Embed presentation
Download to read offline


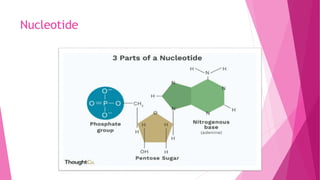
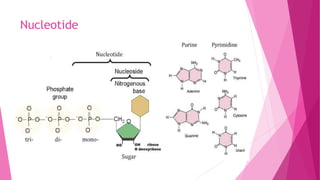




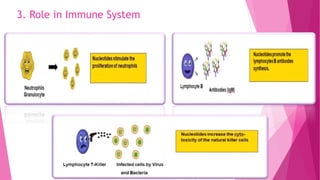



Nucleotides are the structural units that make up DNA and RNA and carry genetic information from parents to offspring. They also act as coenzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions by providing energy, such as ATP which carries out phosphorylation reactions in metabolic pathways. Additionally, nucleotides play a role in the immune system and cellular regulation through molecules like cyclic AMP.










