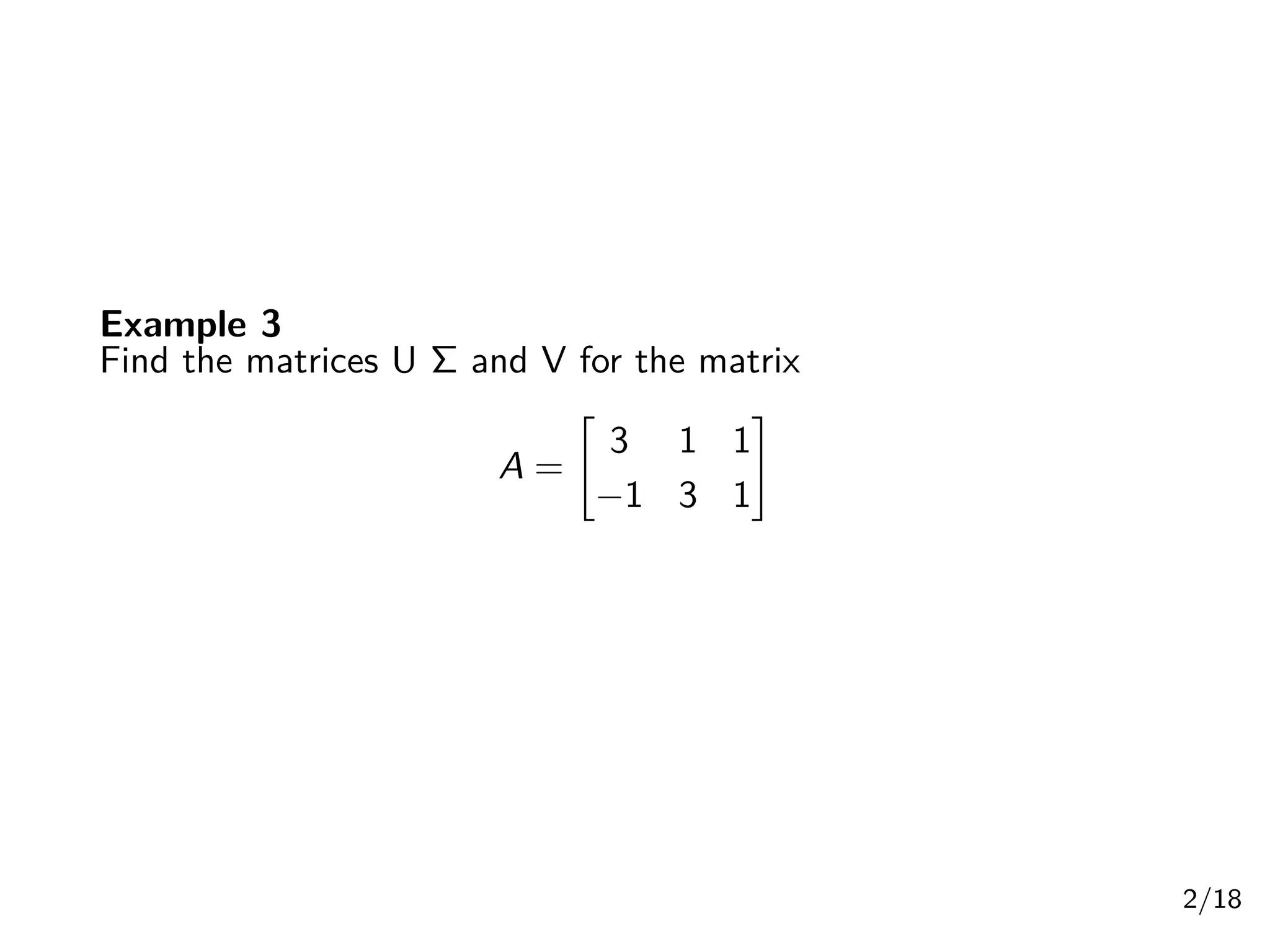
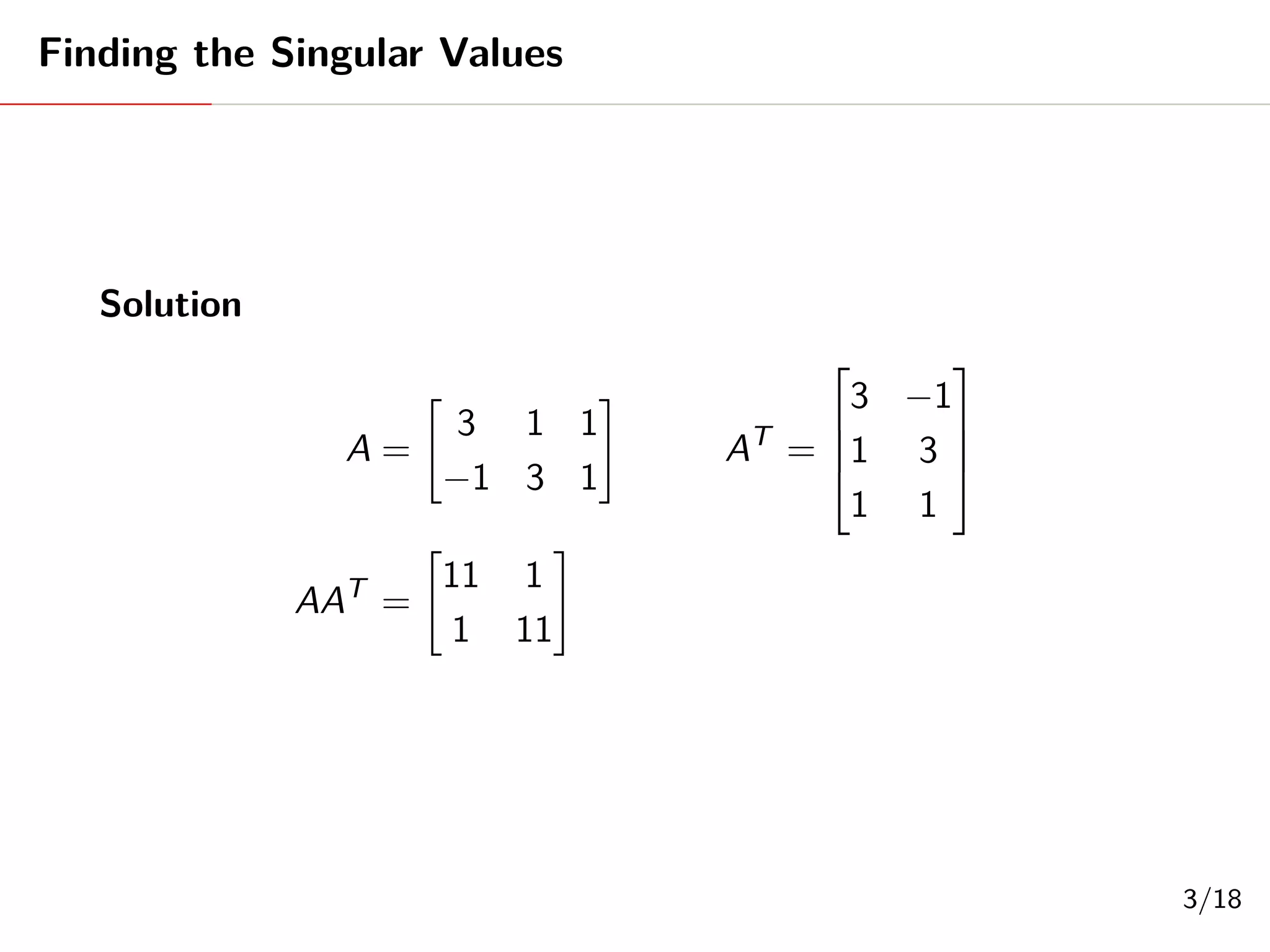
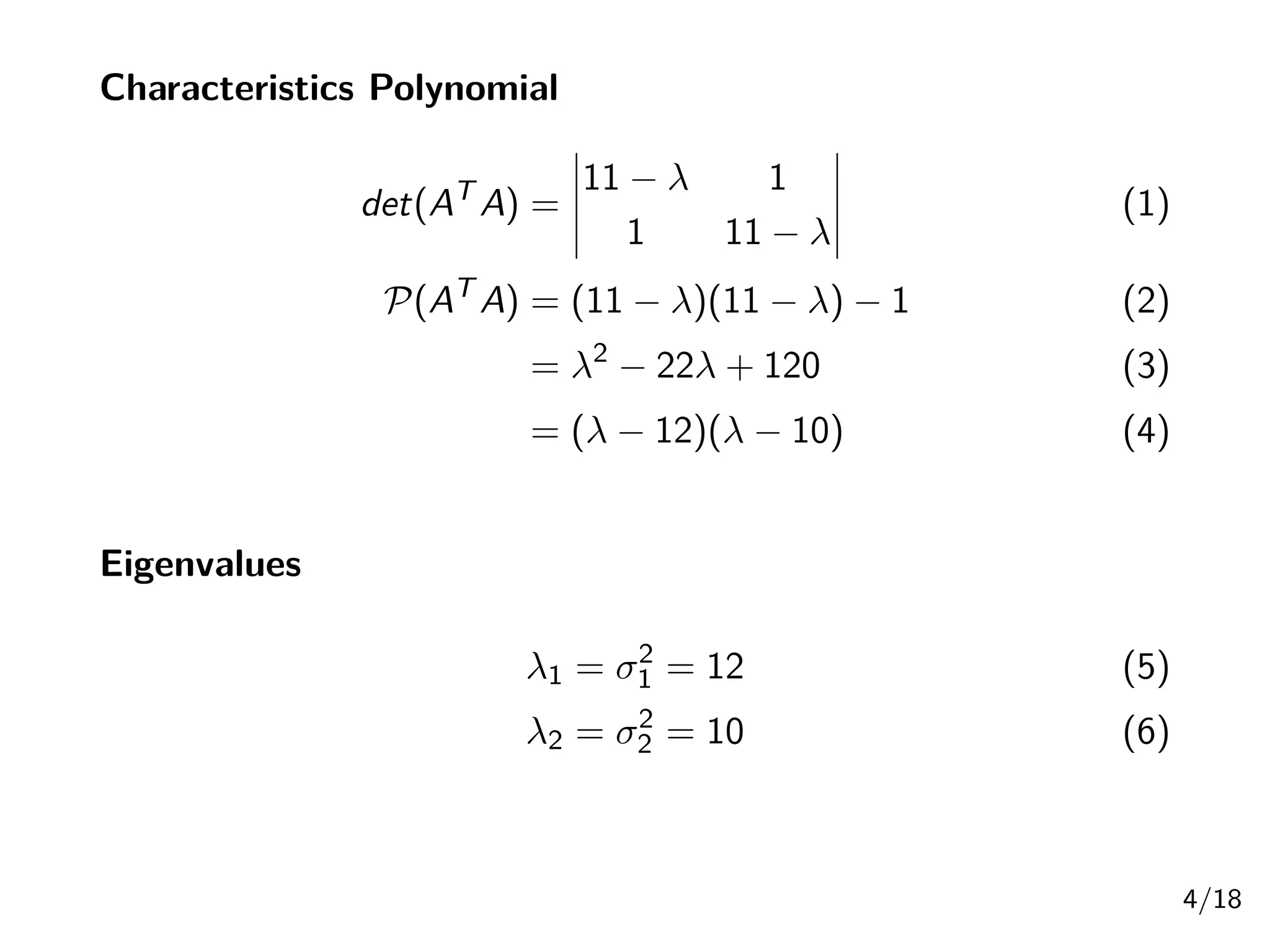
