Cell lines
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
19 likes•13,965 views
This document provides information about cell lines. It defines different types of cell lines including primary cell cultures, continuous cell lines, and transient cell lines. It discusses the HeLa cell line which was the first human cancer cell line. It outlines the process for generating stable cell lines including transfection, selection, cloning, and screening for stability. Steps for freezing and storing cell lines are described. Considerations for choosing an appropriate cell line for experiments are presented. Details are given about specific commonly used cell lines like 3T3, HEK293, PC12, CHO, and BC1. References for further information on cell line generation and characterization are provided.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Cell synchronization

INTRODUCTION
HISTORY
NEED OF SYNCHRONIZATION
SYNCHRONOUS CULTURES CAN BE OBTAINED IN SEVERAL WAYS:
Physical fractionation .
Chemical appro ach
CENTRIFUGAL ELUTRIATION
Inhibition of DNA synthesis
Nutritional deprivation
SYNCHRONIZATION AT LOW TEMPERATURE
CELLULAR TOTIPOTENCY
SOME HIGHLIGHTS OF CELL SYNCHRONIZATION
REFERENCES
Cell line

Cell lines are permanently established cell cultures that can proliferate indefinitely. They are derived from primary cell cultures which have a finite lifespan. Continuous cell lines have undergone transformation to proliferate indefinitely, unlike finite primary cultures. Common types of cell lines include normal and transformed cell lines of epithelial, fibroblast, or lymphoblast morphology derived from human or animal tissues. Primary cultures are used to establish cell lines which are then used for applications like drug screening, toxicity testing, and cancer research.
Organ culture- animal tissue culture

Organ culture involves maintaining small fragments of whole organs or tissues in culture media while retaining their three-dimensional structure and spatial distribution of cells. There are several methods of organ culture including culturing on plasma clots, agar, liquid media, or raft methods. Organ culture has various applications and allows studying cell interactions in a way that mimics the in vivo organ. It is currently being used to develop replacement organs and tissues for applications such as growing bladders, lungs, and heart patches. While progress is being made, developing fully functional human organs remains a challenge.
Biology of cultured cells

The document summarizes key aspects of culturing cells outside of their native biological environment. Cultured cells experience changes to their microenvironment, cell-cell interactions, and exposure to stimuli. Their growth is influenced by factors like the substrate, medium composition, temperature, and gas phase. Most cells require attachment to a substrate to proliferate. Adhesion molecules like integrins and cadherins mediate attachment and formation of intercellular junctions. The extracellular matrix and cytoskeleton also influence cell behavior. Control of the cell cycle, proliferation, differentiation, motility, and response to the culture environment are described at a high level. Challenges like dedifferentiation and evolution of cell lines over multiple passages are also covered.
Maintenance of cell lines

Cell lines need to be routinely maintained and stored long-term to preserve their valuable characteristics. Routine maintenance involves periodic medium changes and subculturing depending on the growth rate of the specific cell line. Long-term storage is achieved through cryopreservation, where cells are frozen at temperatures below -100°C. This process aims to minimize ice crystal formation and associated cell damage through slow freezing in the presence of cryoprotectants like DMSO or glycerol. Proper freezing and storage methods help preserve cell lines for future use and distribution.
Cell synchronization, animal cell culture

INTRODUCTION
HISTORY
NEED OF SYNCHRONIZATION
TYPES OF SYNCHRONIZATION
(I)PHYSICAL CELL SEPARATION
(II)BLOCKADE
PHYSICAL Vs BLOCKADE SYNCHRONIZATION
CONCLUSION
REFFERENCE
Cell culture based vaccine

Cell culture based vaccine??
Cell cultures involve growing cells in a culture dish, often with a supportive growth medium. A primary cell culture consists of cells taken directly from living tissue, and may contain multiple types of cells such as fibroblasts, epithelial, and endothelial cells.
In the United States, 10 different vaccines for chicken pox, hepatitis A, polio, rabies, and rubella are cultured on aborted tissue from two fetal cell lines known as WI-38 and MRC-5. These vaccines are chicken pox, hep-A, hep-A, hep-A/hep-B, polio, rabies, rubella, measles/rubella, mumps/rubella, and MMR II (measles/mumps/rubella).
Primary culture and cell line

Introduction
Primary Culture
Steps In Primary Culture
Isolation Of Tissue
Dissection And/Or Disaggregation
Types Of Primary Culture
Primary Explant Culture
Enzymatic Disaggregation
Mechanical Disaggregation
Cell Line( Finite & Continuous)
Naming A Cell Line
Choosing A Cell Line
Maintenance Of Cell Line
Conclusion
reference
Recommended
Cell synchronization

INTRODUCTION
HISTORY
NEED OF SYNCHRONIZATION
SYNCHRONOUS CULTURES CAN BE OBTAINED IN SEVERAL WAYS:
Physical fractionation .
Chemical appro ach
CENTRIFUGAL ELUTRIATION
Inhibition of DNA synthesis
Nutritional deprivation
SYNCHRONIZATION AT LOW TEMPERATURE
CELLULAR TOTIPOTENCY
SOME HIGHLIGHTS OF CELL SYNCHRONIZATION
REFERENCES
Cell line

Cell lines are permanently established cell cultures that can proliferate indefinitely. They are derived from primary cell cultures which have a finite lifespan. Continuous cell lines have undergone transformation to proliferate indefinitely, unlike finite primary cultures. Common types of cell lines include normal and transformed cell lines of epithelial, fibroblast, or lymphoblast morphology derived from human or animal tissues. Primary cultures are used to establish cell lines which are then used for applications like drug screening, toxicity testing, and cancer research.
Organ culture- animal tissue culture

Organ culture involves maintaining small fragments of whole organs or tissues in culture media while retaining their three-dimensional structure and spatial distribution of cells. There are several methods of organ culture including culturing on plasma clots, agar, liquid media, or raft methods. Organ culture has various applications and allows studying cell interactions in a way that mimics the in vivo organ. It is currently being used to develop replacement organs and tissues for applications such as growing bladders, lungs, and heart patches. While progress is being made, developing fully functional human organs remains a challenge.
Biology of cultured cells

The document summarizes key aspects of culturing cells outside of their native biological environment. Cultured cells experience changes to their microenvironment, cell-cell interactions, and exposure to stimuli. Their growth is influenced by factors like the substrate, medium composition, temperature, and gas phase. Most cells require attachment to a substrate to proliferate. Adhesion molecules like integrins and cadherins mediate attachment and formation of intercellular junctions. The extracellular matrix and cytoskeleton also influence cell behavior. Control of the cell cycle, proliferation, differentiation, motility, and response to the culture environment are described at a high level. Challenges like dedifferentiation and evolution of cell lines over multiple passages are also covered.
Maintenance of cell lines

Cell lines need to be routinely maintained and stored long-term to preserve their valuable characteristics. Routine maintenance involves periodic medium changes and subculturing depending on the growth rate of the specific cell line. Long-term storage is achieved through cryopreservation, where cells are frozen at temperatures below -100°C. This process aims to minimize ice crystal formation and associated cell damage through slow freezing in the presence of cryoprotectants like DMSO or glycerol. Proper freezing and storage methods help preserve cell lines for future use and distribution.
Cell synchronization, animal cell culture

INTRODUCTION
HISTORY
NEED OF SYNCHRONIZATION
TYPES OF SYNCHRONIZATION
(I)PHYSICAL CELL SEPARATION
(II)BLOCKADE
PHYSICAL Vs BLOCKADE SYNCHRONIZATION
CONCLUSION
REFFERENCE
Cell culture based vaccine

