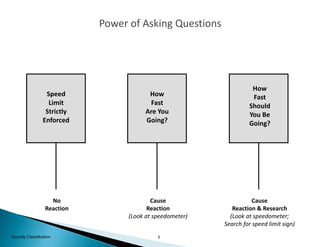
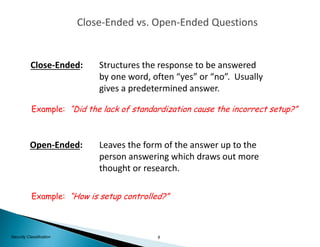
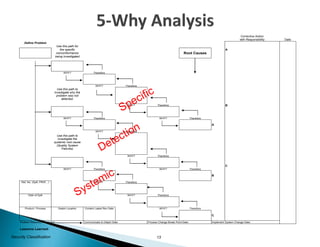
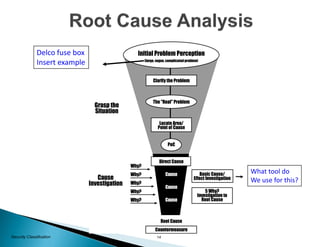
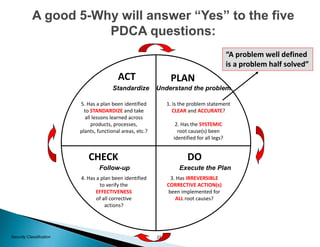
The document provides guidance on conducting a 5-Why analysis to determine the root cause of problems. It explains that 5-Why fits within the problem resolution request (PRR) process and is used to facilitate problem resolution. The document then covers understanding 5-Why, provides an example, and discusses open-ended versus closed-ended questions. It also outlines the steps for a 5-Why analysis, provides a critique sheet for evaluating 5-Why analyses, and offers general guidelines.