Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times
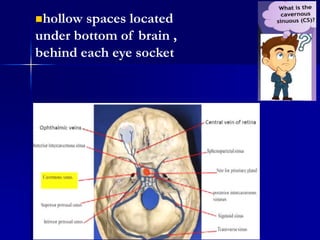
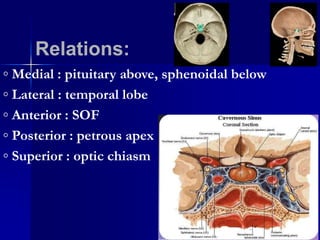
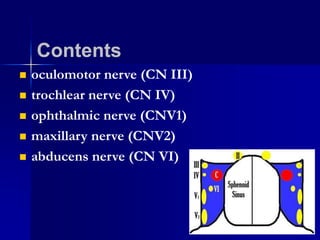
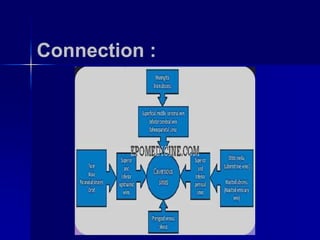

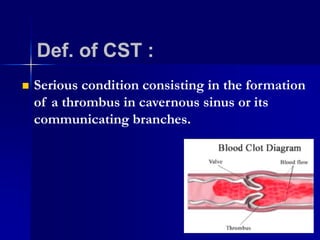















Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a serious condition caused by the formation of a blood clot in the cavernous sinus or its connecting blood vessels. It commonly arises from a middle ear or dental infection that spreads through venous connections. A 60-year-old diabetic man presented with a one-week history of toothache and painful cheek after seeing a dentist. Imaging and laboratory tests aim to identify the infectious source. Complications can include vision problems, lung embolism, or stroke. Aggressive antibiotic treatment and management have reduced mortality from 100% to less than 30%.




