Cell culture based vaccine??
Cell cultures involve growing cells in a culture dish, often with a supportive growth medium. A primary cell culture consists of cells taken directly from living tissue, and may contain multiple types of cells such as fibroblasts, epithelial, and endothelial cells.
In the United States, 10 different vaccines for chicken pox, hepatitis A, polio, rabies, and rubella are cultured on aborted tissue from two fetal cell lines known as WI-38 and MRC-5. These vaccines are chicken pox, hep-A, hep-A, hep-A/hep-B, polio, rabies, rubella, measles/rubella, mumps/rubella, and MMR II (measles/mumps/rubella).
Primary culture and cell line

Introduction
Primary Culture
Steps In Primary Culture
Isolation Of Tissue
Dissection And/Or Disaggregation
Types Of Primary Culture
Primary Explant Culture
Enzymatic Disaggregation
Mechanical Disaggregation
Cell Line( Finite & Continuous)
Naming A Cell Line
Choosing A Cell Line
Maintenance Of Cell Line
Conclusion
reference
History of animal cell culture, cell final

This document provides a history and overview of animal cell culture techniques. It discusses the development of cell culture media and reagents used to support cell growth in vitro. It also describes different techniques for culturing mammalian cells, tissues, and organs, including organ culture, explant culture, and cell culture. The goal of animal cell culture is to maintain cells, tissues, or organs outside of their natural environment for research purposes.
Cell culture media

Cell culture media are designed to support the growth of cells outside their natural environment. They generally contain amino acids, salts, glucose, vitamins and other nutrients. Media can be natural (containing biological fluids) or artificial/synthetic. Artificial media are grouped into serum-containing, serum-free, chemically defined, and protein-free categories based on their ingredients. Key components of media include buffers, amino acids like glutamine, vitamins, inorganic salts, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, trace elements, and supplements specific to cell lines. Selection of the appropriate medium depends on the cell type and purpose of culture. Primary cells especially benefit from ready-to-use conditioned media.
Stem cell culture, its application

Introduction.
Properties of Stem Cells.
Key Research events.
Embryonic Stem Cell.
Stem cell Cultivation.
Stem cells are central to three processes in an organism.
Research & Clinical Application of stem cell.
Research patents.
Conclusion.
Reference.
Histotypic culture

Histotypic culture involves growing cell lines in a three-dimensional matrix at high density to form tissue-like structures. Common techniques include using gels, sponges, hollow fibers, spheroids, and rotating chambers to provide a 3D environment that allows cells to organize similarly to how they would in tissues. This allows for the study of processes like drug penetration and cell differentiation that are not possible with traditional 2D cultures. While histotypic cultures provide a model for certain tissue functions, they also face challenges like loss of cell differentiation over time.
Animal cell culture (Basics)

Cultured animal cells have many important applications. They can be used as (1) model systems to study basic cell biology and interactions between cells and pathogens, (2) for toxicity testing of new drugs and chemicals, and (3) in cancer research to study normal and cancerous cell differences. Animal cell culture is also used for virology research, manufacturing of vaccines and proteins, genetic counseling, genetic engineering of cells, and gene and drug screening and development. Proper growth media, aseptic techniques, cryopreservation, and applications in various fields make animal cell culture a valuable tool.
Bioreactors for animal cell suspension culture

This document discusses bioreactors for animal cell suspension culture. It begins by introducing animal cell culture and some key developments that enabled it. There are two main types of culture: primary culture using explants or enzymes, and secondary culture which is derived from primary culture. Cells can be anchorage-dependent, growing in monolayers, or non-anchorage dependent, growing in suspension. Bioreactors provide conditions for mass cultivation of suspension cells. Properties of animal cells require gentle mixing and aeration in bioreactors. Common bioreactor types for suspension culture include stirred tank, continuous flow, and airlift fermentors. Perfusion culture allows continuous medium exchange to achieve high cell densities and productivity.
Cell lines

Cell lines are permanently established cell cultures that can proliferate indefinitely. They are derived from primary cell cultures isolated from animal or plant tissues. Cell lines may be normal or transformed and can have finite or continuous growth. Different cell lines have various applications including screening drugs, studying cell functions, and producing vaccines and therapeutic proteins. Selecting the appropriate cell line depends on factors like species, growth characteristics, and intended experimental purpose.
Biology and characterization of the cell culture

This document provides an overview of cell culture techniques. It discusses the history of cell culture beginning in the late 1800s. Key terms like cell line, normal cell line, and continuous cell line are defined. The document outlines the biology of cultured cells including adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and energy metabolism. It also discusses the origin of cultured cells and characterization techniques for authenticating cell lines such as morphology, chromosome content, and DNA analysis. The applications of animal cell culture and conclusions are presented.
Stem cells , culture and technologies

Stem cells have the ability to renew themselves and differentiate into specialized cell types. There are two main sources of stem cells: embryonic stem cells derived from blastocysts and adult stem cells found in adult tissues. Stem cell research aims to understand development and cell differentiation processes and develop therapies for diseases. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent while adult stem cells are multipotent or unipotent. Stem cells are cultured in controlled conditions to maintain their undifferentiated state and are characterized based on gene expression and differentiation potential.
Animal cell culture media

This document discusses various applications of tissue culture, including intracellular studies, elucidation of intracellular processes, studies of cell-cell interactions, and evaluation of environmental interactions. It also notes that animal cell culture can be used to produce medically important proteins like interferon, blood clotting factors, and monoclonal antibodies. Major developments in cell culture technology included the use of antibiotics, trypsin to subculture cells, and chemically defined culture media. Common cell culture media include Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium, and RPMI-1640.
Animal cell culture

This document discusses animal cell culture techniques. It describes primary cell culture which uses cells directly from tissue and is heterogeneous and finite. Secondary culture is produced by sub-culturing primary cells, which can become cell lines that are homogeneous and can divide indefinitely. Cell lines are categorized as finite, which senesce after limited divisions, or continuous, which can divide indefinitely. Common cell lines discussed include MCF-7, HL-60, and HeLa. Requirements for cell culture include media and lab equipment, and it aims to maintain pH between 7.2-7.4.
8. Biology and characterization of cultured cells

Immediate environment and environment of surrounding medium governs the various properties of cell. The in vitro condition markedly affects the cellular property of cultured cells. For e.g. Reduction in Cell–cell and cell-material interaction. Therefore, it is imperative to develop understanding of biology of cells in response to various environmental conditions. Characterization of cells helps to identify the origin, purity and authenticity of cells and cell lines.
reporter gene

This document discusses different types of reporter genes that are used in plant functional genomics studies. It describes scorable reporter genes like green fluorescent protein (GFP), yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), and β-glucuronidase (GUS) which produce quantifiable phenotypes through enzyme assays. It also describes selectable reporter genes like antibiotic and herbicide resistance genes which allow for selection of transformed cells. Reporter genes are useful for identifying gene expression patterns, performing gene expression assays by fusing the reporter to a gene of interest, and assessing transformation/transfection efficiency. The document provides examples of using GFP fused to the XPR1 gene to study its subcellular localization in tobacco cells.
Types of animal cell culture; characterization & Their preservation.

