Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




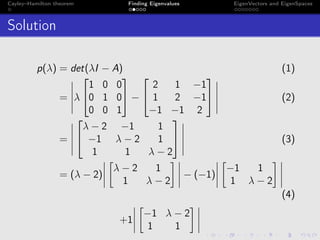

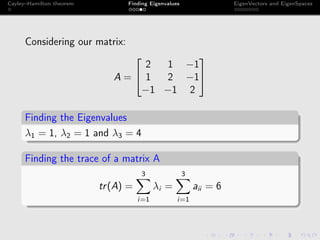
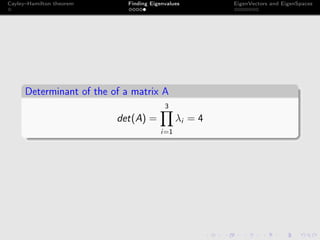





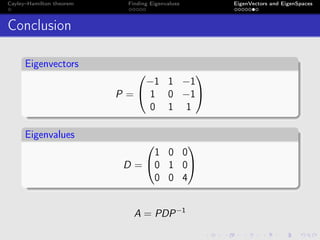


The document discusses the Cayley-Hamilton theorem, which states that every square matrix satisfies its own characteristic equation. It provides a detailed example of finding the eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and eigenspaces for a specific matrix using this theorem. The findings include characteristic equations, traces, and determinants associated with the given matrix.