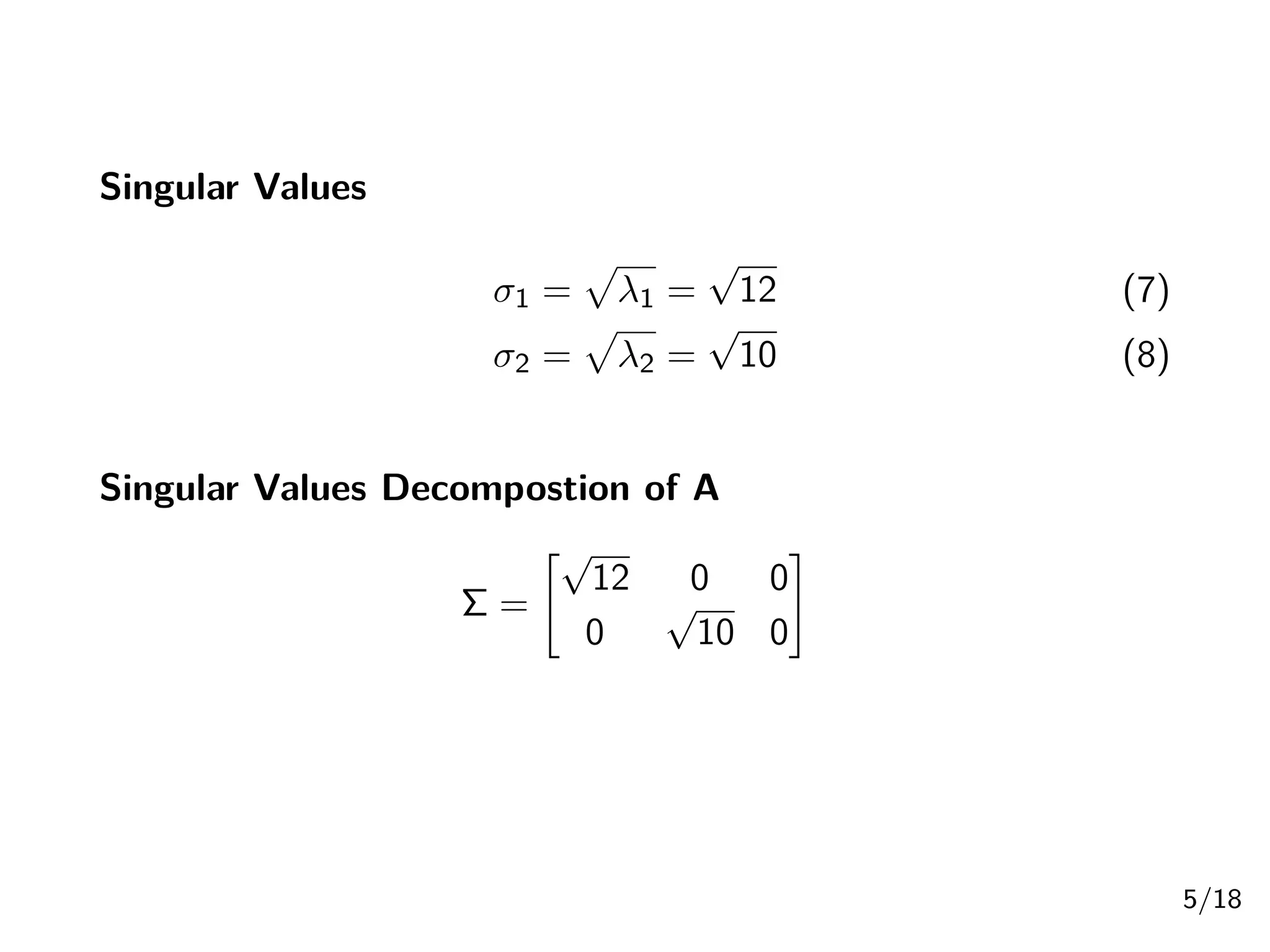
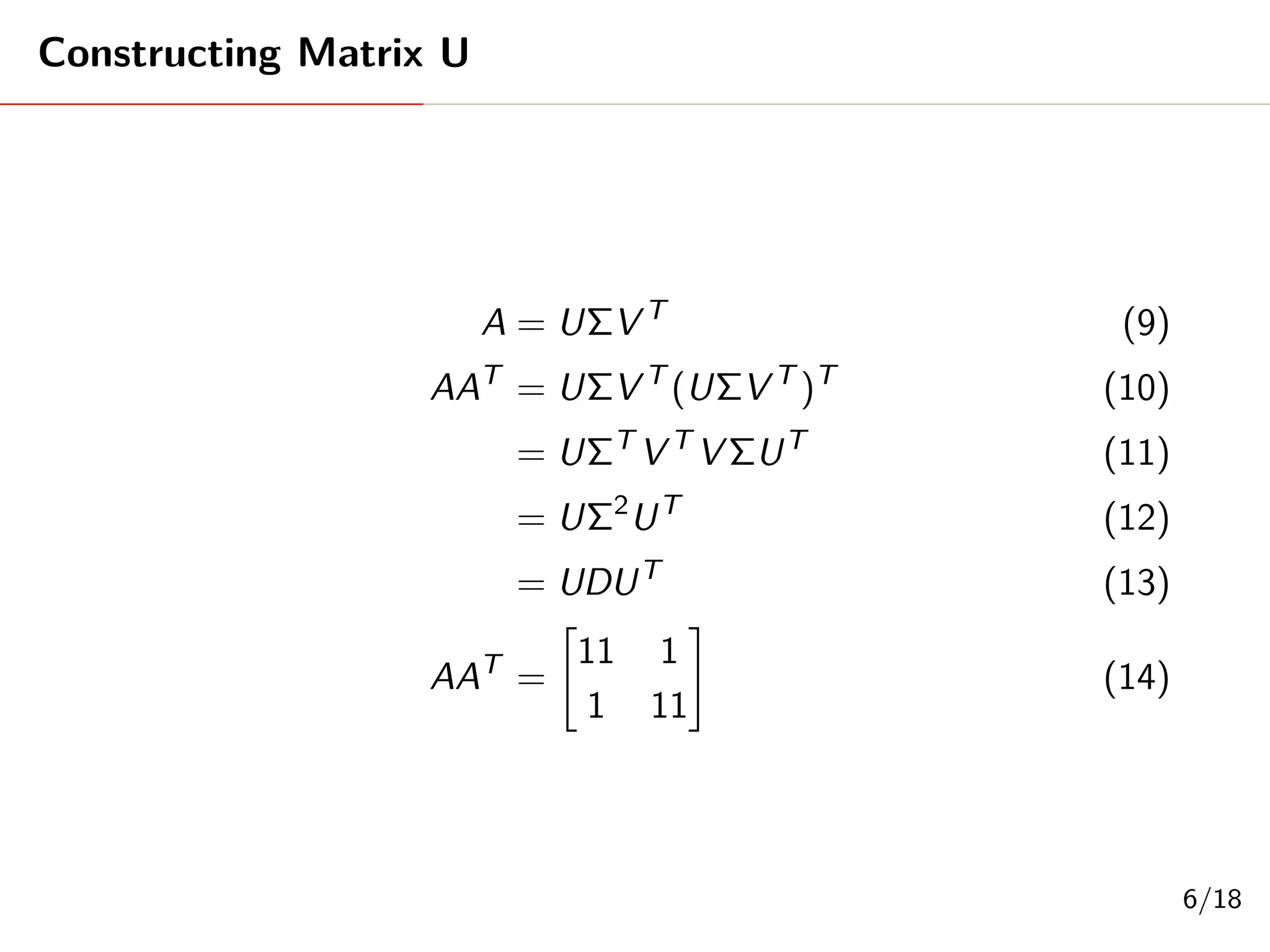
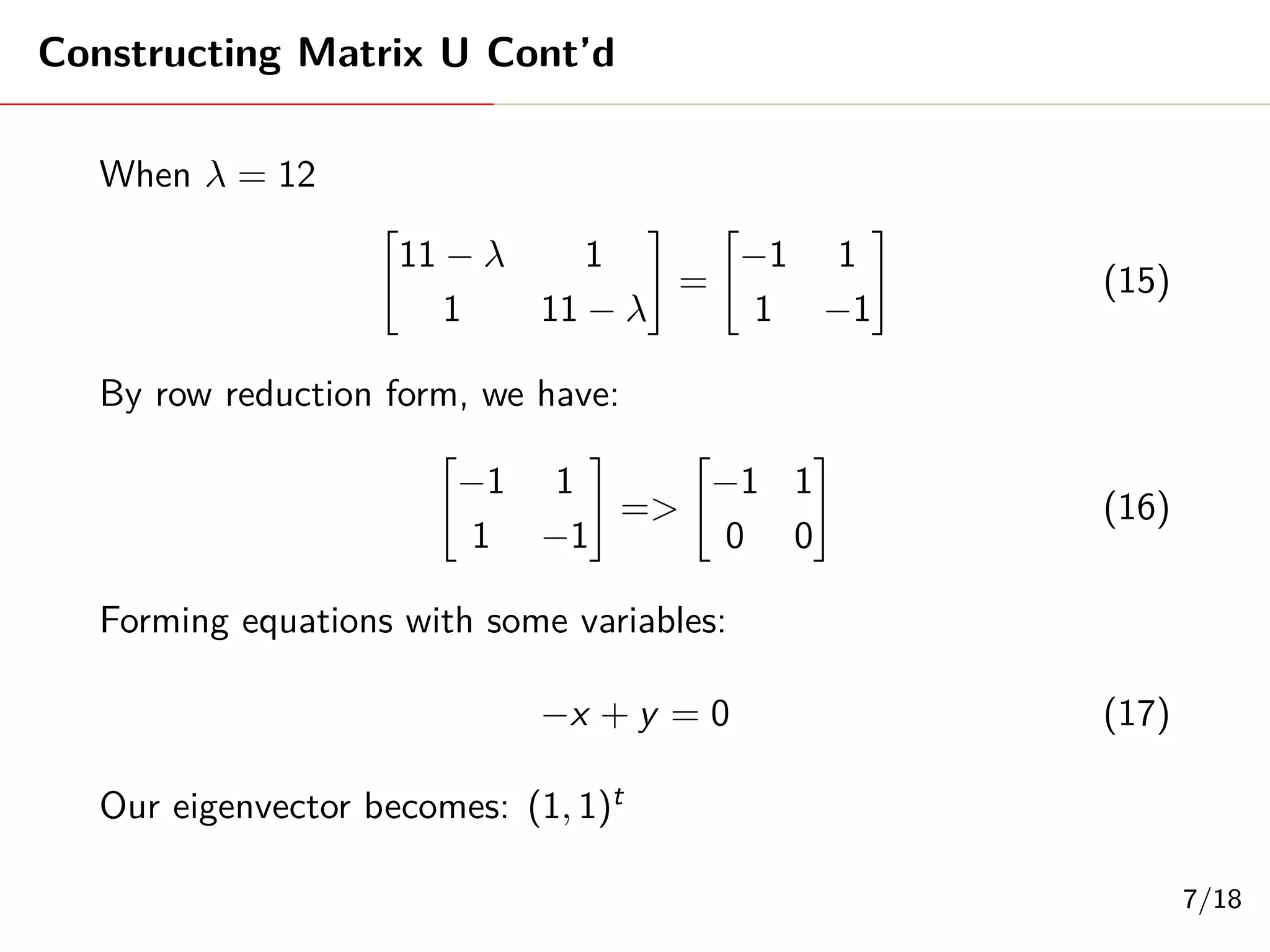
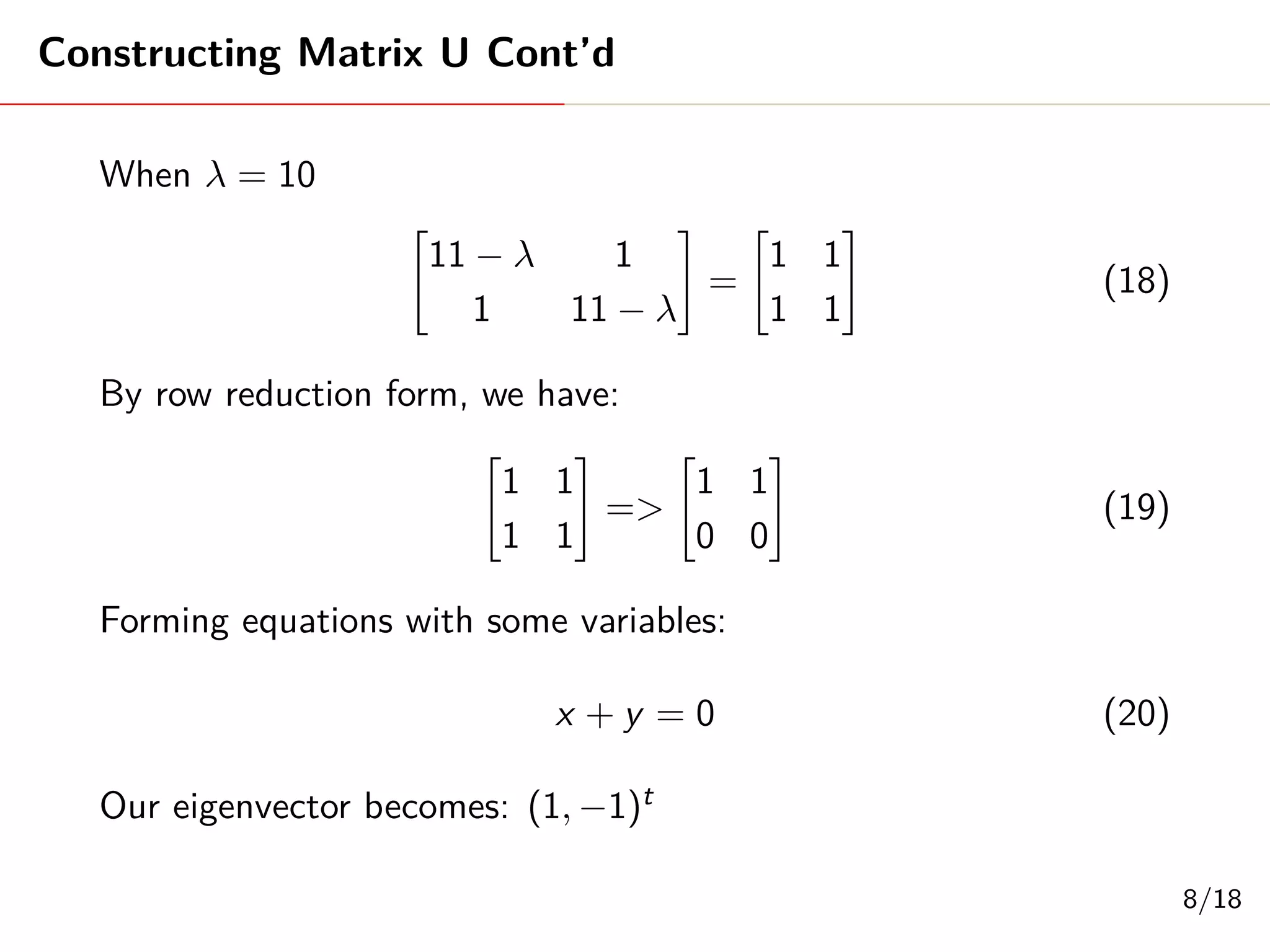