This document provides an overview of animal cell culture, including the different types (primary and secondary cell culture, cell lines), techniques used for primary culture, and characterization and preservation of animal cells. It discusses how primary cell culture involves separating cells directly from tissue and allowing them to grow under controlled conditions. Secondary cell culture refers to sub-culturing primary cells by transferring them to new vessels with fresh media. Cell lines can be propagated repeatedly and sometimes indefinitely. The document also describes cryopreservation as a method for preserving live cells and tissues at ultra-low temperatures in liquid nitrogen.
Mtt Assay for cell viability

This document describes the MTT assay, a colorimetric assay used to measure cell viability and cytotoxicity. The MTT assay works by using the enzyme mitochondrial dehydrogenase in living cells to reduce the yellow tetrazolium dye MTT to purple insoluble formazan. The amount of formazan produced is directly proportional to the number of viable cells. The document outlines the principle, reagents, procedure, troubleshooting, advantages, and disadvantages of the MTT assay. Commonly available MTT assay kits are also listed.
Role of serum and supplements in culture medium k.s

ROLE OF SERUM AND SUPPLEMENTS IN CULTURE MEDIA
Serum is a complex mix of albumins, growth factors and growth inhibitors.
Serum is one of the most important components of cell culture media and serves as a source for amino acids, proteins, vitamins (particularly fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K), carbohydrates, lipids, hormones, growth factors, minerals, and trace elements.
Serum from fetal and calf bovine sources are commonly used to support the growth of cells in culture.
Fetal serum is a rich source of growth factors and is appropriate for cell cloning and for the growth of fastidious cells.
Calf serum is used in contact-inhibition studies because of its lower growth-promoting properties.
Normal growth media often contain 2-10% of serum.
Supplementation of media with serum serves the following functions :
Serum provides the basic nutrients (both in the solution as well as bound to the proteins) for cells.
Serum provides several growth factors and hormones involved in growth promotion and specialized cell function.
It provides several binding proteins like albumin, transferrin, which can carry other molecules into the cell. For example: albumin carries lipids, vitamins, hormones, etc. into cells.
It also supplies proteins, like fibronectin, which promote the attachment of cells to the substrate. It also provides spreading factors that help the cells to spread out before they begin to divide.
It provides protease inhibitors which protect cells from proteolysis.
It also provides minerals, like Na+, K+, Zn2+, Fe2+, etc.
It increases the viscosity of the medium and thus, protects cells from mechanical damages during agitation of suspension cultures.
It also acts a buffer.
Due to the presence of both growth factors and inhibitors, the role of serum in cell culture is very complex.
Unfortunately, in addition to serving various functions, the use of serum in tissue culture applications has several drawbacks .
Contamination in Cultured Cells

This document discusses cell culture contamination, including sources, types, signs, and methods for monitoring and preventing contamination. Common sources of contamination include failed sterilization of equipment, airborne particulates, and poorly maintained incubators. Major types of microbial contaminants are bacteria, molds, mycoplasma, yeasts, and viruses. Signs of contamination vary but may include cloudy cultures, pH changes, and visible microbes under a microscope. Proper aseptic technique and regular monitoring of cell cultures can help reduce contamination. Cross-contamination between cell lines must also be avoided.
Cytotoxicity

This document discusses cytotoxicity and methods for measuring it in vitro. It defines cytotoxicity as the ability of chemicals or cells to destroy living cells, which can lead to necrosis, apoptosis, or cytostasis. Measuring cytotoxicity is important for drug development and safety testing. In vitro assays are now commonly used as they are faster, cheaper, and more accurate than animal models. Several types of cytotoxicity assays are described, including dye exclusion assays like trypan blue, colorimetric assays like MTT, fluorometric assays like CFDA-AM, and luminometric assays like ATP assays. These assays measure endpoints such as membrane integrity, enzyme activity, proliferation, and ATP production to determine cytotoxic effects of chemicals on cells.
12. Cell synchronization and Immortalization

Cell synchronization helps in obtaining distinct sub population of cells representing different stages of cell cycle.It helps in collecting population wide data of cells progressing through various stages of cell cycle. Immortalization, refers to cells having capability of undergoing cell division infinitely. Immortal cells are particularly preferred in cell culture to enable long time storage and use. This presentation teaches about cell synchronization, methods of cell synchronization, cellular transformation, immortalization and mechanism of immortalization.
Cell culture media

- Cell culture media is the most important factor in cell culture technology as it supports cell survival, proliferation, and functions. This directly impacts research results and biopharmaceutical production.
- There are two main types of cell culture media: natural media consisting of biological fluids/extracts, and artificial/synthetic media composed of defined components like salts, nutrients, and serum.
- Early natural media included blood plasma and tissue extracts. Later, defined artificial media were developed with basal solutions and supplements to meet specific cell needs. Serum remains a common artificial media supplement providing growth factors and nutrients.
Secondary cell culture

Secondary cell cultures refer to cells that have been subcultured, or transferred, from a primary culture to a new culture vessel. Subculturing provides fresh nutrients and space for continuously growing cell lines. Cell lines can be finite or continuous depending on their lifespan in culture. Characterization of cell lines is important to confirm identity and purity through analysis of biochemical, genetic, and chromosomal parameters such as karyotyping.
Cell lines and maintanence

It contains cell lines and its types and topmost cell lines and criteria for the selection of cell lines
More Related Content
What's hot
History of animal cell culture, cell final

This document provides a history and overview of animal cell culture techniques. It discusses the development of cell culture media and reagents used to support cell growth in vitro. It also describes different techniques for culturing mammalian cells, tissues, and organs, including organ culture, explant culture, and cell culture. The goal of animal cell culture is to maintain cells, tissues, or organs outside of their natural environment for research purposes.
Cell culture media

Cell culture media are designed to support the growth of cells outside their natural environment. They generally contain amino acids, salts, glucose, vitamins and other nutrients. Media can be natural (containing biological fluids) or artificial/synthetic. Artificial media are grouped into serum-containing, serum-free, chemically defined, and protein-free categories based on their ingredients. Key components of media include buffers, amino acids like glutamine, vitamins, inorganic salts, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, trace elements, and supplements specific to cell lines. Selection of the appropriate medium depends on the cell type and purpose of culture. Primary cells especially benefit from ready-to-use conditioned media.
Stem cell culture, its application

Introduction.
Properties of Stem Cells.
Key Research events.
Embryonic Stem Cell.
Stem cell Cultivation.
Stem cells are central to three processes in an organism.
Research & Clinical Application of stem cell.
Research patents.
Conclusion.
Reference.
Histotypic culture

Histotypic culture involves growing cell lines in a three-dimensional matrix at high density to form tissue-like structures. Common techniques include using gels, sponges, hollow fibers, spheroids, and rotating chambers to provide a 3D environment that allows cells to organize similarly to how they would in tissues. This allows for the study of processes like drug penetration and cell differentiation that are not possible with traditional 2D cultures. While histotypic cultures provide a model for certain tissue functions, they also face challenges like loss of cell differentiation over time.
Animal cell culture (Basics)

Cultured animal cells have many important applications. They can be used as (1) model systems to study basic cell biology and interactions between cells and pathogens, (2) for toxicity testing of new drugs and chemicals, and (3) in cancer research to study normal and cancerous cell differences. Animal cell culture is also used for virology research, manufacturing of vaccines and proteins, genetic counseling, genetic engineering of cells, and gene and drug screening and development. Proper growth media, aseptic techniques, cryopreservation, and applications in various fields make animal cell culture a valuable tool.
Bioreactors for animal cell suspension culture

This document discusses bioreactors for animal cell suspension culture. It begins by introducing animal cell culture and some key developments that enabled it. There are two main types of culture: primary culture using explants or enzymes, and secondary culture which is derived from primary culture. Cells can be anchorage-dependent, growing in monolayers, or non-anchorage dependent, growing in suspension. Bioreactors provide conditions for mass cultivation of suspension cells. Properties of animal cells require gentle mixing and aeration in bioreactors. Common bioreactor types for suspension culture include stirred tank, continuous flow, and airlift fermentors. Perfusion culture allows continuous medium exchange to achieve high cell densities and productivity.
Cell lines

Cell lines are permanently established cell cultures that can proliferate indefinitely. They are derived from primary cell cultures isolated from animal or plant tissues. Cell lines may be normal or transformed and can have finite or continuous growth. Different cell lines have various applications including screening drugs, studying cell functions, and producing vaccines and therapeutic proteins. Selecting the appropriate cell line depends on factors like species, growth characteristics, and intended experimental purpose.
Biology and characterization of the cell culture

