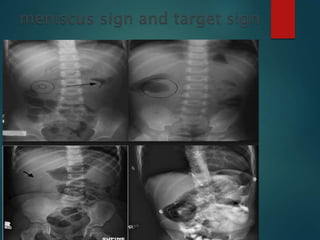
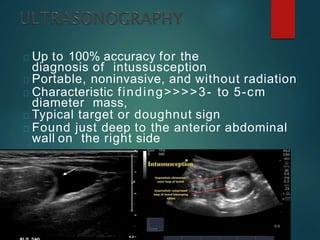
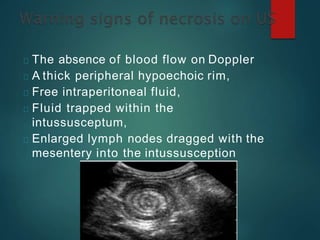
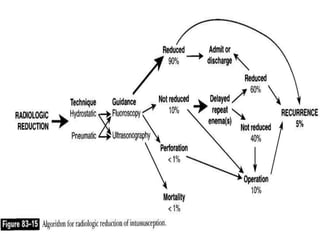
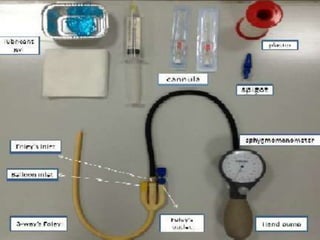
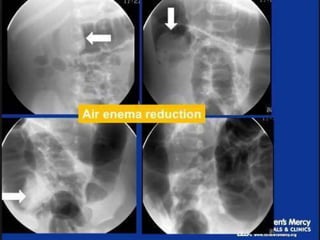
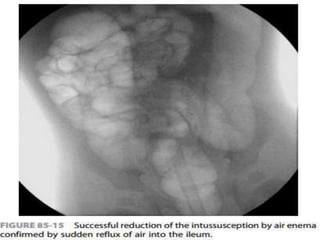
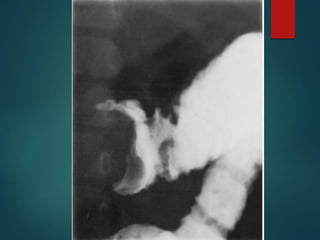
Intussusception is the prolapse of one part of the intestine into the lumen of the immediately adjoining part. It is most common in infants and children under 3 years old. Clinical diagnosis is based on symptoms like abdominal pain and vomiting. Ultrasound is very accurate for diagnosis and shows the pathognomonic "target" or "doughnut sign". Initial treatment is usually non-surgical reduction with hydrostatic or pneumatic enema under fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance. Surgical reduction or resection is needed if non-surgical reduction fails or if there are signs of perforation or peritonitis.





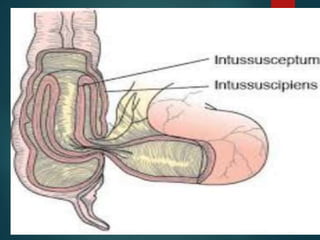
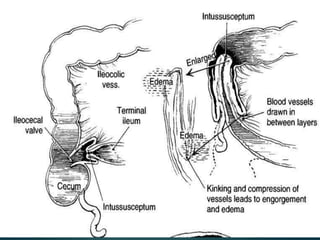







![The specific types can be described as
Idiopathic (no pathologic lead point
[PLP], 95%),
PLP (4%),
Postoperative (1%);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intussusceptions-200726135958/85/Intussusceptions-15-320.jpg)