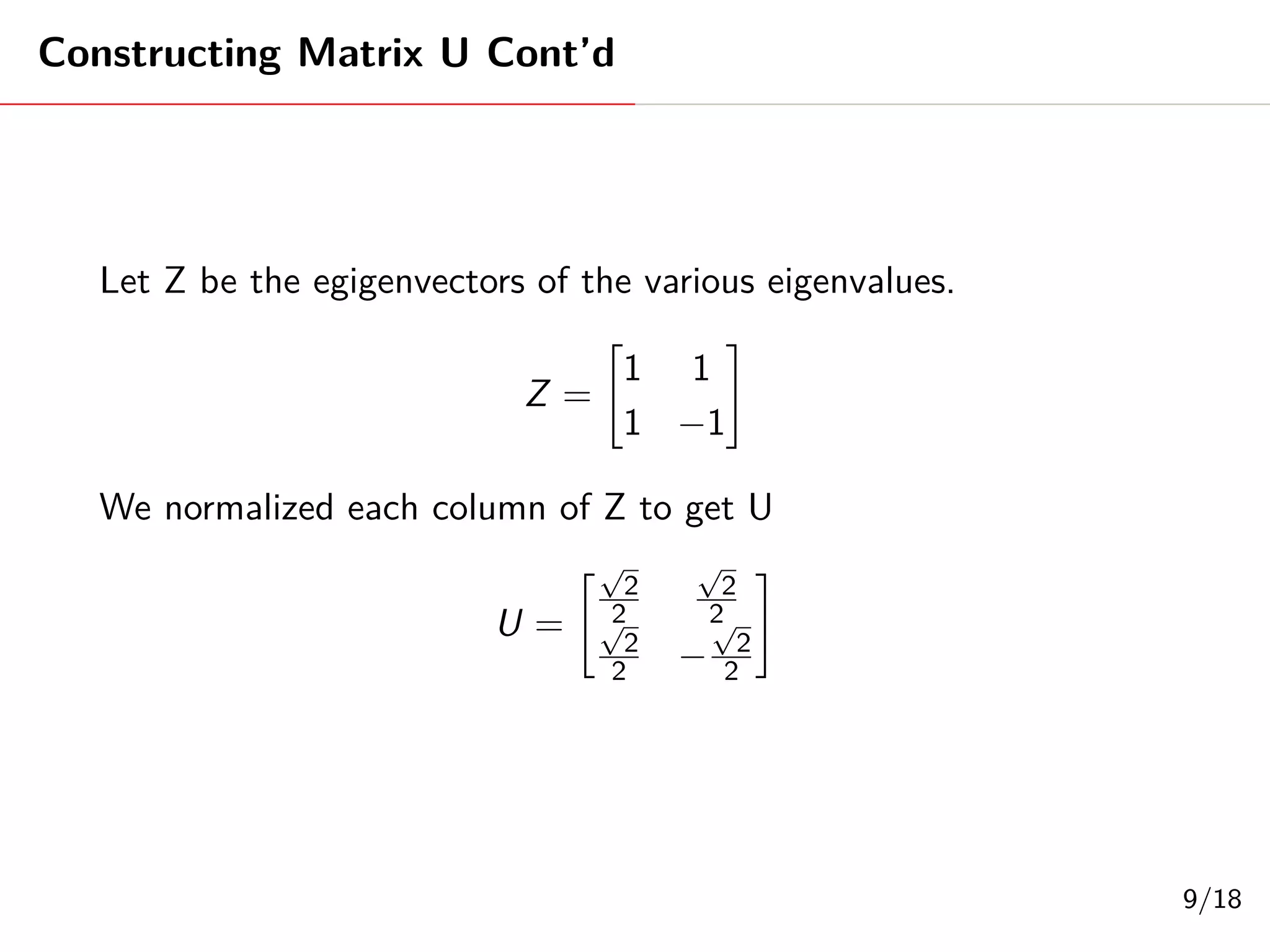
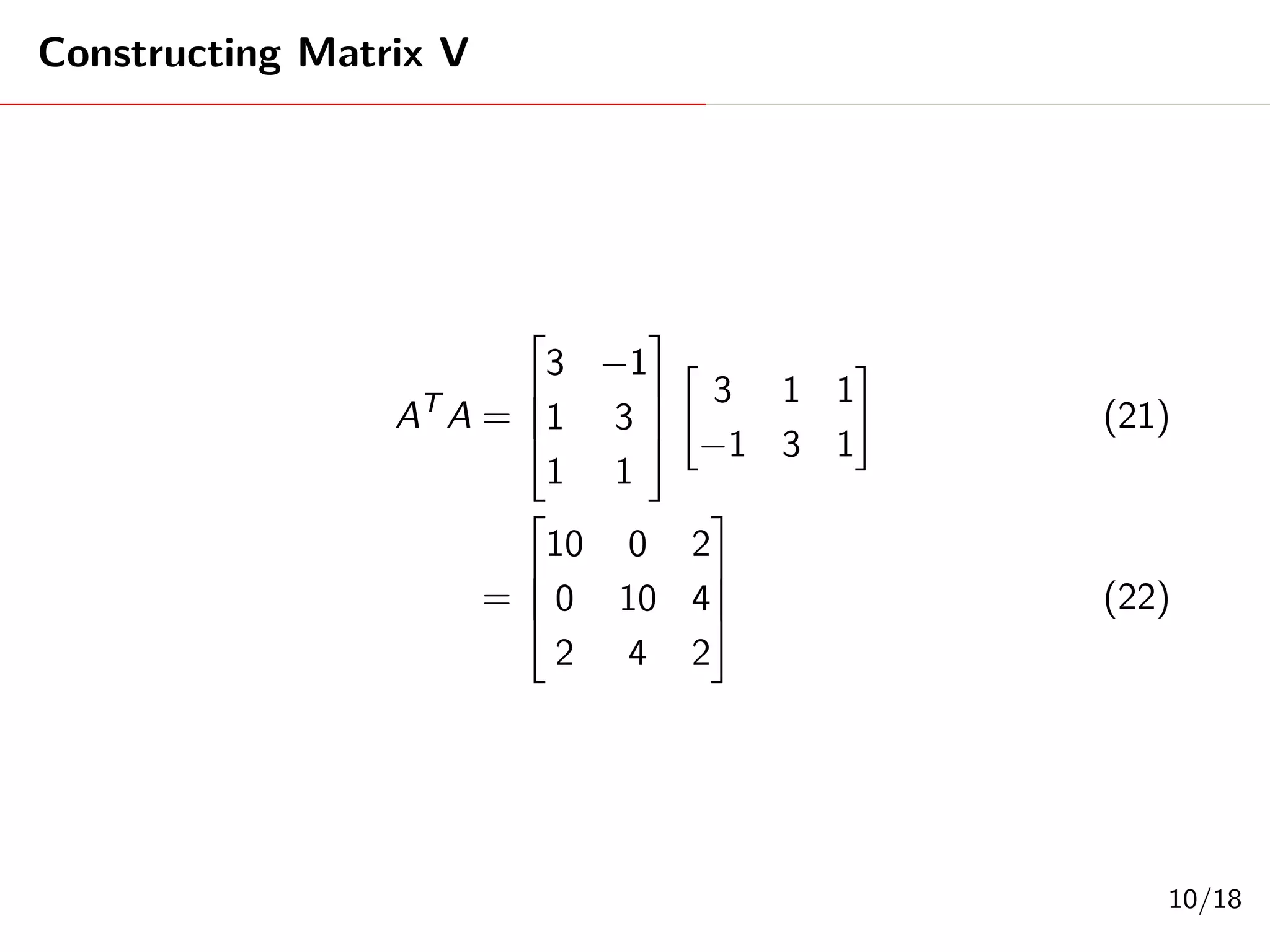
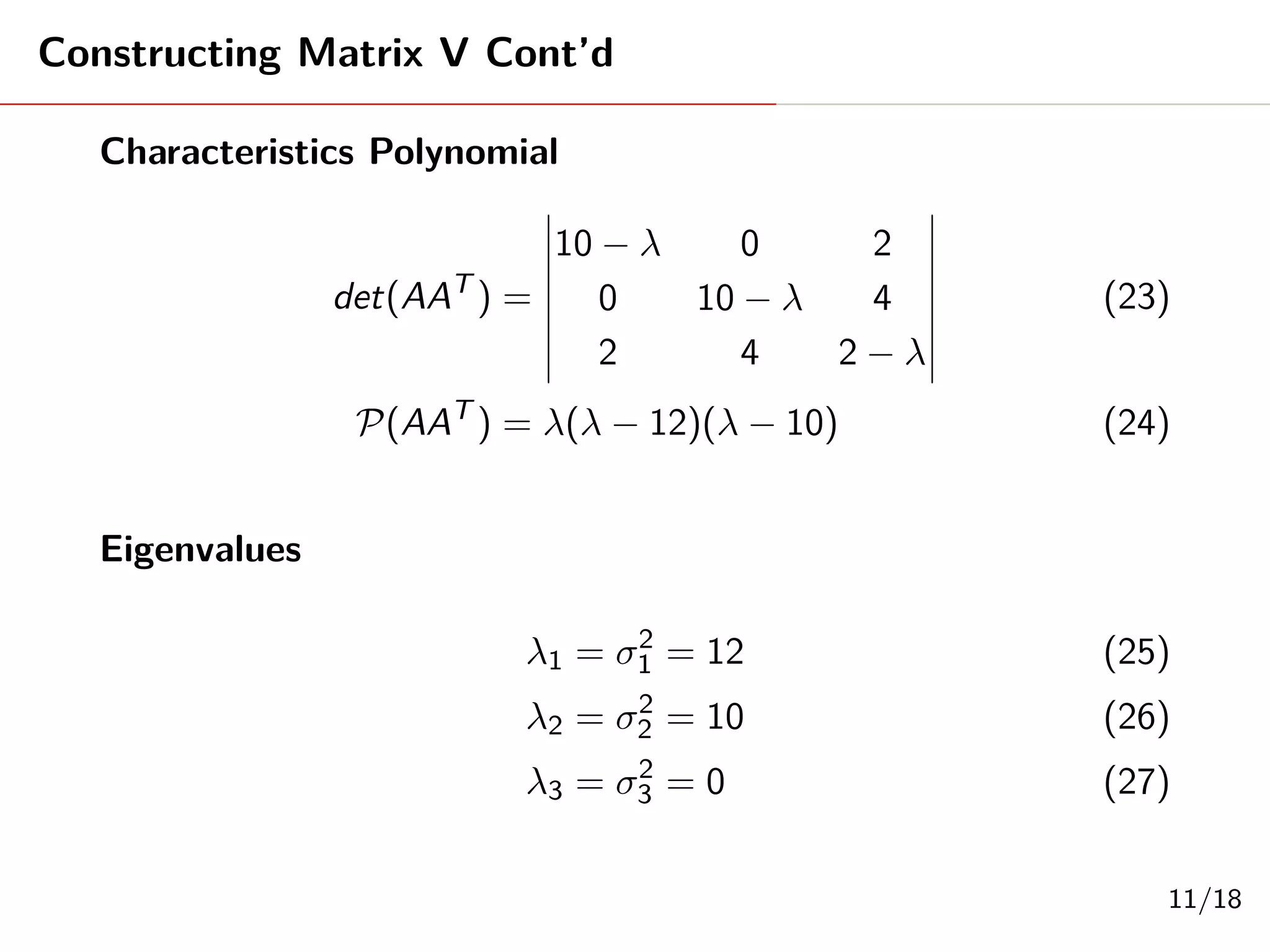