This document provides an overview of cell culture techniques. It discusses the history of cell culture beginning in the late 1800s. Key terms like cell line, normal cell line, and continuous cell line are defined. The document outlines the biology of cultured cells including adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and energy metabolism. It also discusses the origin of cultured cells and characterization techniques for authenticating cell lines such as morphology, chromosome content, and DNA analysis. The applications of animal cell culture and conclusions are presented.
Stem cells , culture and technologies

Stem cells have the ability to renew themselves and differentiate into specialized cell types. There are two main sources of stem cells: embryonic stem cells derived from blastocysts and adult stem cells found in adult tissues. Stem cell research aims to understand development and cell differentiation processes and develop therapies for diseases. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent while adult stem cells are multipotent or unipotent. Stem cells are cultured in controlled conditions to maintain their undifferentiated state and are characterized based on gene expression and differentiation potential.
Animal cell culture media

This document discusses various applications of tissue culture, including intracellular studies, elucidation of intracellular processes, studies of cell-cell interactions, and evaluation of environmental interactions. It also notes that animal cell culture can be used to produce medically important proteins like interferon, blood clotting factors, and monoclonal antibodies. Major developments in cell culture technology included the use of antibiotics, trypsin to subculture cells, and chemically defined culture media. Common cell culture media include Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium, and RPMI-1640.
Animal cell culture

This document discusses animal cell culture techniques. It describes primary cell culture which uses cells directly from tissue and is heterogeneous and finite. Secondary culture is produced by sub-culturing primary cells, which can become cell lines that are homogeneous and can divide indefinitely. Cell lines are categorized as finite, which senesce after limited divisions, or continuous, which can divide indefinitely. Common cell lines discussed include MCF-7, HL-60, and HeLa. Requirements for cell culture include media and lab equipment, and it aims to maintain pH between 7.2-7.4.
8. Biology and characterization of cultured cells

Immediate environment and environment of surrounding medium governs the various properties of cell. The in vitro condition markedly affects the cellular property of cultured cells. For e.g. Reduction in Cell–cell and cell-material interaction. Therefore, it is imperative to develop understanding of biology of cells in response to various environmental conditions. Characterization of cells helps to identify the origin, purity and authenticity of cells and cell lines.
reporter gene

This document discusses different types of reporter genes that are used in plant functional genomics studies. It describes scorable reporter genes like green fluorescent protein (GFP), yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), and β-glucuronidase (GUS) which produce quantifiable phenotypes through enzyme assays. It also describes selectable reporter genes like antibiotic and herbicide resistance genes which allow for selection of transformed cells. Reporter genes are useful for identifying gene expression patterns, performing gene expression assays by fusing the reporter to a gene of interest, and assessing transformation/transfection efficiency. The document provides examples of using GFP fused to the XPR1 gene to study its subcellular localization in tobacco cells.
Types of animal cell culture; characterization & Their preservation.

This document provides an overview of animal cell culture, including the different types (primary and secondary cell culture, cell lines), techniques used for primary culture, and characterization and preservation of animal cells. It discusses how primary cell culture involves separating cells directly from tissue and allowing them to grow under controlled conditions. Secondary cell culture refers to sub-culturing primary cells by transferring them to new vessels with fresh media. Cell lines can be propagated repeatedly and sometimes indefinitely. The document also describes cryopreservation as a method for preserving live cells and tissues at ultra-low temperatures in liquid nitrogen.
Mtt Assay for cell viability

This document describes the MTT assay, a colorimetric assay used to measure cell viability and cytotoxicity. The MTT assay works by using the enzyme mitochondrial dehydrogenase in living cells to reduce the yellow tetrazolium dye MTT to purple insoluble formazan. The amount of formazan produced is directly proportional to the number of viable cells. The document outlines the principle, reagents, procedure, troubleshooting, advantages, and disadvantages of the MTT assay. Commonly available MTT assay kits are also listed.
Role of serum and supplements in culture medium k.s

ROLE OF SERUM AND SUPPLEMENTS IN CULTURE MEDIA
Serum is a complex mix of albumins, growth factors and growth inhibitors.
Serum is one of the most important components of cell culture media and serves as a source for amino acids, proteins, vitamins (particularly fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K), carbohydrates, lipids, hormones, growth factors, minerals, and trace elements.
Serum from fetal and calf bovine sources are commonly used to support the growth of cells in culture.
Fetal serum is a rich source of growth factors and is appropriate for cell cloning and for the growth of fastidious cells.
Calf serum is used in contact-inhibition studies because of its lower growth-promoting properties.
Normal growth media often contain 2-10% of serum.
Supplementation of media with serum serves the following functions :
Serum provides the basic nutrients (both in the solution as well as bound to the proteins) for cells.
Serum provides several growth factors and hormones involved in growth promotion and specialized cell function.
It provides several binding proteins like albumin, transferrin, which can carry other molecules into the cell. For example: albumin carries lipids, vitamins, hormones, etc. into cells.
It also supplies proteins, like fibronectin, which promote the attachment of cells to the substrate. It also provides spreading factors that help the cells to spread out before they begin to divide.
It provides protease inhibitors which protect cells from proteolysis.
It also provides minerals, like Na+, K+, Zn2+, Fe2+, etc.
It increases the viscosity of the medium and thus, protects cells from mechanical damages during agitation of suspension cultures.
It also acts a buffer.
Due to the presence of both growth factors and inhibitors, the role of serum in cell culture is very complex.
Unfortunately, in addition to serving various functions, the use of serum in tissue culture applications has several drawbacks .
Contamination in Cultured Cells

This document discusses cell culture contamination, including sources, types, signs, and methods for monitoring and preventing contamination. Common sources of contamination include failed sterilization of equipment, airborne particulates, and poorly maintained incubators. Major types of microbial contaminants are bacteria, molds, mycoplasma, yeasts, and viruses. Signs of contamination vary but may include cloudy cultures, pH changes, and visible microbes under a microscope. Proper aseptic technique and regular monitoring of cell cultures can help reduce contamination. Cross-contamination between cell lines must also be avoided.
Cytotoxicity

This document discusses cytotoxicity and methods for measuring it in vitro. It defines cytotoxicity as the ability of chemicals or cells to destroy living cells, which can lead to necrosis, apoptosis, or cytostasis. Measuring cytotoxicity is important for drug development and safety testing. In vitro assays are now commonly used as they are faster, cheaper, and more accurate than animal models. Several types of cytotoxicity assays are described, including dye exclusion assays like trypan blue, colorimetric assays like MTT, fluorometric assays like CFDA-AM, and luminometric assays like ATP assays. These assays measure endpoints such as membrane integrity, enzyme activity, proliferation, and ATP production to determine cytotoxic effects of chemicals on cells.
12. Cell synchronization and Immortalization

Cell synchronization helps in obtaining distinct sub population of cells representing different stages of cell cycle.It helps in collecting population wide data of cells progressing through various stages of cell cycle. Immortalization, refers to cells having capability of undergoing cell division infinitely. Immortal cells are particularly preferred in cell culture to enable long time storage and use. This presentation teaches about cell synchronization, methods of cell synchronization, cellular transformation, immortalization and mechanism of immortalization.
Cell culture media

- Cell culture media is the most important factor in cell culture technology as it supports cell survival, proliferation, and functions. This directly impacts research results and biopharmaceutical production.
- There are two main types of cell culture media: natural media consisting of biological fluids/extracts, and artificial/synthetic media composed of defined components like salts, nutrients, and serum.
- Early natural media included blood plasma and tissue extracts. Later, defined artificial media were developed with basal solutions and supplements to meet specific cell needs. Serum remains a common artificial media supplement providing growth factors and nutrients.
What's hot (20)
Types of animal cell culture; characterization & Their preservation.

