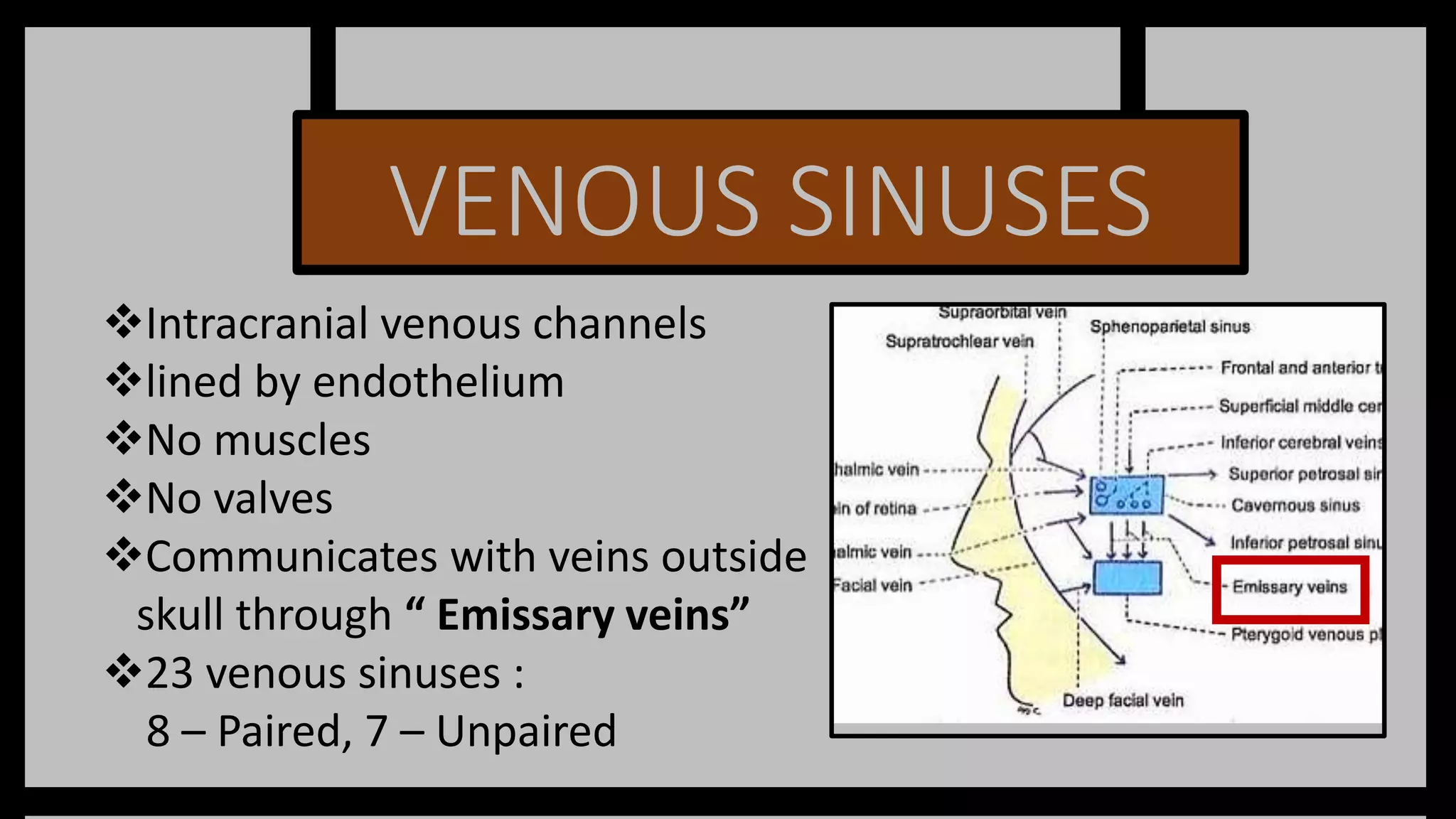
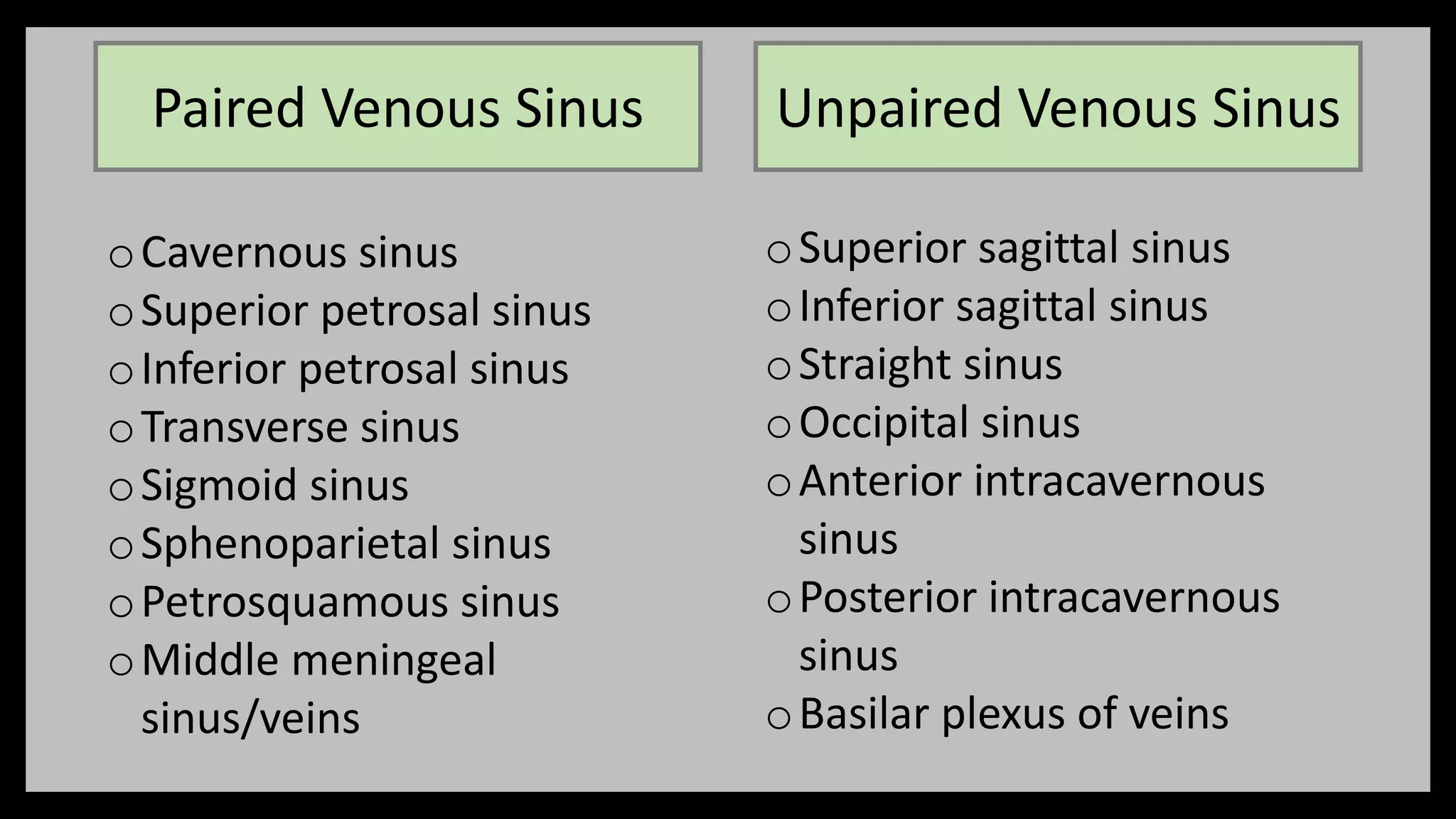
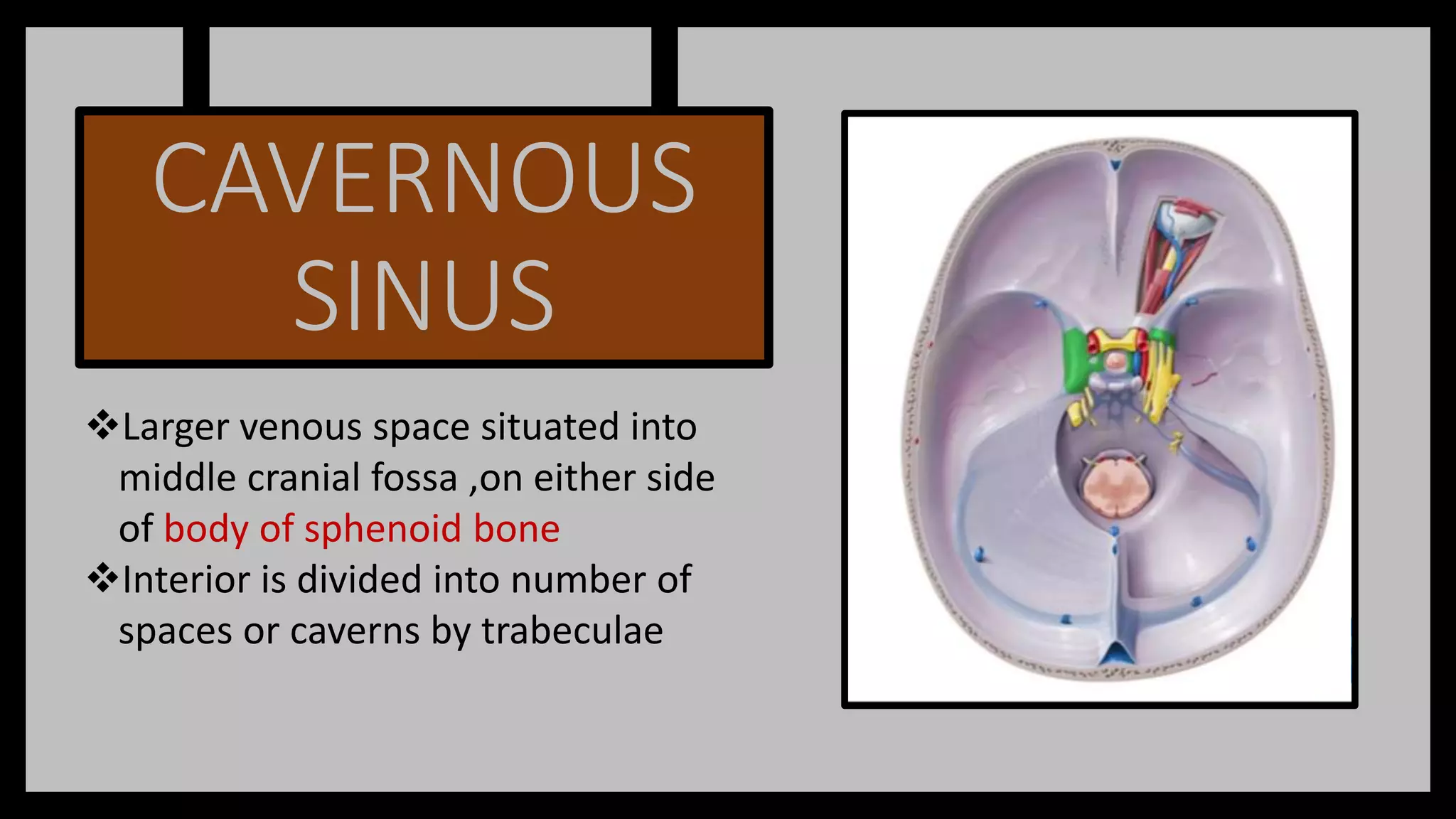
