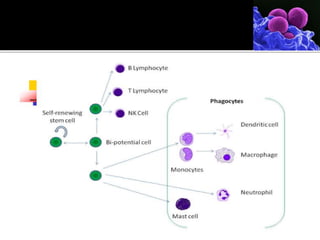
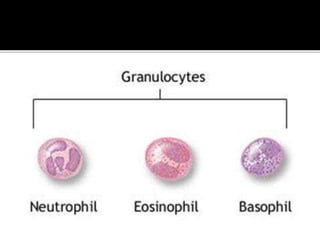
White blood cells, also called leukocytes, circulate throughout the body in blood and lymphatic vessels. They are stored in lymphoid organs such as the thymus, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. The main cells of the immune system are lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells), phagocytes (monocytes, macrophages), granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils), and dendritic cells. Lymphocytes develop from bone marrow and have roles in destroying compromised cells or producing antibodies. Phagocytes surround and destroy pathogens through phagocytosis. Granulocytes contain granules and have roles in attacking bacteria. Dendritic cells