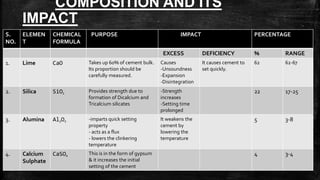
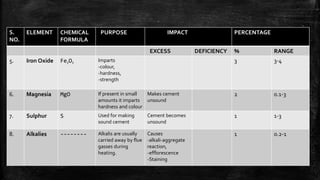
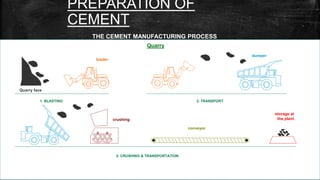
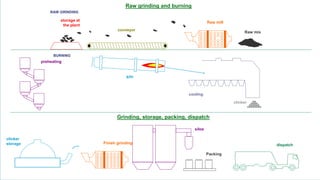
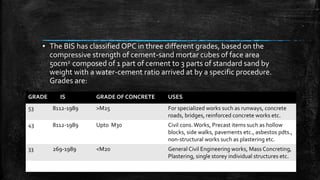
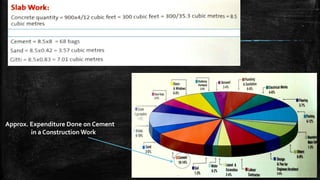
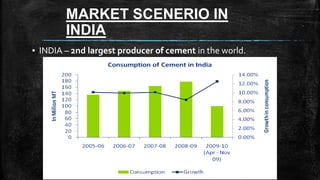
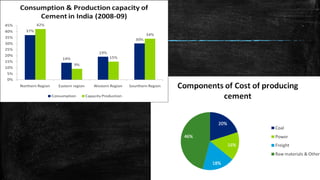
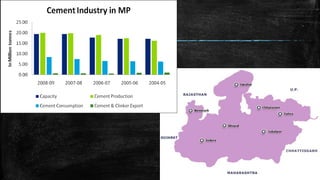
The document provides an overview of the history, types, production, and applications of cement, highlighting India's status as the second-largest producer. It discusses various types of cement, their chemical compositions, manufacturing processes, quality tests, and implications for construction and environmental impact. Additionally, it outlines the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) classification of cement grades and the major cement companies in India.