Types of animal cell culture; characterization & Their preservation.
Role of serum and supplements in culture medium k.s

Role of serum and supplements in culture medium k.s
Similar to Cell lines
Secondary cell culture

Secondary cell cultures refer to cells that have been subcultured, or transferred, from a primary culture to a new culture vessel. Subculturing provides fresh nutrients and space for continuously growing cell lines. Cell lines can be finite or continuous depending on their lifespan in culture. Characterization of cell lines is important to confirm identity and purity through analysis of biochemical, genetic, and chromosomal parameters such as karyotyping.
Cell lines and maintanence

It contains cell lines and its types and topmost cell lines and criteria for the selection of cell lines
Various cell line & utilities in detection of

Cell lines are established cell cultures that can proliferate indefinitely in vitro. They are used in basic research and early drug development studies. Cell lines are categorized as finite or continuous based on their lifespan. Finite cell lines have limited proliferation while continuous cell lines can proliferate indefinitely. Characterization of cell lines is important to determine their species of origin, tissue of origin, and genetic stability. Common cell lines used in research include human cell lines like HeLa, mouse cell lines like 3T3 fibroblasts, and rat cell lines. Cell lines are useful for investigating disease pathways and developing therapies.
autologous bone marrow transplant

Autologous bone marrow transplant involves harvesting a patient's own bone marrow stem cells, storing them, and later re-infusing them after high-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment to destroy cancerous cells. The stem cells help repopulate the bone marrow and restore the immune system. Complications can include infections during the neutropenic phase, graft-versus-host disease, and mucositis. Long term effects may include secondary cancers or sterility. Autologous transplants are commonly used to treat blood cancers like lymphoma or multiple myeloma.
cultivation of virus 1.pdf

This document discusses various methods for cultivating and propagating viruses, including in tissue and cell cultures as well as in live animals. It describes primary cell cultures established from organ fragments that contain a mix of cell types and can be infected by a broad range of viruses. Diploid cell lines retain their diploid character through repeated passage. Heteroploid cell lines are derived from tumor cells and can divide indefinitely. Certain viruses that cannot replicate in differentiated cells require cultivation in experimental animals or embryonated hen's eggs. While animal and egg systems provide options when cell cultures are unavailable, there is a push to reduce animal use where possible through advances in cell culture techniques.
cell culturing

This document provides information on cell culture and the establishment of cell lines. It discusses the history of cell culture, major developments in the technology, and common uses of cell culture. It also describes primary cell culture, finite and continuous cell lines, culture conditions, cryopreservation, cell morphology, and factors to consider when selecting an appropriate cell line.
Tissue culture

This document provides information on cell culture and the establishment of cell lines. It discusses the history of cell culture, major developments in the technology, and common uses of cell culture. It also describes primary cell culture, finite and continuous cell lines, culture conditions, cryopreservation, cell morphology, and factors to consider when selecting an appropriate cell line.
Cell lining technique 

This document provides information on cell culture and the establishment of cell lines. It discusses the history of cell culture, major developments in the technology, and common uses of cell culture. It also describes primary cell culture, finite and continuous cell lines, culture conditions, cryopreservation, cell morphology, and factors to consider when selecting an appropriate cell line.
cell and tissue culturing and cell line

Cell culture involves growing cells under controlled conditions outside of their natural environment. The document discusses the history and major developments of cell culture, including the use of antibiotics, trypsin, and defined culture media. It also outlines common uses of cell culture such as in cancer research, virology, genetic engineering, and gene therapy. The document provides details on primary cell culture, continuous cell lines, morphology of cells in culture, and considerations for selecting an appropriate cell line.
International Journal of Stem Cells & Research

Normal tissues and tumors arise from a population of cells termed stem cells. In vivo experiments have provided evidence of the presence of stem cells throughout the mouse mammary gland. Premalignant mammary outgrowths that faithfully recapitulate the mammary epithelial cell lineage upon transplantation contain cells with tumor-forming potential. Cell sorting techniques have identified putative mouse mammary stem cell surface markers and human breast cancer stem cell surface markers. These markers do not identify only stem cells but in fact distinguish a mixed population of cells containing stem cell activity. Previous studies have demonstrated that clones arising from single cells in vitro can be categorized into three types based on the clone morphology. Here, we report the characterization, both in vitro and in vivo, of clonogenic cells from a non-tumorigenic mammary epithelial population and those from an erbB2-induced mammary tumor. We found that clones arising from normal mammary cells expressed different patterns of stem and developmental marker between the clone types and compared to the expression patterns observed on clones that developed from tumorigenic mammary cells.
Stem cell and regenerative medicine

How stem cell help regenerate tissues and its applications in Medicine? How stem cells can give us future medicine
Monoclonal antibodies stem cell 2018

Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by identical immune cells that are clones of a single parent cell. They are produced by fusing antibody-producing cells with tumor cells to create a hybridoma cell line that continuously produces the same antibody. Monoclonal antibodies have important medical uses such as diagnosing pregnancy or HIV infection through detection of specific antigens, and treating cancer by targeting tumor-associated antigens on cancer cells. However, monoclonal antibodies produced in mice can trigger an immune response in humans, so genetically engineered antibodies are being developed to avoid this.
Arsh copy

Cell lines are immortal cell cultures that are used extensively in biomedical research. Some key uses of cell lines include studying basic cell biology, testing drug toxicity, cancer research, virology studies, and gene therapy. Common cell lines include HeLa cells from cervical cancer tissue and MCF-7 cells from breast cancer tissue. Cell lines are also important in the production of vaccines, antibodies, and other biological products through recombinant protein expression in cultured cells. Respiratory and pancreatic beta cell lines have applications in research on inflammation, diabetes, and other diseases.
Application of cell line

Cell lines are immortal cell cultures that are used extensively in biomedical research. Some key uses of cell lines include modeling disease and testing drug toxicity. Common cell lines include HeLa cells, MCF-7 breast cancer cells, and VERO monkey kidney cells. Cell lines are also used to produce biological products like vaccines, antibodies, and recombinant proteins. Respiratory cell lines help study lung diseases while pancreatic beta cell lines aid diabetes research. The duck cell line EB66 is being used commercially for viral vaccine production.
Virus culture and cytopathic effect

This document discusses protoplast isolation and cell culture. It begins by defining a protoplast as a plant cell without a cell wall that contains normal cell organelles. Protoplasts can be isolated from actively growing tissues using mechanical and enzymatic methods. The mechanical method involves plasmolysis and cutting of tissues, while the enzymatic method uses lytic enzymes to remove the cell wall. Cell culture methods are also discussed, including primary cell cultures derived directly from tissues that have a finite lifespan, and continuous cell lines derived from tumors that can divide indefinitely. Different cell types, culture media, and tissue culture techniques are described.
Monoclonal antibodies

Monoclonal antibodies are produced from single clones of B cells and are therefore specific for a single epitope. The technique of fusing B cells with myeloma cells produces hybridomas that are immortal and secrete monoclonal antibodies. This allows for unlimited production of homogeneous antibodies that are useful for research and clinical purposes due to their specificity, homogeneity, and ability to be produced in large quantities. Clinical applications of monoclonal antibodies include using them as vaccines to induce immune responses against tumors by mimicking tumor antigens.
CULTIVATION OF VIRUS.pptx

Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites which means they can only grow or reproduce inside a host cell.
The primary purpose of virus cultivation:
To isolate and identify viruses in clinical samples.
To do research on the viral structure, replication, genetics, and effects on the host cell.
To prepare viruses for vaccine production.
Isolation of the virus is always considered a gold standard for establishing the viral origin of the disease
topics covered
CULTIVATION OF VIRUSES
Animal inoculation
Embryonated eggs
CAM
Allantoic cavity
Amniotic cavity
Yolk sac
Tissue culture
Organ culture
Explant culture
Cell culture
Primary cell culture
diploid cell culture
Continues cell lines
stem cell research

stem cell research is yet to be advanced , once fully developed can alleviate human suffering, this ppt reviews the contemporary evidence, pitfalls and challenges
Applications of cell lines

A cell line is a product of immortal cells that are used for biological research.
Cells used for cell lines are immortal, that happens if a cell is cancerous.
The cells can perpetuate division indefinitely which is unlike regular cells which can only divide approximately 50 times.
Human cell lines
MCF-7 breast cancer
HL 60 Leukemia
HEK-293 Human embryonic kidney
HeLa Henrietta lacks
Primate cell lines
Vero African green monkey kidney epithelial cells
Cos-7 African green monkey kidney cells
And others such as CHO from hamster, sf9 & sf21 from insect cells.
Animal Cell Culture and its application

Cell culture refers to the removal of cells from an animal or plant and their subsequent growth in a favourable artificial environment.
Similar to Cell lines (20)
Recently uploaded
EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...

