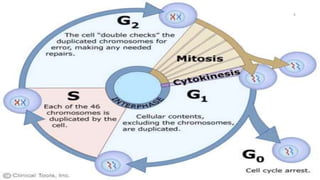
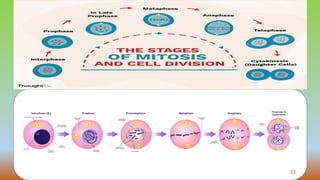
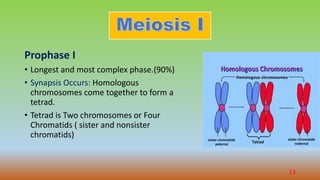
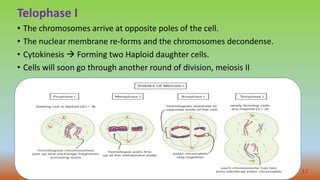
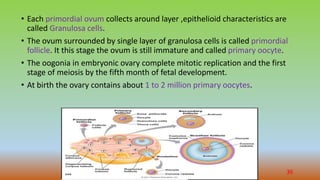
Cell division is the process by which cells duplicate their DNA and divide to produce two daughter cells. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis, which produces identical daughter cells, and meiosis, which reduces the chromosome count to produce gametes. The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA, and the mitotic phase where the cell divides. Mitosis involves prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis to split the cell. Meiosis occurs in germ cells and involves two cell divisions to reduce the chromosome count from diploid to haploid. Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are the processes by which male and