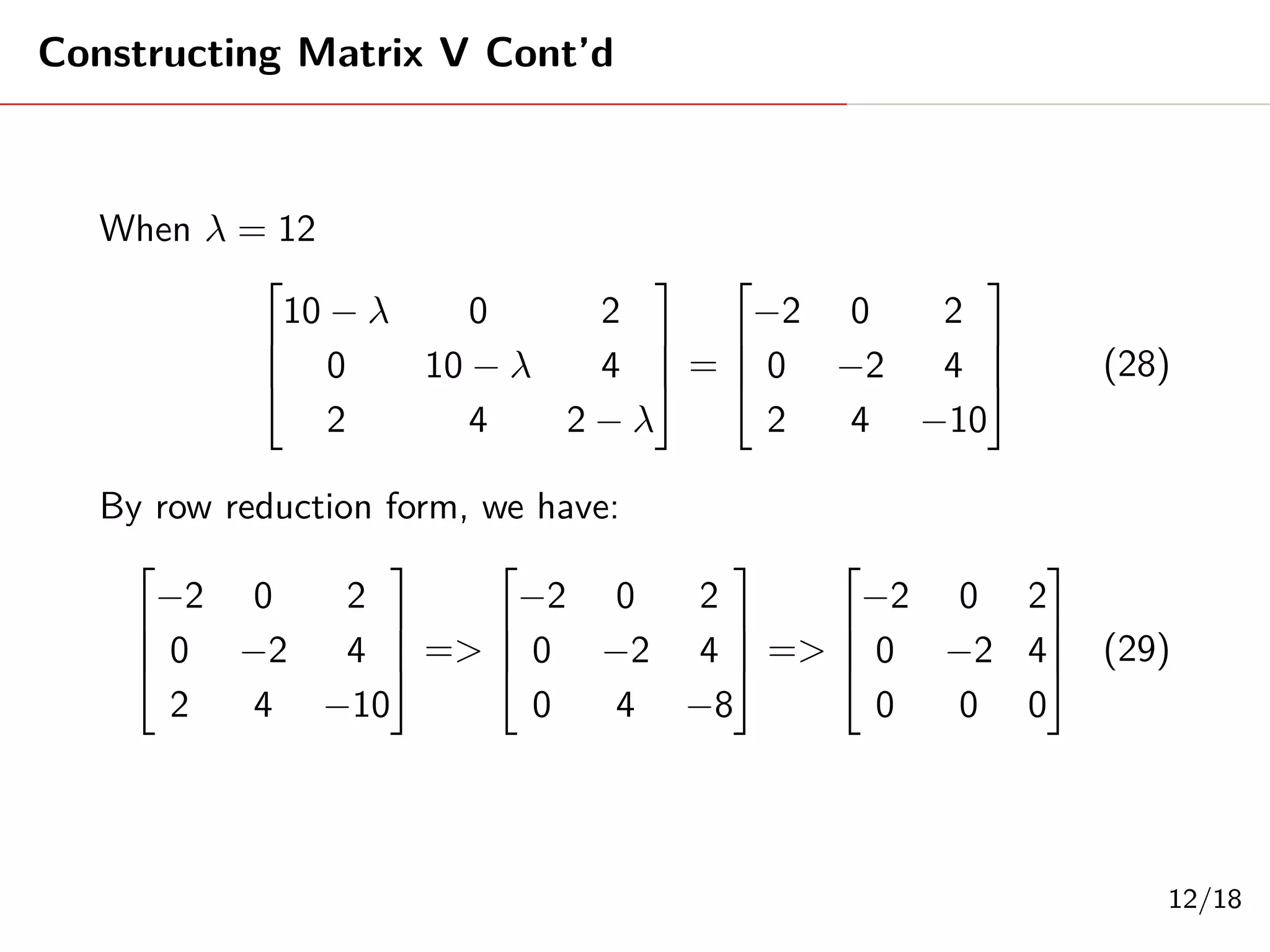
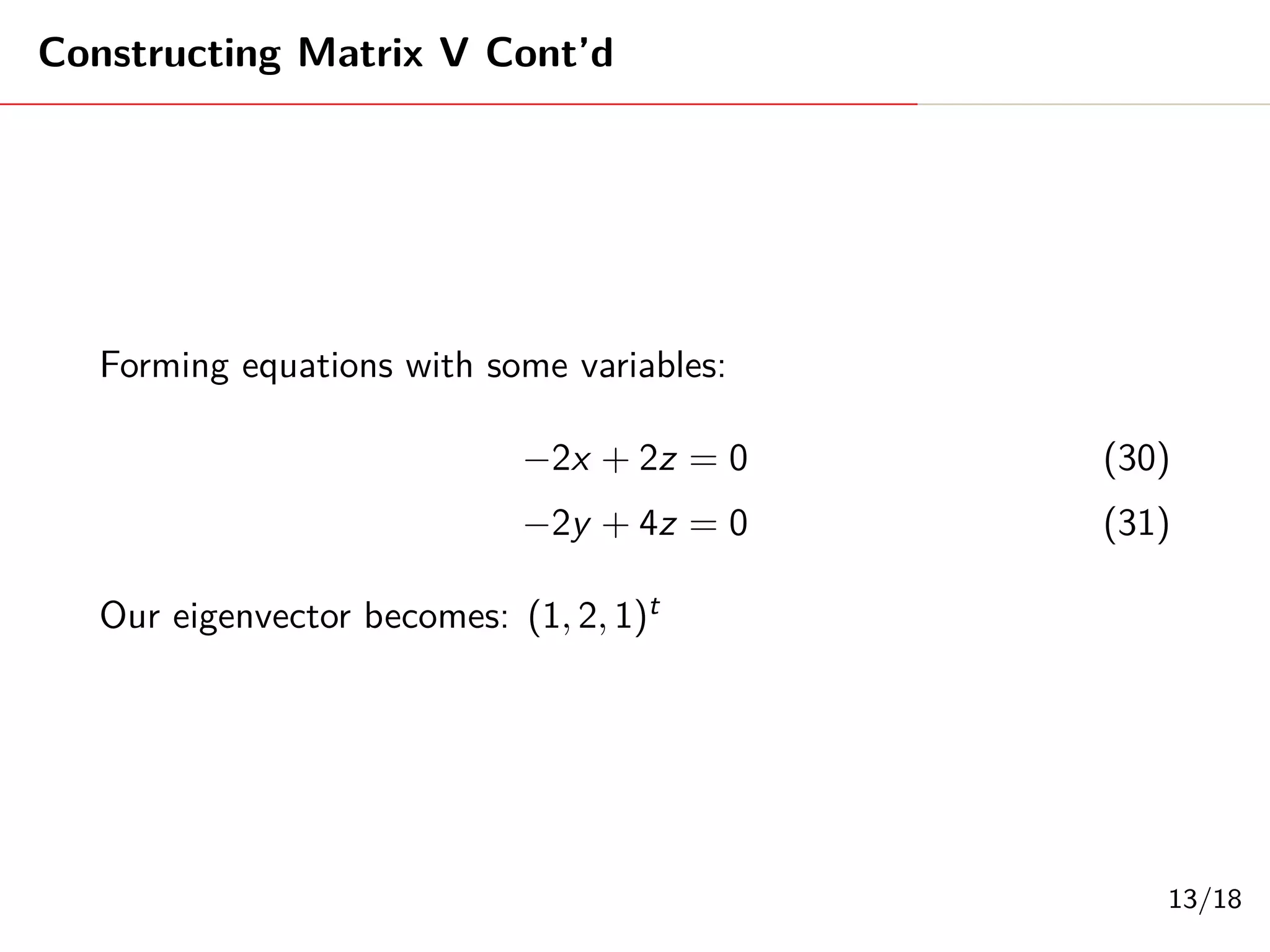
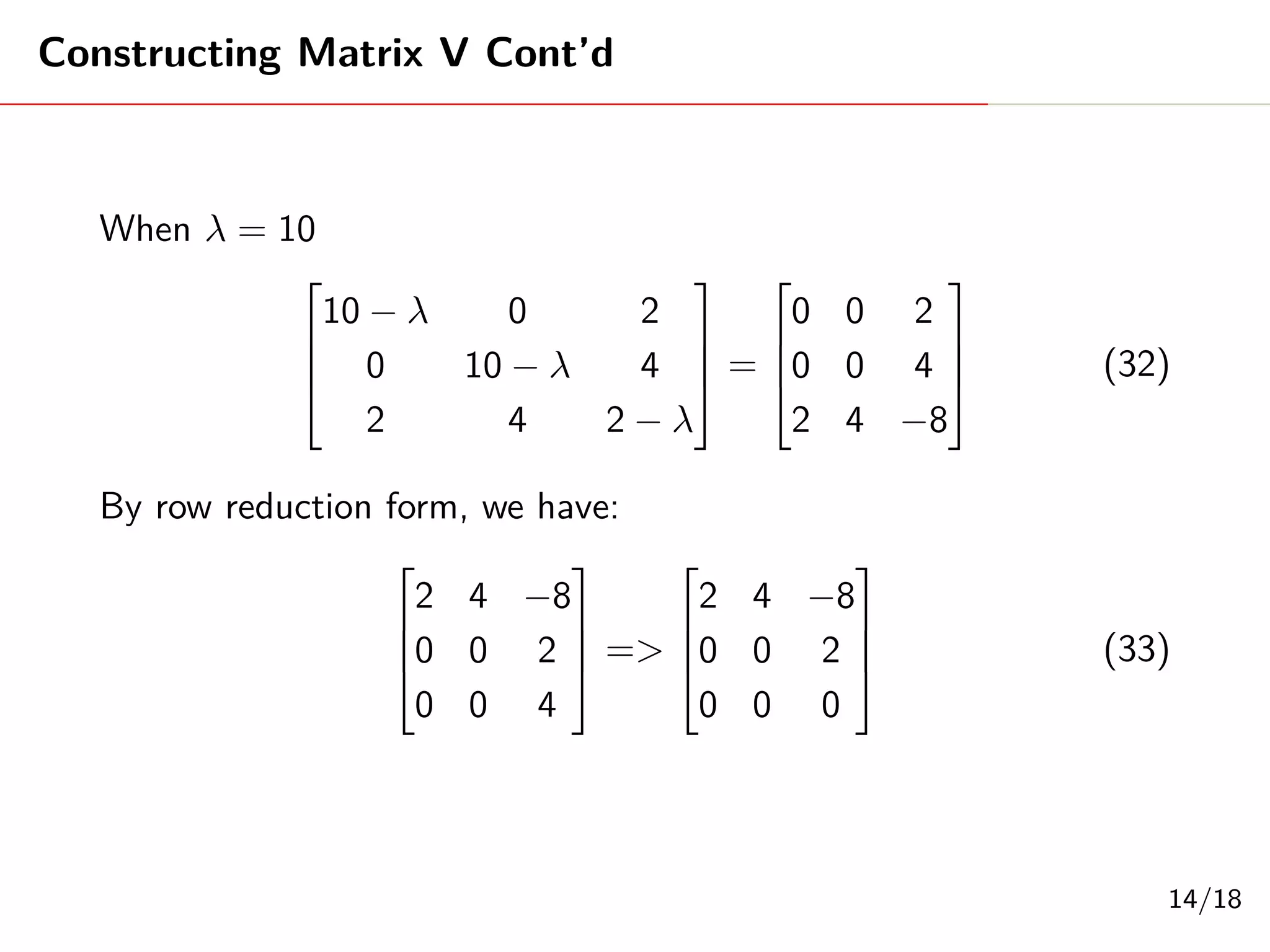
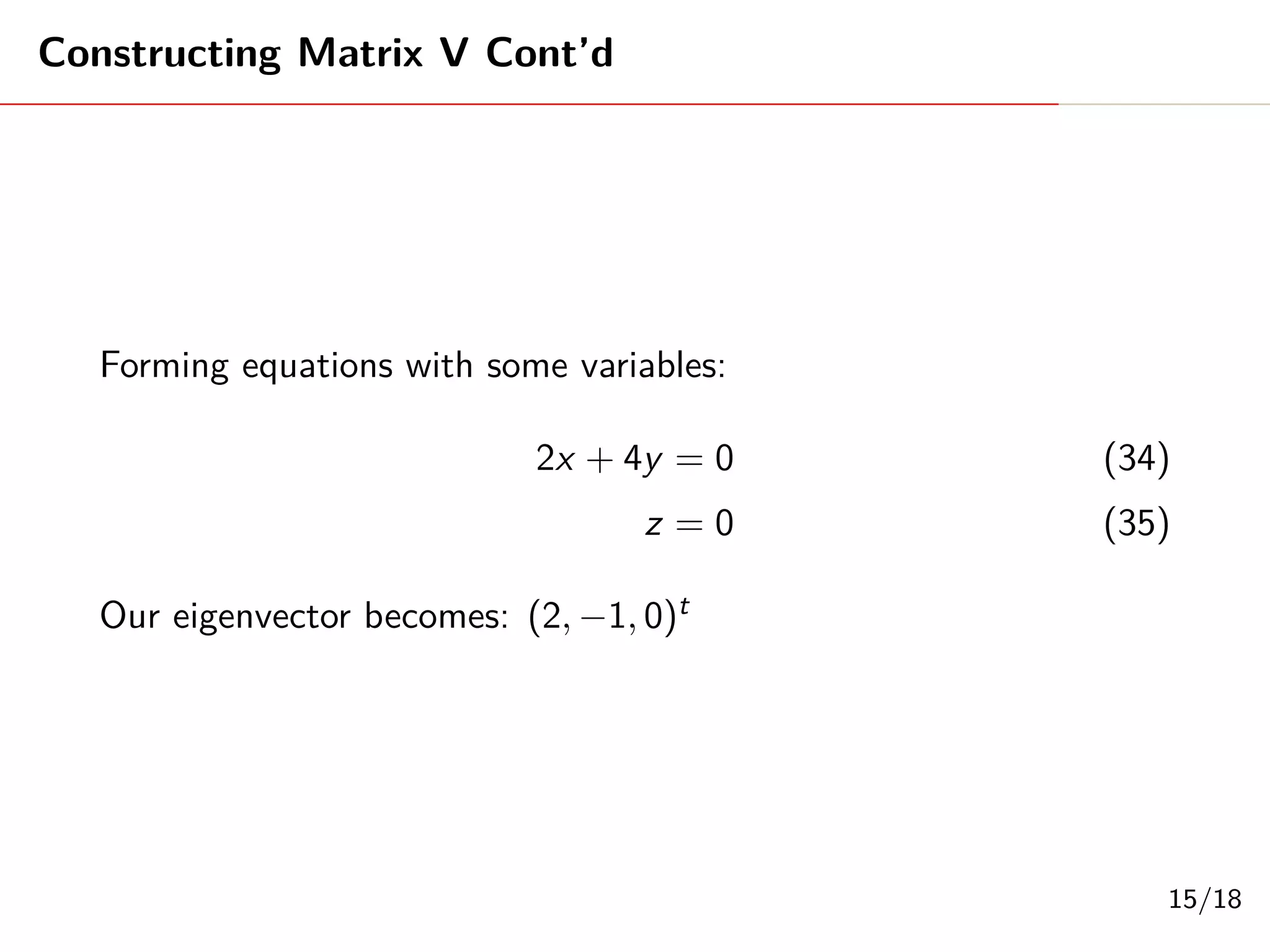