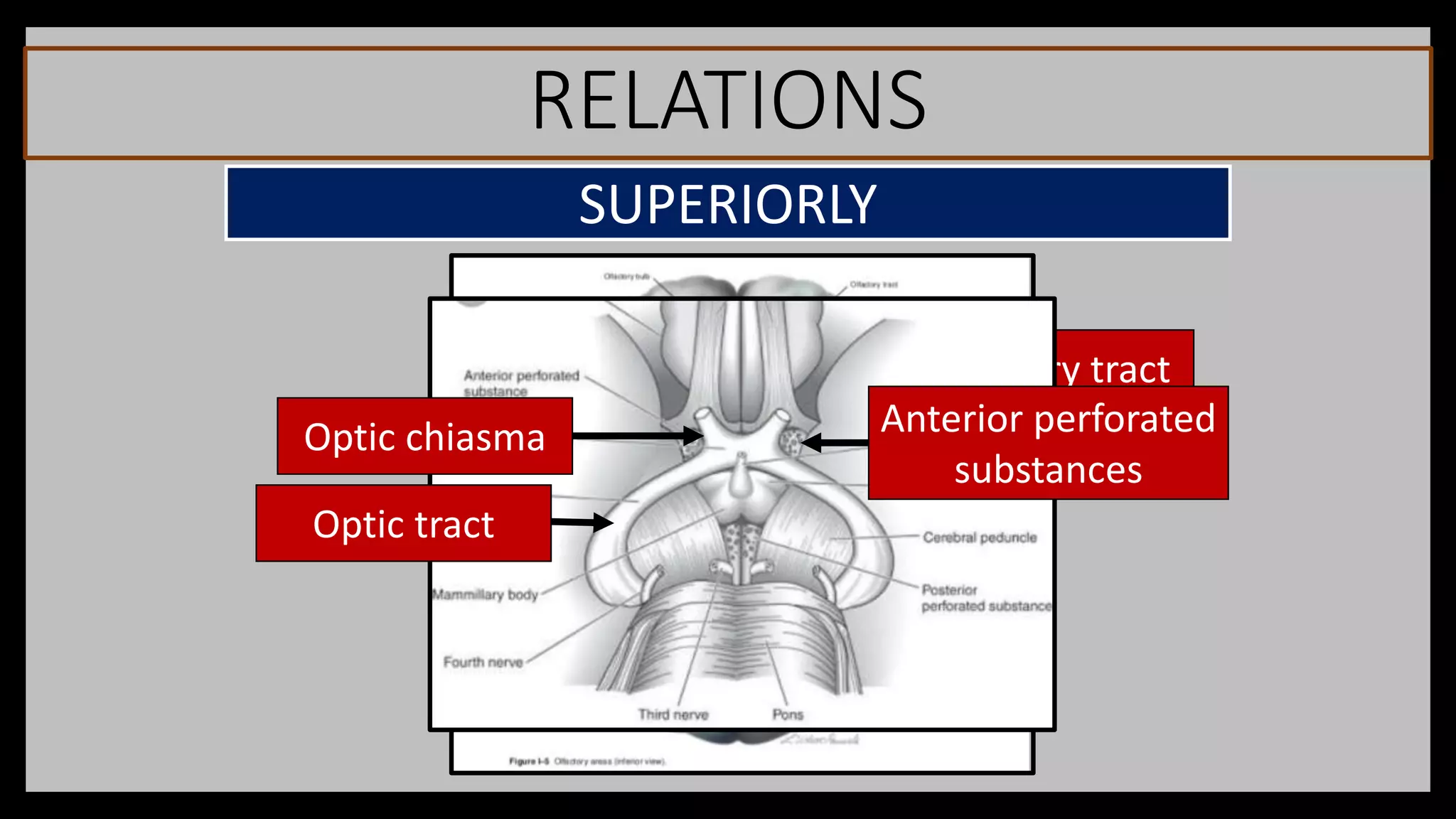
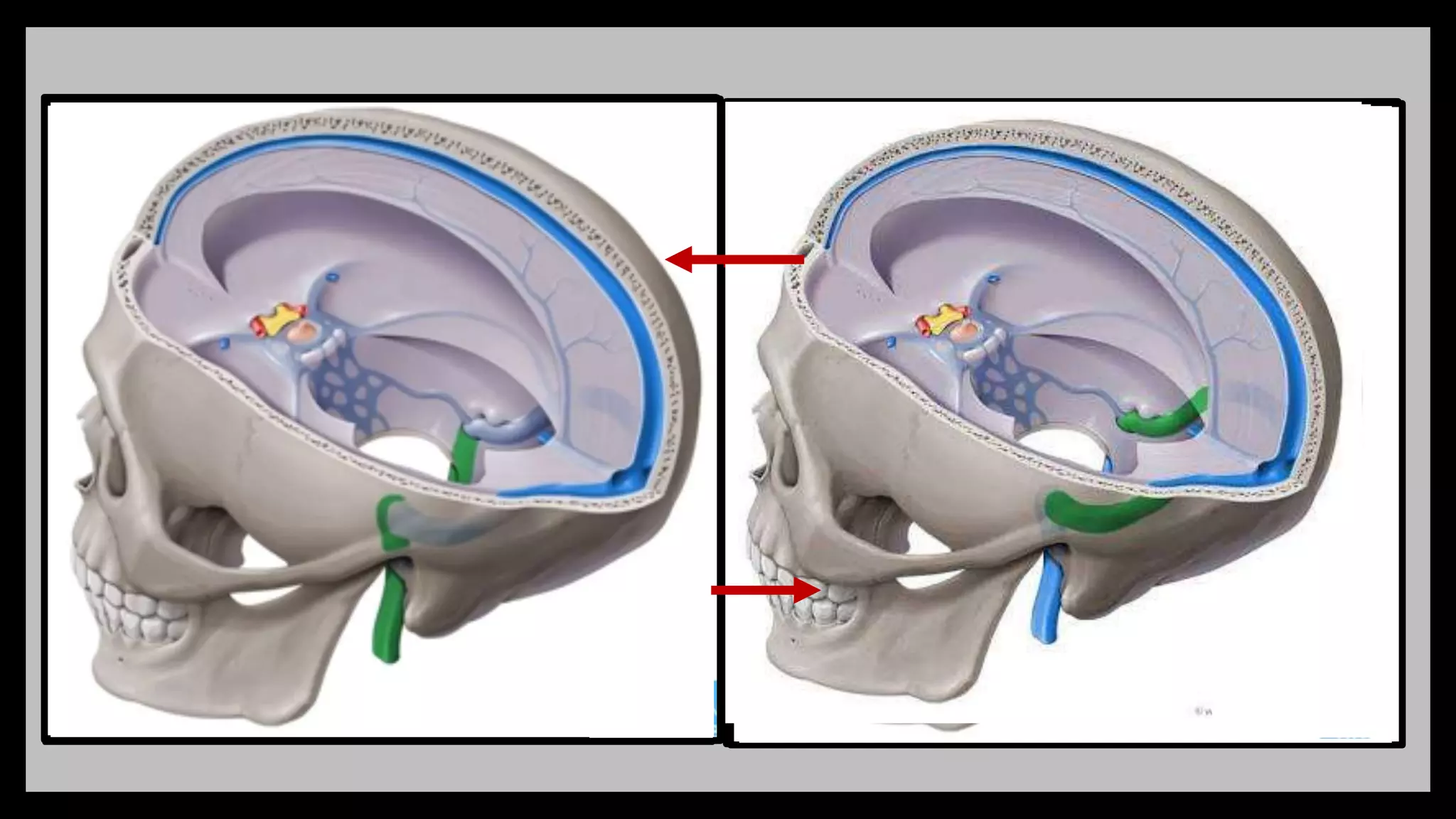
