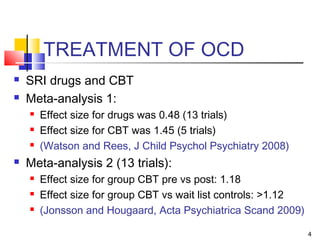
CBT is an effective treatment for OCD due to its ability to trigger lasting neural changes through learning. It involves psychoeducation, challenging irrational assumptions, exposure to feared situations without compulsions, and response prevention. Studies show large effect sizes for CBT compared to medications alone. CBT aims to reduce anxiety and distress from obsessions by stopping thoughts and using distractions, while exposure therapy targets compulsions. Success requires understanding all symptoms, motivated patients, and therapists able to systematically implement the CBT techniques.



![5
ADVANTAGES OF CBT
Effective as monotherapy.
Large effect size [caveat: biases
could arise from sample selection
and consenting processes].
Improves long-term outcomes
with drugs.
Treating with drugs+CBT may
offer the best outcomes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-5-320.jpg)


![9
OBSESSIONS AND
COMPULSIONS
Obsessions are repeated thoughts.
E.g. “My son is going to die.”
E.g. “I will get AIDS.”
Compulsions are repeated actions.
E.g. Handwashing.
Every time a patient sees a picture of a deity, he
feels compelled to say a short, mental prayer to
the deity. Is this an obsession or a compulsion.
[In CBT, the approach to treatment differs between
obsessions and compulsions.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-9-320.jpg)



![13
TYPES OF OBSESSIONS
[obsessions provoke anxiety]
Obsessive thoughts
Obsessive ruminations
Obsessive doubts
Obsessive vacillations
Obsessive phobias
Obsessive impulses
Obsessive images](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-13-320.jpg)
![14
TYPES OF COMPULSIONS
[compulsions relieve anxiety]
Almost always secondary to obsessions
May be behavioral or mental
Yielding:
Counting
Checking
Ordering
Cleaning/washing
Resisting:
Repeating thoughts or actions to prevent or undo a
feared event
(Overlap may be present)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-14-320.jpg)



![19
CORNERSTONES OF CBT
Common to both obsessions and compulsions:
Psychoeducation
Challenging assumptions
[Family support, if indicated]
Obsessions:
Thought-stopping
Distraction
Compulsions:
Exposure
Response prevention](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-19-320.jpg)


![22
CHALLENGING
ASSUMPTIONS
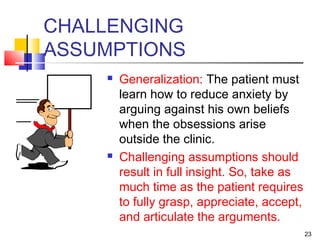
Obsessions are, by definition, irrational thoughts.
Patients don’t always recognize their irrationality.
Taking each obsession by turn, challenge the
flawed logic that underlies it.
Goal: To reduce anxiety through the realization
that the thought is irrational and can be ignored.
E.g. Obsessive fears: “What if that man [on the bus] is
carrying a bomb?”
E.g. “What if I get AIDS?” [by using public cutlery]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-22-320.jpg)

![25
OTHER DISTRACTOR
TECHNIQUES
Taking up a chore that demands attention
Phoning a friend
Speaking to a family member
Examining details in the environment
Etc. [plan these out]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-25-320.jpg)

![28
CHALLENGING ASSUMPTIONS:
CHECKING COMPLSIONS
Did I lock the door?
Strategy
Be aware that this is a problem.
When locking, say “I have done it” [lays memory trace].
When the doubt arises, recall the memory.
Learn to trust the memory [if you cannot trust yourself,
whom will you trust?]
Recall past experience [has there been any occasion that
you checked and repeatedly checked and found that the
door was unlocked?]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-28-320.jpg)


![31
CHALLENGING
ASSUMPTIONS
[Same as with obsessions]
E.g. for checking whether a door was locked
E.g. for removing dirt from the hand
E.g. for repeated rituals lest a deity be offended
E.g. for repeated rituals after stepping on paper
E.g. for rituals that seek to ward off harm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-31-320.jpg)



![35
DEALING WITH
BATHING RITUALS
Identify and tackle underlying obsessions.
Break up the rituals into their component parts
[wetting, soaping, rinsing, wiping].
Define what is the purpose of each, and what is the
normal limit of behavior for each.
Practice behavior within these set limits while
simultaneously challenging the assumptions which
were responsible for the obsessions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-35-320.jpg)



![39
SESSIONS
3-5 sessions a week for 3-5 weeks.
Each session up to 2 hours.
15 min for review of previous session, homework.
45-90 min for exposure and response prevention.
15 min for setting homework.
Ideally, when a symptom is addressed, there should be
100% compliance with therapy directions [e.g. response
prevention]; otherwise, the therapy work is undermined.
Booster sessions (maintenance therapy).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtocd-140425202157-phpapp02/85/Cbt-Ocd-39-320.jpg)

