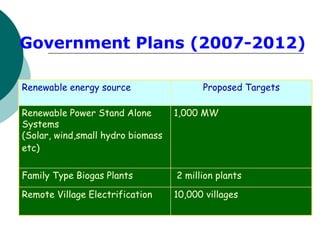
This presentation discusses non-conventional renewable energy sources that can help provide rural populations with energy access. It notes that over 2 billion people worldwide lack electricity access, including 400 million in rural India. The presentation then outlines various renewable technologies being deployed in India, including family biogas plants, solar home systems, and solar lighting for remote villages. Specific non-conventional energy sources discussed include solar lanterns, solar water heaters, solar cookers, solar collectors, solar panels, and wind power. The objective is to increase awareness of these solutions and their ability to achieve rural energy security.