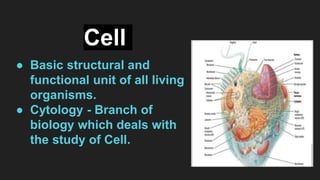
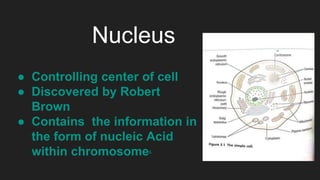
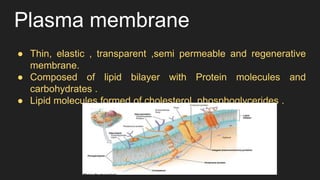
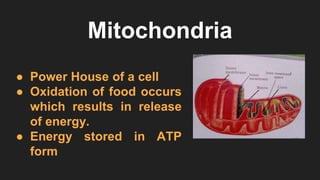
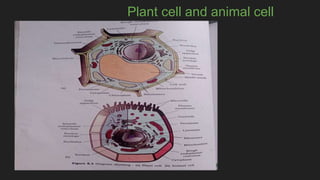
The document provides an overview of cells, the basic structural and functional units of life, detailing the history of cell discovery and key figures such as Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke. It distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, describes cell components like the nucleus, plasma membrane, mitochondria, and ribosomes, and outlines their functions. Additionally, it covers organelles such as the Golgi apparatus and lysosomes, as well as plastids specific to plant cells.