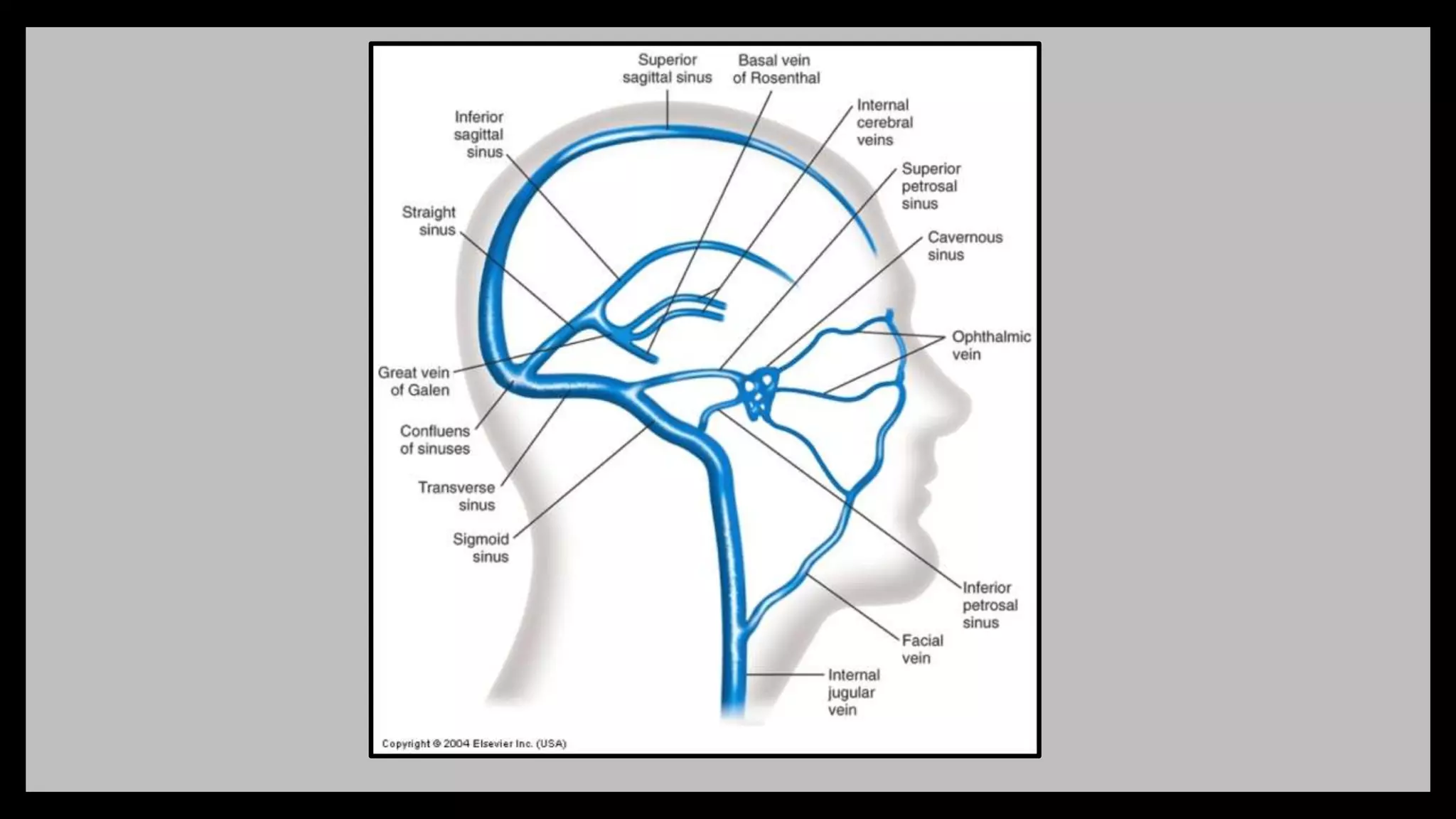
The document summarizes key anatomical structures related to the dura mater and venous sinuses in the skull. It discusses:
1) The dura mater is the outermost meningeal layer that lines the inner skull. It contains infoldings like the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli.
