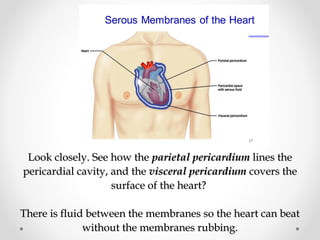
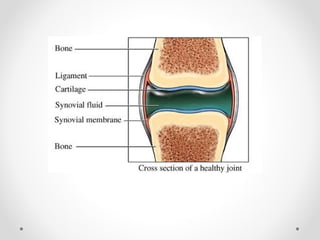
Membranes cover and line all parts of the body, both inside and out. There are four basic types of membranes in the body: mucous membranes line openings to the outside world and contain sticky mucus; serous membranes line body cavities and cover organs, with fluid allowing easy movement; cutaneous membranes form the thick, waterproof skin; and synovial membranes surround joints, containing synovial fluid to allow smooth movement. Membranes are made primarily of epithelial tissue except for synovial membranes, which are connective tissue. Inflammation of serous membranes can cause serious illnesses like pleurisy, peritonitis, or pericarditis.