Context. With a mass exceeding several 104 M⊙ and a rich and dense population of massive stars, supermassive young star clusters
represent the most massive star-forming environment that is dominated by the feedback from massive stars and gravitational interactions
among stars.
Aims. In this paper we present the Extended Westerlund 1 and 2 Open Clusters Survey (EWOCS) project, which aims to investigate
the influence of the starburst environment on the formation of stars and planets, and on the evolution of both low and high mass stars.
The primary targets of this project are Westerlund 1 and 2, the closest supermassive star clusters to the Sun.
Methods. The project is based primarily on recent observations conducted with the Chandra and JWST observatories. Specifically,
the Chandra survey of Westerlund 1 consists of 36 new ACIS-I observations, nearly co-pointed, for a total exposure time of 1 Msec.
Additionally, we included 8 archival Chandra/ACIS-S observations. This paper presents the resulting catalog of X-ray sources within
and around Westerlund 1. Sources were detected by combining various existing methods, and photon extraction and source validation
were carried out using the ACIS-Extract software.
Results. The EWOCS X-ray catalog comprises 5963 validated sources out of the 9420 initially provided to ACIS-Extract, reaching a
photon flux threshold of approximately 2 × 10−8 photons cm−2
s
−1
. The X-ray sources exhibit a highly concentrated spatial distribution,
with 1075 sources located within the central 1 arcmin. We have successfully detected X-ray emissions from 126 out of the 166 known
massive stars of the cluster, and we have collected over 71 000 photons from the magnetar CXO J164710.20-455217.
Deep Software Variability and Frictionless Reproducibility

Deep Software Variability and Frictionless ReproducibilityUniversity of Rennes, INSA Rennes, Inria/IRISA, CNRS
The ability to recreate computational results with minimal effort and actionable metrics provides a solid foundation for scientific research and software development. When people can replicate an analysis at the touch of a button using open-source software, open data, and methods to assess and compare proposals, it significantly eases verification of results, engagement with a diverse range of contributors, and progress. However, we have yet to fully achieve this; there are still many sociotechnical frictions.
Inspired by David Donoho's vision, this talk aims to revisit the three crucial pillars of frictionless reproducibility (data sharing, code sharing, and competitive challenges) with the perspective of deep software variability.
Our observation is that multiple layers — hardware, operating systems, third-party libraries, software versions, input data, compile-time options, and parameters — are subject to variability that exacerbates frictions but is also essential for achieving robust, generalizable results and fostering innovation. I will first review the literature, providing evidence of how the complex variability interactions across these layers affect qualitative and quantitative software properties, thereby complicating the reproduction and replication of scientific studies in various fields.
I will then present some software engineering and AI techniques that can support the strategic exploration of variability spaces. These include the use of abstractions and models (e.g., feature models), sampling strategies (e.g., uniform, random), cost-effective measurements (e.g., incremental build of software configurations), and dimensionality reduction methods (e.g., transfer learning, feature selection, software debloating).
I will finally argue that deep variability is both the problem and solution of frictionless reproducibility, calling the software science community to develop new methods and tools to manage variability and foster reproducibility in software systems.
Exposé invité Journées Nationales du GDR GPL 2024
Randomised Optimisation Algorithms in DAPHNE

Slides from talk:
Aleš Zamuda: Randomised Optimisation Algorithms in DAPHNE .
Austrian-Slovenian HPC Meeting 2024 – ASHPC24, Seeblickhotel Grundlsee in Austria, 10–13 June 2024
https://ashpc.eu/
Travis Hills' Endeavors in Minnesota: Fostering Environmental and Economic Pr...

Travis Hills of Minnesota developed a method to convert waste into high-value dry fertilizer, significantly enriching soil quality. By providing farmers with a valuable resource derived from waste, Travis Hills helps enhance farm profitability while promoting environmental stewardship. Travis Hills' sustainable practices lead to cost savings and increased revenue for farmers by improving resource efficiency and reducing waste.
20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx

Evaporation step counter work. I have done a physical experiment.
(Work in progress.)
Describing and Interpreting an Immersive Learning Case with the Immersion Cub...

Current descriptions of immersive learning cases are often difficult or impossible to compare. This is due to a myriad of different options on what details to include, which aspects are relevant, and on the descriptive approaches employed. Also, these aspects often combine very specific details with more general guidelines or indicate intents and rationales without clarifying their implementation. In this paper we provide a method to describe immersive learning cases that is structured to enable comparisons, yet flexible enough to allow researchers and practitioners to decide which aspects to include. This method leverages a taxonomy that classifies educational aspects at three levels (uses, practices, and strategies) and then utilizes two frameworks, the Immersive Learning Brain and the Immersion Cube, to enable a structured description and interpretation of immersive learning cases. The method is then demonstrated on a published immersive learning case on training for wind turbine maintenance using virtual reality. Applying the method results in a structured artifact, the Immersive Learning Case Sheet, that tags the case with its proximal uses, practices, and strategies, and refines the free text case description to ensure that matching details are included. This contribution is thus a case description method in support of future comparative research of immersive learning cases. We then discuss how the resulting description and interpretation can be leveraged to change immersion learning cases, by enriching them (considering low-effort changes or additions) or innovating (exploring more challenging avenues of transformation). The method holds significant promise to support better-grounded research in immersive learning.
Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero Water

Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero WaterTexas Alliance of Groundwater Districts
Presented at June 6-7 Texas Alliance of Groundwater Districts Business Meeting如何办理(uvic毕业证书)维多利亚大学毕业证本科学位证书原版一模一样

原版纸张【微信:741003700 】【(uvic毕业证书)维多利亚大学毕业证】【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原海外各大学 Bachelor Diploma degree, Master Degree Diploma
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
Compexometric titration/Chelatorphy titration/chelating titration

Classification
Metal ion ion indicators
Masking and demasking reagents
Estimation of Magnisium sulphate
Calcium gluconate
Complexometric Titration/ chelatometry titration/chelating titration, introduction, Types-
1.Direct Titration
2.Back Titration
3.Replacement Titration
4.Indirect Titration
Masking agent, Demasking agents
formation of complex
comparition between masking and demasking agents,
Indicators/Metal ion indicators/ Metallochromic indicators/pM indicators,
Visual Technique,PM indicators (metallochromic), Indicators of pH, Redox Indicators
Instrumental Techniques-Photometry
Potentiometry
Miscellaneous methods.
Complex titration with EDTA.
Remote Sensing and Computational, Evolutionary, Supercomputing, and Intellige...

