The cell membrane is composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer that acts as a selectively permeable barrier. Cholesterol molecules maintain the integrity and fluidity of the membrane. Membrane proteins perform important functions like transporting molecules, acting as enzymes, and receiving signals. The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a fluid structure with components that can move freely within it.







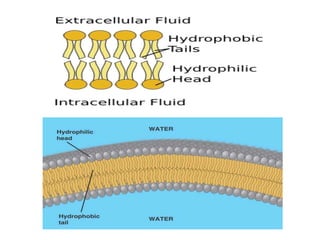
![• The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions,
proteins and other molecules where they are
needed and prevents them from diffusing into
areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are
ideally suited to this role because, even though
they are only a few nanometers in width,[1] they
are impermeable to most water-soluble
(hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly
impermeable to ions, which allows cells to
regulate salt concentrations and pH by
transporting ions across their membranes using
proteins called ion pumps.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation123-161121192930/85/Presentation1-23-9-320.jpg)