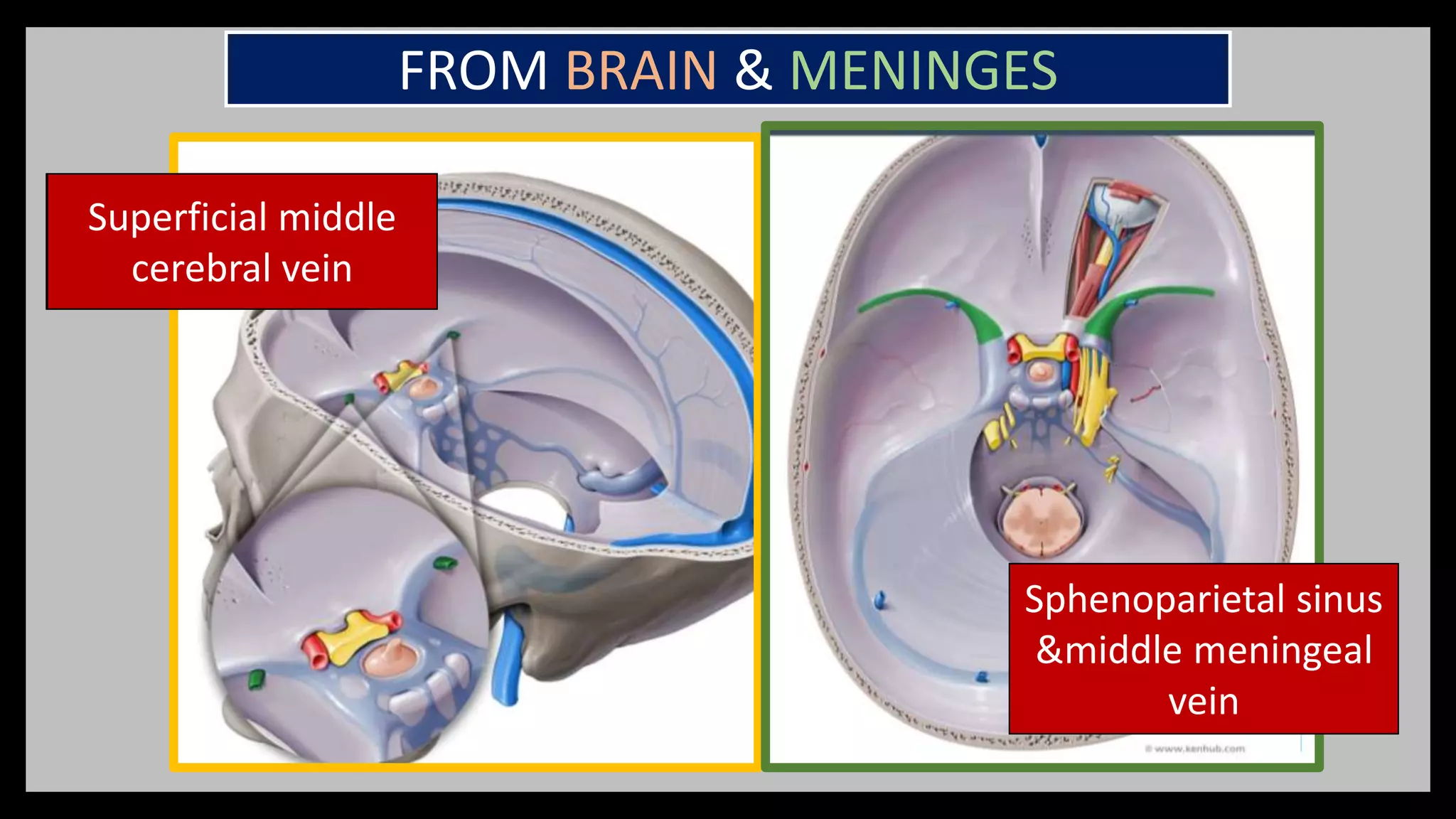
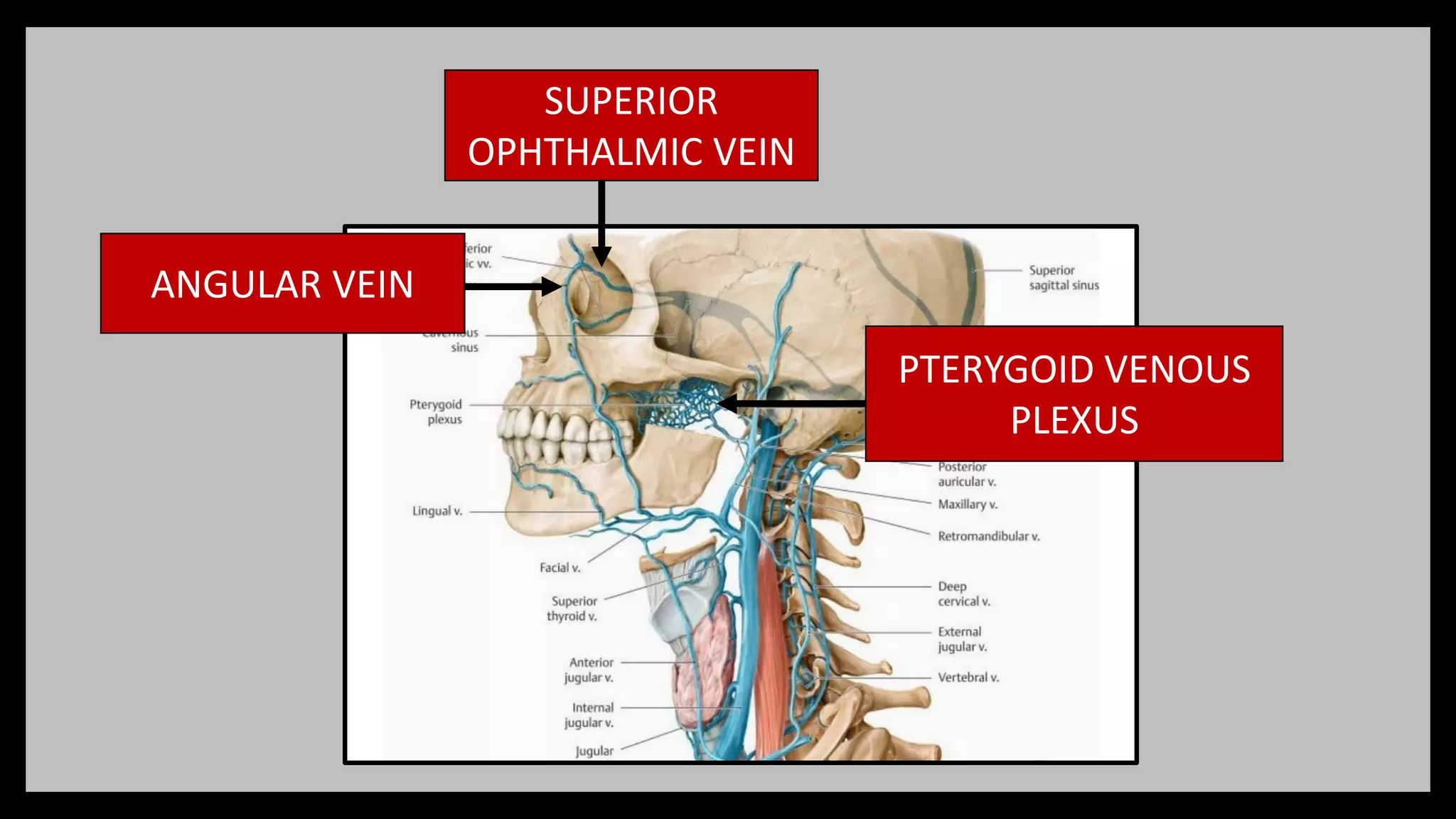
2) Venous sinuses are channels located within the dura mater that drain blood from the