Remote Sensing and Computational, Evolutionary, Supercomputing, and Intellige...University of Maribor
Slides from talk:
Aleš Zamuda: Remote Sensing and Computational, Evolutionary, Supercomputing, and Intelligent Systems.
11th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (IcETRAN), Niš, 3-6 June 2024
Inter-Society Networking Panel GRSS/MTT-S/CIS Panel Session: Promoting Connection and Cooperation
https://www.etran.rs/2024/en/home-english/Phenomics assisted breeding in crop improvement

As the population is increasing and will reach about 9 billion upto 2050. Also due to climate change, it is difficult to meet the food requirement of such a large population. Facing the challenges presented by resource shortages, climate
change, and increasing global population, crop yield and quality need to be improved in a sustainable way over the coming decades. Genetic improvement by breeding is the best way to increase crop productivity. With the rapid progression of functional
genomics, an increasing number of crop genomes have been sequenced and dozens of genes influencing key agronomic traits have been identified. However, current genome sequence information has not been adequately exploited for understanding
the complex characteristics of multiple gene, owing to a lack of crop phenotypic data. Efficient, automatic, and accurate technologies and platforms that can capture phenotypic data that can
be linked to genomics information for crop improvement at all growth stages have become as important as genotyping. Thus,
high-throughput phenotyping has become the major bottleneck restricting crop breeding. Plant phenomics has been defined as the high-throughput, accurate acquisition and analysis of multi-dimensional phenotypes
during crop growing stages at the organism level, including the cell, tissue, organ, individual plant, plot, and field levels. With the rapid development of novel sensors, imaging technology,
and analysis methods, numerous infrastructure platforms have been developed for phenotyping.
Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf

When I was asked to give a companion lecture in support of ‘The Philosophy of Science’ (https://shorturl.at/4pUXz) I decided not to walk through the detail of the many methodologies in order of use. Instead, I chose to employ a long standing, and ongoing, scientific development as an exemplar. And so, I chose the ever evolving story of Thermodynamics as a scientific investigation at its best.
Conducted over a period of >200 years, Thermodynamics R&D, and application, benefitted from the highest levels of professionalism, collaboration, and technical thoroughness. New layers of application, methodology, and practice were made possible by the progressive advance of technology. In turn, this has seen measurement and modelling accuracy continually improved at a micro and macro level.
Perhaps most importantly, Thermodynamics rapidly became a primary tool in the advance of applied science/engineering/technology, spanning micro-tech, to aerospace and cosmology. I can think of no better a story to illustrate the breadth of scientific methodologies and applications at their best.
Thornton ESPP slides UK WW Network 4_6_24.pdf

ESPP presentation to EU Waste Water Network, 4th June 2024 “EU policies driving nutrient removal and recycling
and the revised UWWTD (Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive)”
Micronuclei test.M.sc.zoology.fisheries.

Current Ms word generated power point presentation covers major details about the micronuclei test. It's significance and assays to conduct it. It is used to detect the micronuclei formation inside the cells of nearly every multicellular organism. It's formation takes place during chromosomal sepration at metaphase.
Unlocking the mysteries of reproduction: Exploring fecundity and gonadosomati...

The pygmy halfbeak Dermogenys colletei, is known for its viviparous nature, this presents an intriguing case of relatively low fecundity, raising questions about potential compensatory reproductive strategies employed by this species. Our study delves into the examination of fecundity and the Gonadosomatic Index (GSI) in the Pygmy Halfbeak, D. colletei (Meisner, 2001), an intriguing viviparous fish indigenous to Sarawak, Borneo. We hypothesize that the Pygmy halfbeak, D. colletei, may exhibit unique reproductive adaptations to offset its low fecundity, thus enhancing its survival and fitness. To address this, we conducted a comprehensive study utilizing 28 mature female specimens of D. colletei, carefully measuring fecundity and GSI to shed light on the reproductive adaptations of this species. Our findings reveal that D. colletei indeed exhibits low fecundity, with a mean of 16.76 ± 2.01, and a mean GSI of 12.83 ± 1.27, providing crucial insights into the reproductive mechanisms at play in this species. These results underscore the existence of unique reproductive strategies in D. colletei, enabling its adaptation and persistence in Borneo's diverse aquatic ecosystems, and call for further ecological research to elucidate these mechanisms. This study lends to a better understanding of viviparous fish in Borneo and contributes to the broader field of aquatic ecology, enhancing our knowledge of species adaptations to unique ecological challenges.
3D Hybrid PIC simulation of the plasma expansion (ISSS-14)

3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) algorithm,
Plasma expansion in the dipole magnetic field.
waterlessdyeingtechnolgyusing carbon dioxide chemicalspdf

The technology uses reclaimed CO₂ as the dyeing medium in a closed loop process. When pressurized, CO₂ becomes supercritical (SC-CO₂). In this state CO₂ has a very high solvent power, allowing the dye to dissolve easily.
Recently uploaded (20)
EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...

EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...
Deep Software Variability and Frictionless Reproducibility

Deep Software Variability and Frictionless Reproducibility
Travis Hills' Endeavors in Minnesota: Fostering Environmental and Economic Pr...

Travis Hills' Endeavors in Minnesota: Fostering Environmental and Economic Pr...
20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx

20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx
Describing and Interpreting an Immersive Learning Case with the Immersion Cub...

Describing and Interpreting an Immersive Learning Case with the Immersion Cub...
Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero Water

Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero Water
Compexometric titration/Chelatorphy titration/chelating titration

Compexometric titration/Chelatorphy titration/chelating titration
Remote Sensing and Computational, Evolutionary, Supercomputing, and Intellige...

Remote Sensing and Computational, Evolutionary, Supercomputing, and Intellige...
Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf

Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf
Unlocking the mysteries of reproduction: Exploring fecundity and gonadosomati...

Unlocking the mysteries of reproduction: Exploring fecundity and gonadosomati...
3D Hybrid PIC simulation of the plasma expansion (ISSS-14)

3D Hybrid PIC simulation of the plasma expansion (ISSS-14)
waterlessdyeingtechnolgyusing carbon dioxide chemicalspdf