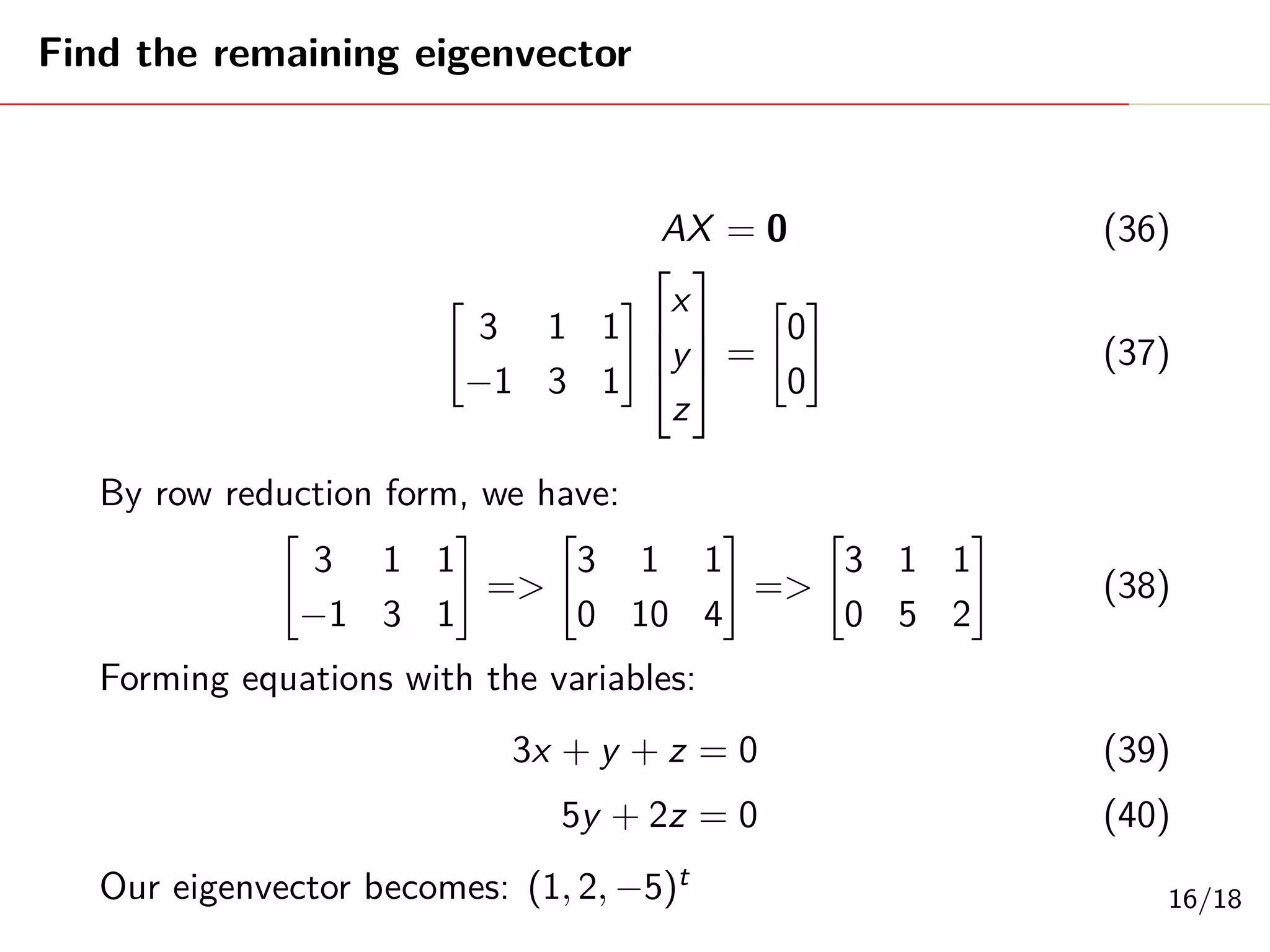
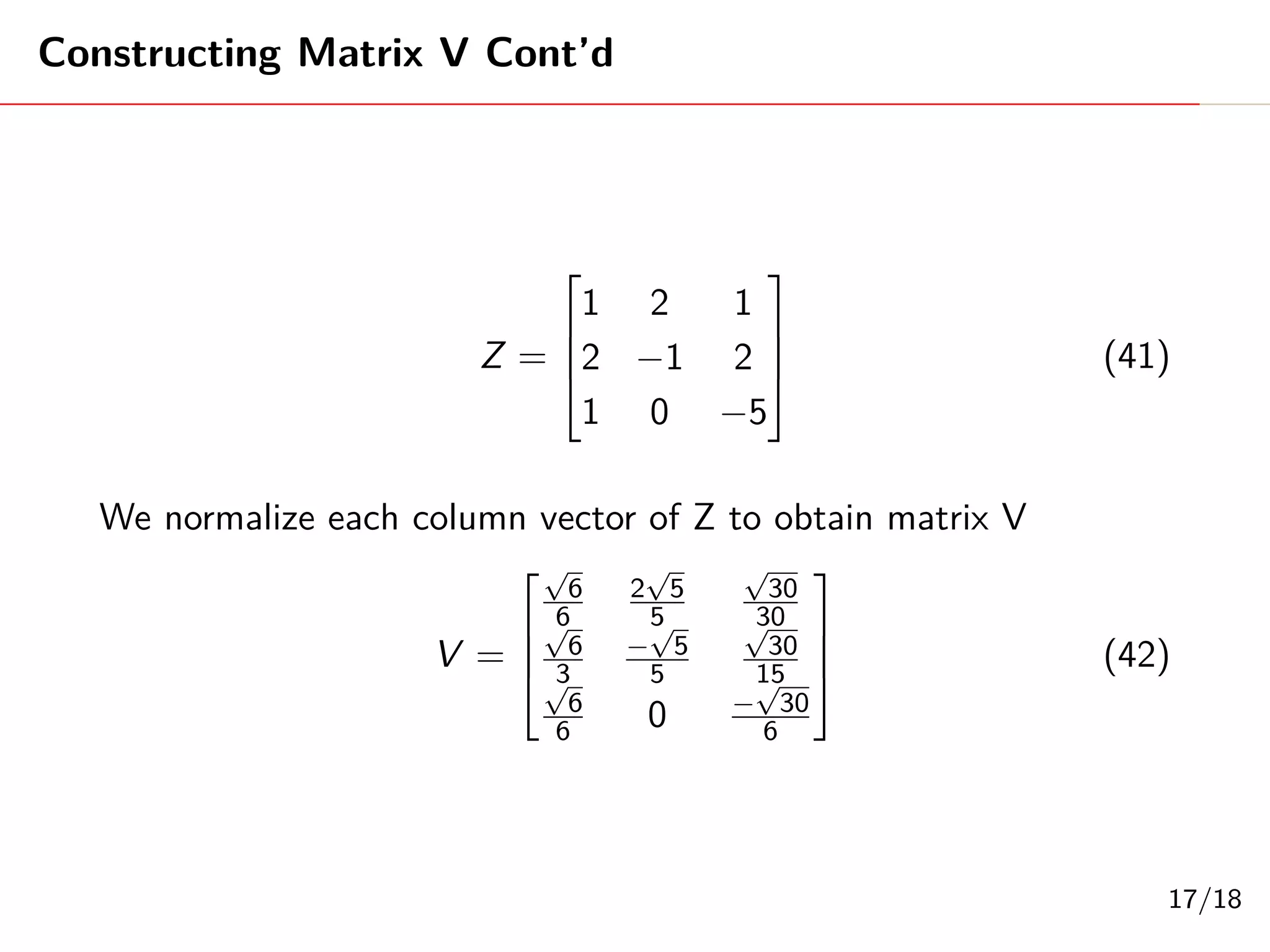
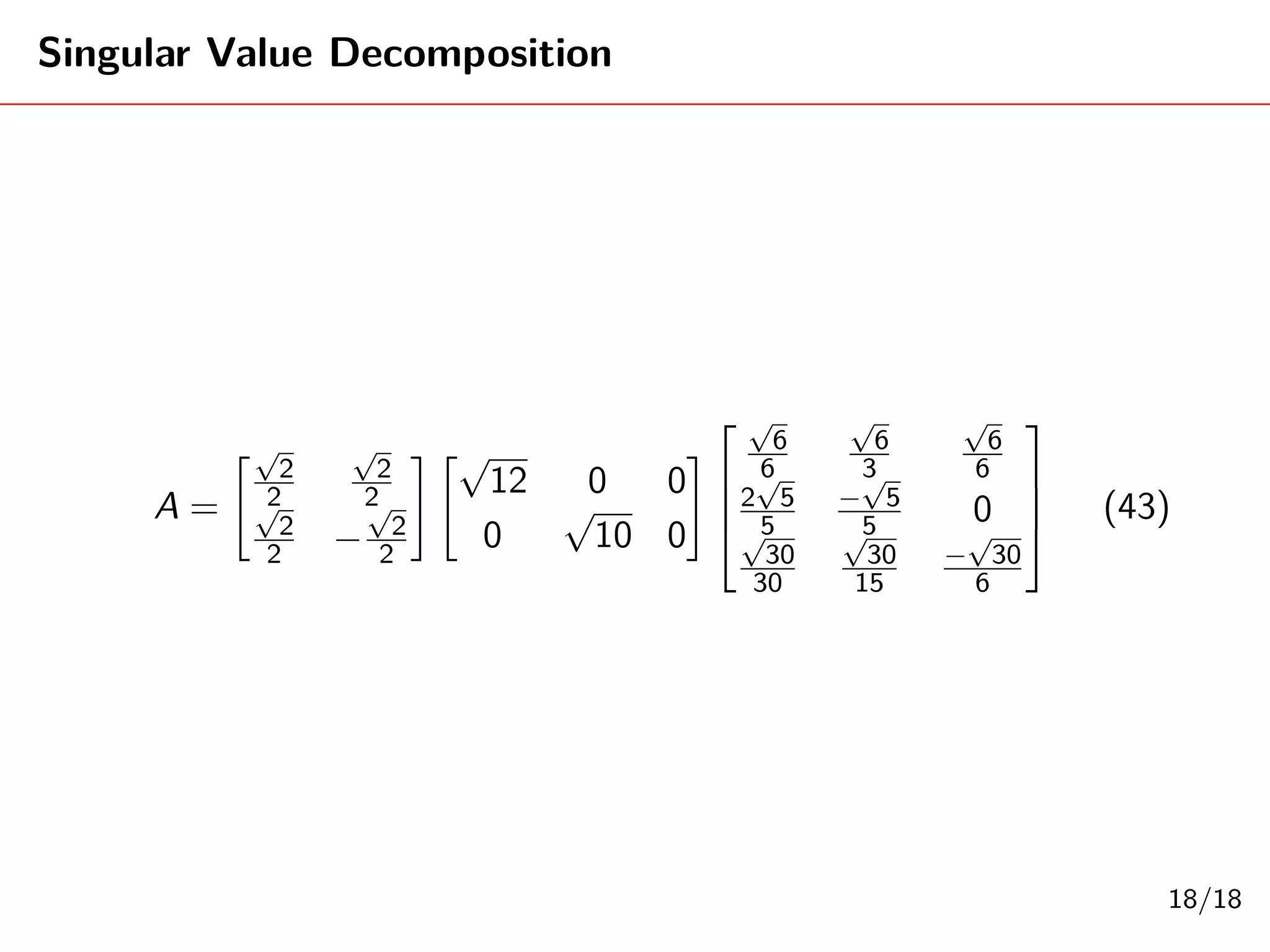
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) decomposes a matrix A into three matrices: U, Σ, and V. The document provides an example of using SVD to decompose the matrix A = [[3, 1, 1], [-1, 3, 1]]. It finds the singular values and constructs the U, Σ, and V matrices. The SVD of A is written as A = UΣV^T, where U and V are orthogonal matrices and Σ is a diagonal matrix containing the singular values of A.