brain. Major sinuses include the superior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and transverse sinus.
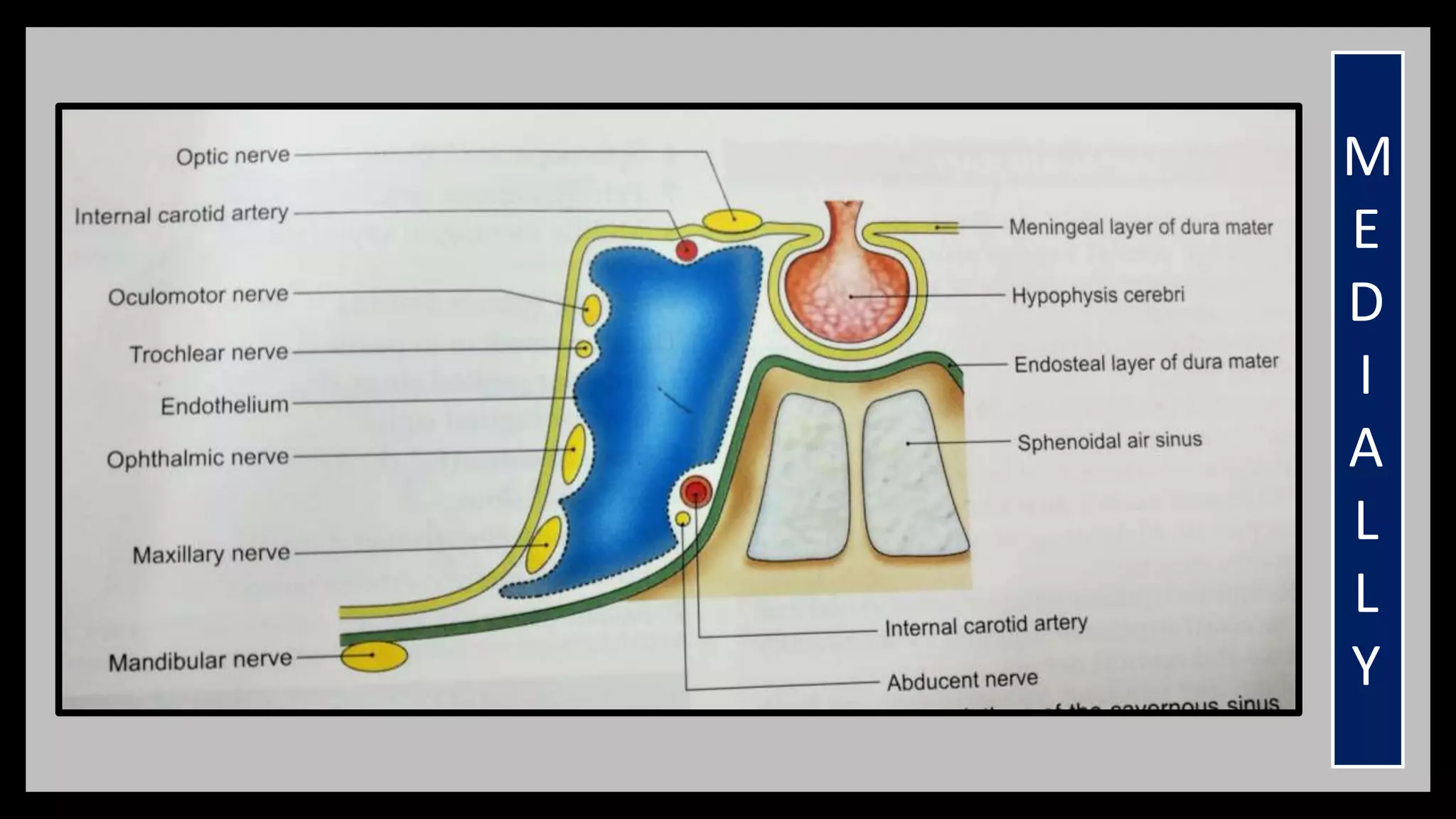
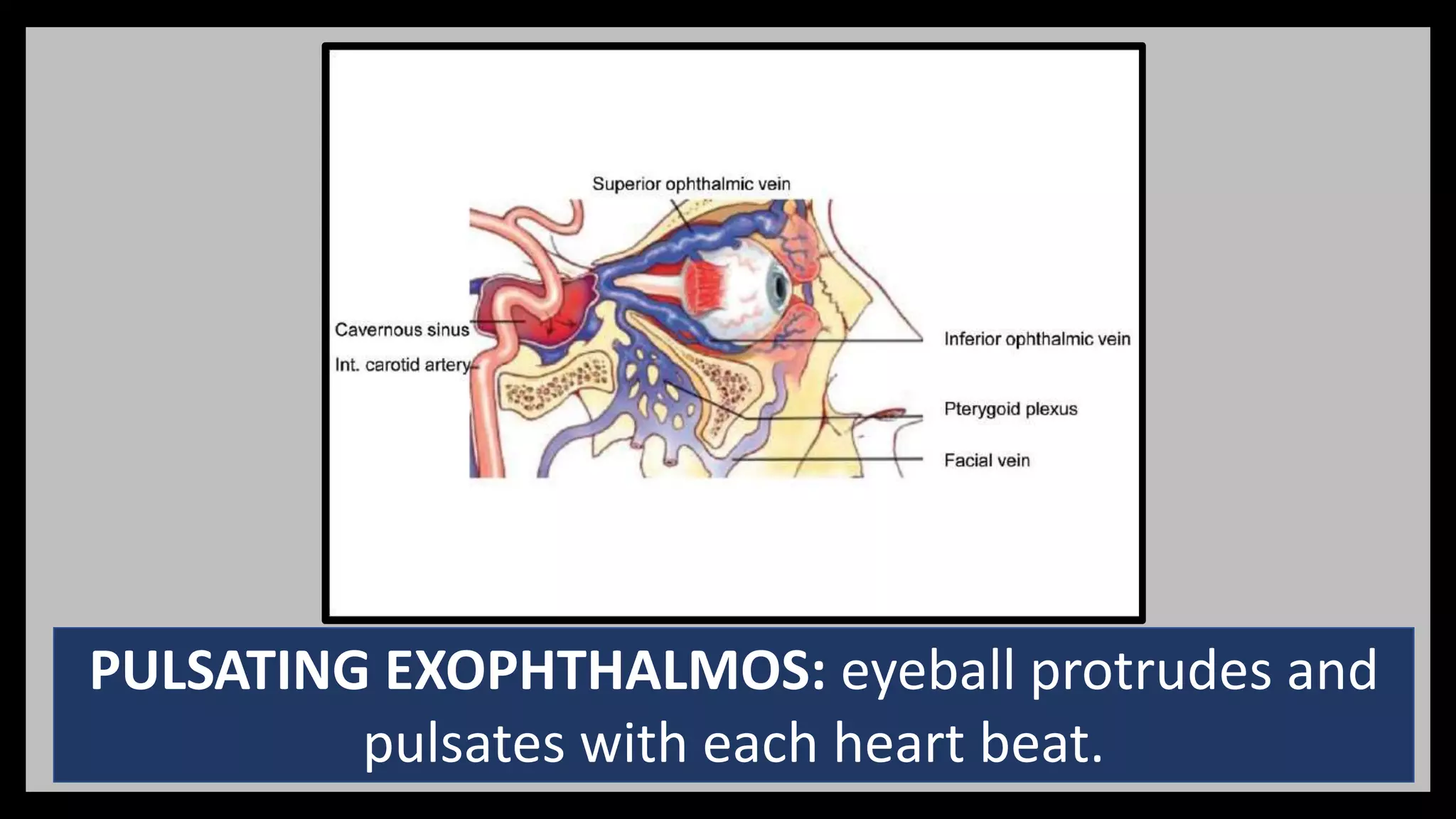
3) The cavernous sinus is a large venous channel located on each side of the sphenoid bone. It contains the internal carotid artery and cranial nerves III, IV,