waterlessdyeingtechnolgyusing carbon dioxide chemicalspdf
Cell lines
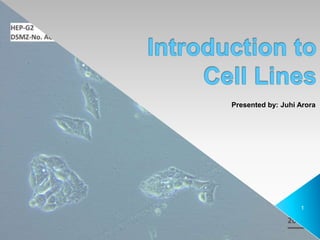
- 1. Presented by: Juhi Arora 1
- 2. A cell line can be defined as a cell culture derived from a single cell and therefore, consists of cells with a uniform genetic make-up. Primary Cell Culture: Primary cell culture consists of cells before subculturing is carried out.These are directly derived from tissue explants or disaggregrated tissue samples and therefore contain a mixture of cell types. Unlike ‘immortalised cell lines’, primary cells have not been altered in anyway and have a finite lifespan. Continuous/Stable cell line: Cell lines which either occur spontaneously or induced virally are chemically transformed into continuous cell lines. The hallmark of stably transfected cells is that the foreign gene becomes part of the genome and is therefore replicated. Descendants of these transfected cells, therefore, will also express the new gene, resulting in a stably transfected cell line. Transient cell line: Transiently transfected cells express the foreign gene but do not integrate it into their genome.Thus the new gene will not be replicated. These cells express the transiently transfected gene for a finite period of time, usually several days, after which the foreign gene is lost through cell division or other factors. 2
- 3. In february 1951, Henrietta Lacks was diagnosed with cervical cancer at the John Hopkins Gynecology clinic in Baltimore. While Henrietta Lacks was treated at Johns Hopkins, Dr Gey was attempting to fulfill ambitious goals for theTissue Culture Laboratory, that is, “the isolation and maintenance of normal and malignant or otherwise diseased tissues as temporary or stable organoids or as derived cell strains.” Approximately 30 specimens of cervical cancer had been sent to the laboratory of Dr Gey by the time Ms Lacks presented to the gynecology clinic. Cells obtained from the biopsy specimen of Henrietta Lacks into culture by using the roller-tube technique; the cells grew robustly, contrary to the results with previous specimens, becoming the first human cancer cell line immortalized in tissue culture. Dr. GeorgeGey HeLa Cells Henrietta Lacks 3
- 4. Transfected cells are grown in selective media to generate stable pools. Once the pools are fully recovered, the productivity and quality of pools is evaluated and top 3 pools are selected. Three pools are plated into semi-solid medium in 6-well plates for clone-picking. High-expressing clones can be captured and visualized by a fluorescently labeled antibody. 20 to 30 clones from each pool are selected and expanded into shake flasks. The top 20 to 30 clones from each pool are further evaluated based on growth rates. Propagate a small portion of selected cells for 50-90 doublings to confirm stability of expression by verifying expression of the target gene at multiple time points. Once expression is verified, clones of interest can be scaled up to larger volumes and subsequently frozen in appropriate frozen media. Construction / subcloning of high expression vectors Transfection Selection of stably transfected cells Clone picking Stability screening Expand and freeze down high expressing stocks 4
- 5. Create master cell banks and working cell banks (depending on the requirement). If possible, store these in separate nitrogen storage tanks. For use: Cells must be quickly thawed to prevent formation of ice crystals. Pellet down cells. Remove DMSO. Resuspend cells in tissue culture medium (e.g DMEM) and perform cell counting.Accordingly, determine the volume of cells required. Transfer cells to a sterile petri plate containing appropriate amount of media and incubate at 37ᵒC, 5% CO2. Observe for 2-3 days for recovery of cells. Keep cells in 10% FBS until cell line is established. For subculturing & freezing of cells, the plates are trypnised. For storage, cells are suspended in the freezing medium (10% DMSO, FBS) and 1 ml aliquotes are prepared.These are then stored at -20ᵒC for 1 hr and at -80ᵒC before transferring to nitrogen storage tanks. 5
- 6. 6 Species: Non-human and non-primate cell lines usually have fewer biosafety restrictions, but ultimately your experiments will dictate whether to use species-specific cultures or not. Functional characteristics: What is the purpose of your experiments? For example, liver- and kidney-derived cell lines may be more suitable for toxicity testing. Finite or continuous: While choosing from finite cell lines may give you more options to express the correct functions, continuous cell lines are often easier to clone and maintain. Normal or transformed: Transformed cell lines usually have an increased growth rate and higher plating efficiency, are continuous, and require less serum in media, but they have undergone a permanent change in their phenotype through a genetic transformation. Growth conditions & characteristics: What are your requirements with respect to growth rate, saturation density, cloning efficiency, and the ability to grow in suspension? For example, to express a recombinant protein in high yields, you might want to choose a cell line with a fast growth rate and an ability to grow in suspension. Other criteria: If you are using a finite cell line, are there sufficient stocks available? Is the cell line well-characterized, or do you have to perform the validation yourself? If you are using an abnormal cell line, do you have an equivalent normal cell line that you can use as a control? Is the cell line stable? If not, how easy it is to clone it and generate sufficient frozen stocks for your experiments?
- 7. 7
- 8. Cell Line: 3T3 Species: Mus Musculus Cell type: fibroblasts Origin: established from disaggregated Swiss albino mouse embryos in 1962; cells are used for transfection studies with DNA viruses and as assay system for transformation studies; cells have a high sensitivity to contact inhibition Morphology: fibroblasts growing adherently as monolayer with contact inhibition. Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: SMRV - 8
- 9. 9
- 10. Cell Line: HELA Species: Homo Sapiens Cell type: Cervix carcinoma Origin: established from the epitheloid cervix carcinoma of a 31- year-old black woman in 1951; later diagnosis changed to adenocarcinoma; first aneuploid, continuously cultured human cell line Morphology: epithelial-like cells growing in monolayers Risk assessment:The cell line is infected with papilloma virus type 18 (HPV-18).The cells contain several copies as proviruses integrated into the eukaryotic genome.The integrated virus genomes are incomplete and exhibit 2-3 kb deletions of the E2-L2 region. An activation and transmission of the HPV-18 during handling of the cell line is improbable.The cell line is categorized biosafety level 1. Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HHV- 8 -, HIV -, HPV +, HTLV-I/II -, MLV -, SMRV - 10
- 11. 11
- 12. Cell Line: 293 Species: Homo Sapiens Cell type: Embryonic Kidney Origin: established from a human primary embryonal kidney transformed by adenovirus type 5 (Ad 5); classified as risk category 1 according to the German Central Commission for Biological Safety (ZKBS); cell line also known as HEK-293 (human embryonic kidney- 293) Morphology: adherent fibroblastoid cells growing as monolayer; Risk assessment:The cell line was established by transfection of the cells with sheared DNA of adenovirus type 5.The cells contain 4 to 5 copies of the left end of the virus (12% of the viral genome) including E1a and E1b genes and one copy of the right end of the virus (10% of the genome) including the E4 gene. No active viruses are produced. Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-8 -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, MLV -, SMRV - 12
- 13. 13
- 14. Cell Line: PC 12 Species: rat (Rattus norvegicus) Cell type: adrenal pheochromocytoma Origin: established from a transplantable rat adrenalpheochromocytoma in 1976; cells were described to synthesize catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine); in response to nerve growth factor (NGF) a neuronal phenotype could be induced reversibly Morphology: small cells growing in clumps in suspension, adhering poorly to plastic; Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: SMRV - 14
- 15. 15
- 16. Cell Line: CHO K1 Species: Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus) Cell type: ovary cells Origin: subclone from parental CHO cell line that was initiated from an ovary biopsy of an adult Chinese hamster in 1957 Morphology: adherent, fibroblastoid cells, may be induced to undergo additional differentiation Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: SMRV - 16
- 17. 17
- 18. Cell Line: BC 1 Species: human (Homo sapiens) Cell type: B cell lymphoma Origin: established from the malignant effusion samples of a 46-year-old man with AIDS-related primary effusion lymphoma (PEL, stage IE-B) at diagnosis in 1992; cells are described to be positive for human herpesvirus type 8 (HHV-8) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Morphology: round cells growing singly and in small clusters in suspension Risk Assessment: The cell line carries HHV-8 sequences which were detected by PCR and Southern blot.We did not determine the infection mode of this herpes virus and cannot exclude the secretion of the viruses. The cell line is also positive for EBV (HHV-4) by PCR analysis.Additionally, expression of immediate-early protein BZLF-1 and lately expressed capsid protein were also positive by western blot and immunostaining, respectively, in untreated and phorbol ester / sodium butyrate stimulated cells.The infection was classified as lytic associated with production of active viruses. A transmission of EBV during handling of the cells is possible and the cell line is thus categorized biosafety level 2. Viruses: PCR: EBV +, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-8 +, HIV -, HTLV-I/-II -, MLV - 18
- 19. 19
- 20. 20 https://www.mirusbio.com/applications/stable-cell-line-generation http://www.profacgen.com/stable-cell-line-construction.htm http://www.genscript.com/production-stable-cell-lines.html http://www.wuxiapptec.com/pdf/914-CellLineDevelopment-413wl.pdf http://www.abcam.com/index.html?pageconfig=resource&rid=11742 http://vlab.amrita.edu/?sub=3&brch=188&sim=331&cnt=2 https://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/catalogue-human-and-animal-cell- lines.html#searchResult http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26851/table/A1515/ http://www.biocompare.com/Editorial-Articles/126324-Transfection/ https://www.thermofisher.com/in/en/home/references/gibco-cell-culture-basics/cell- lines.html
- 21. THANKYOU. 21