This document provides a summary of steel structures, including:
- Steel structures are made of structural steel components connected to carry loads and provide rigidity. Common elements include I-beams, channels, angles, and plates.
- Steel structures offer benefits like cost savings, design flexibility, efficient construction, and durability in harsh conditions.
- Different types of steel structures include braced frames, rigid frames, shear walls, and trusses.
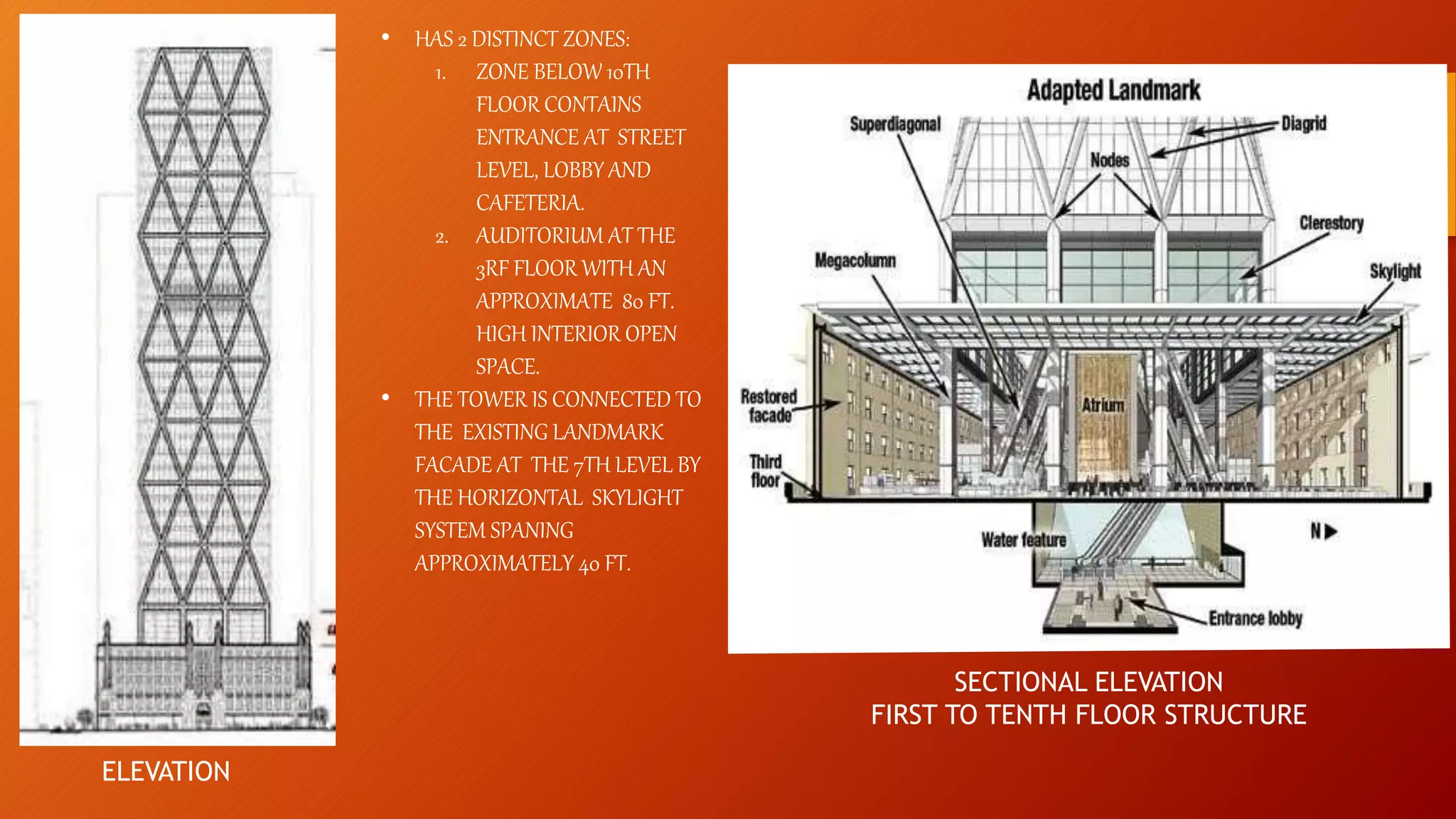
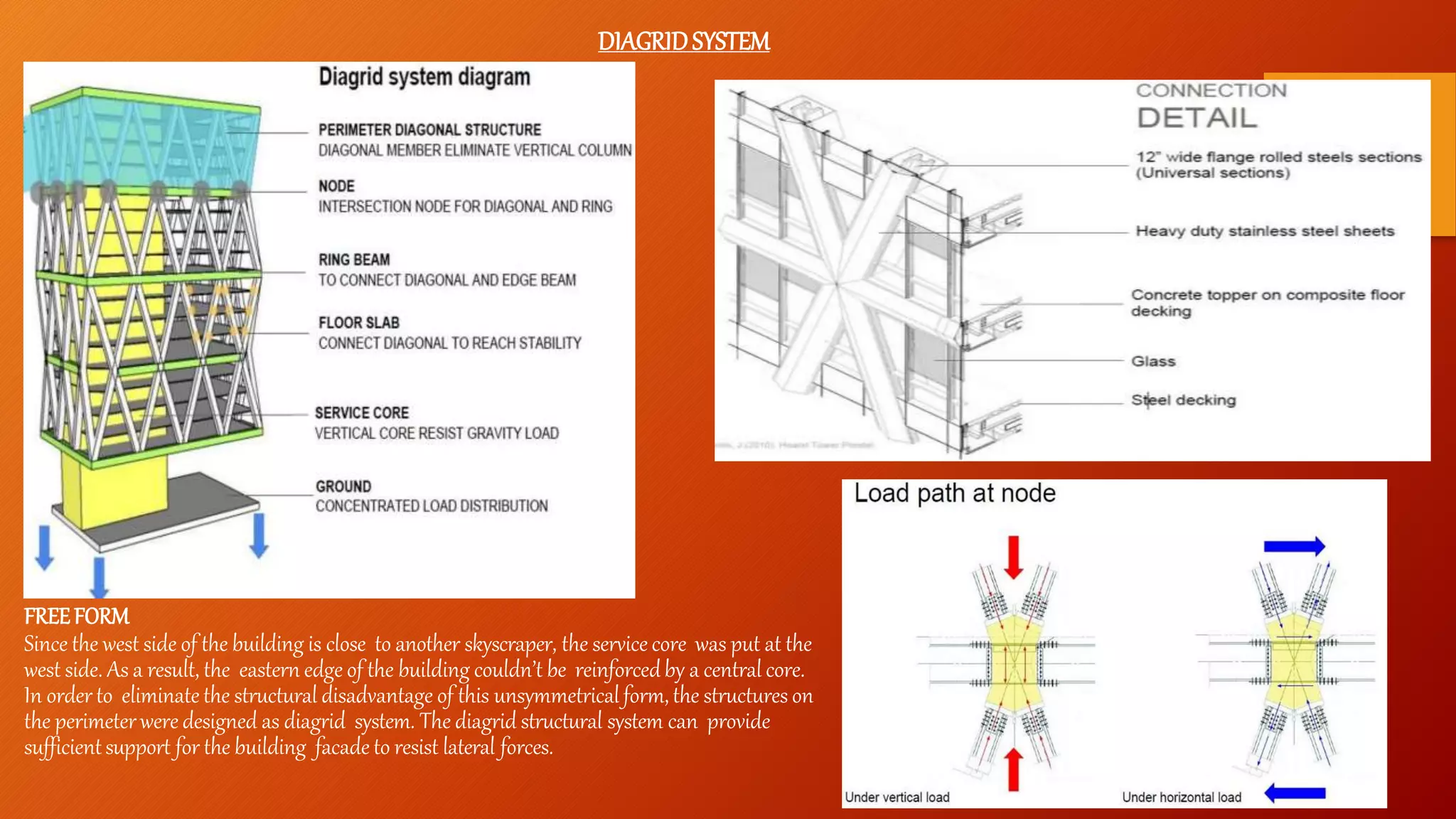
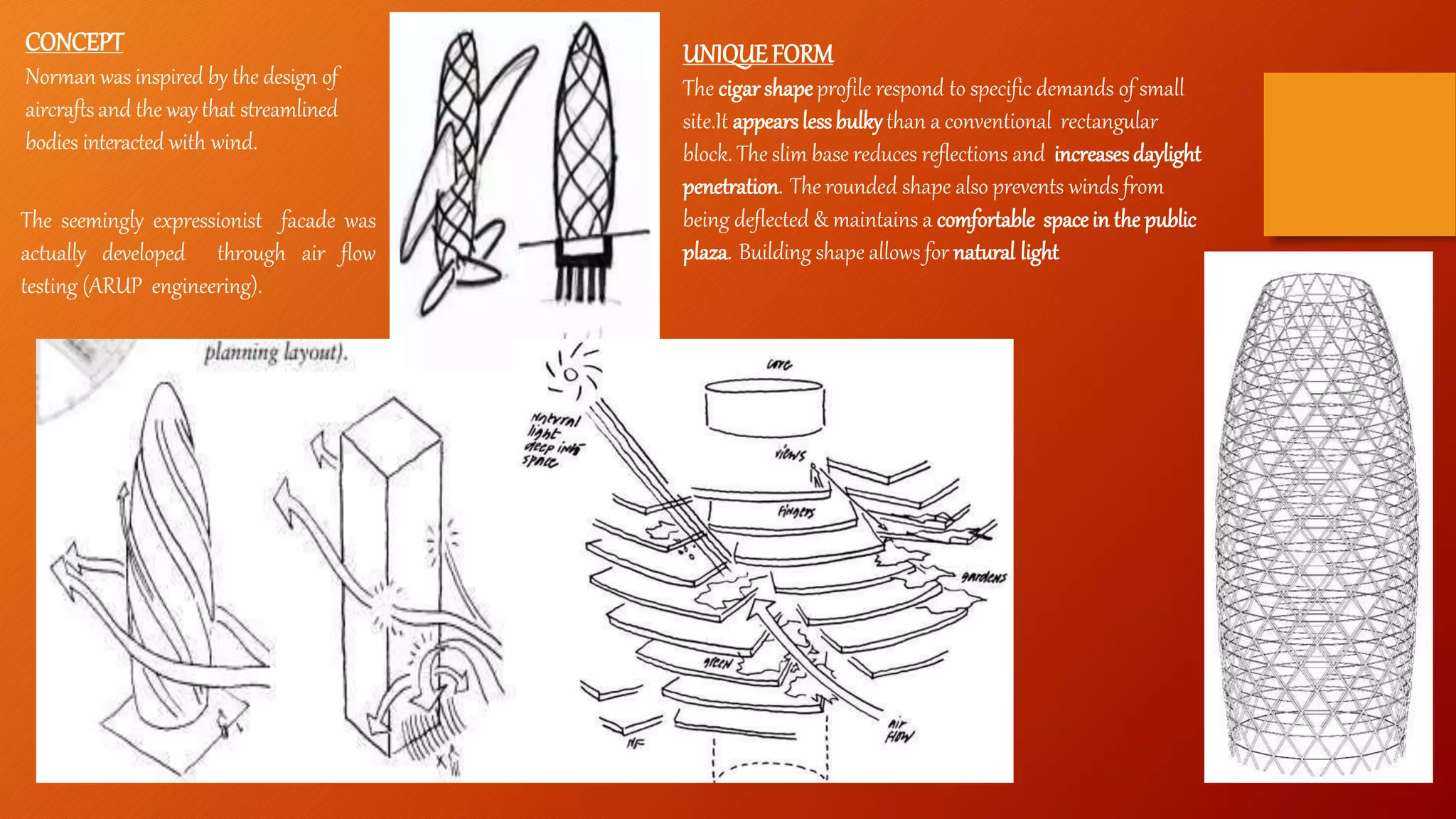
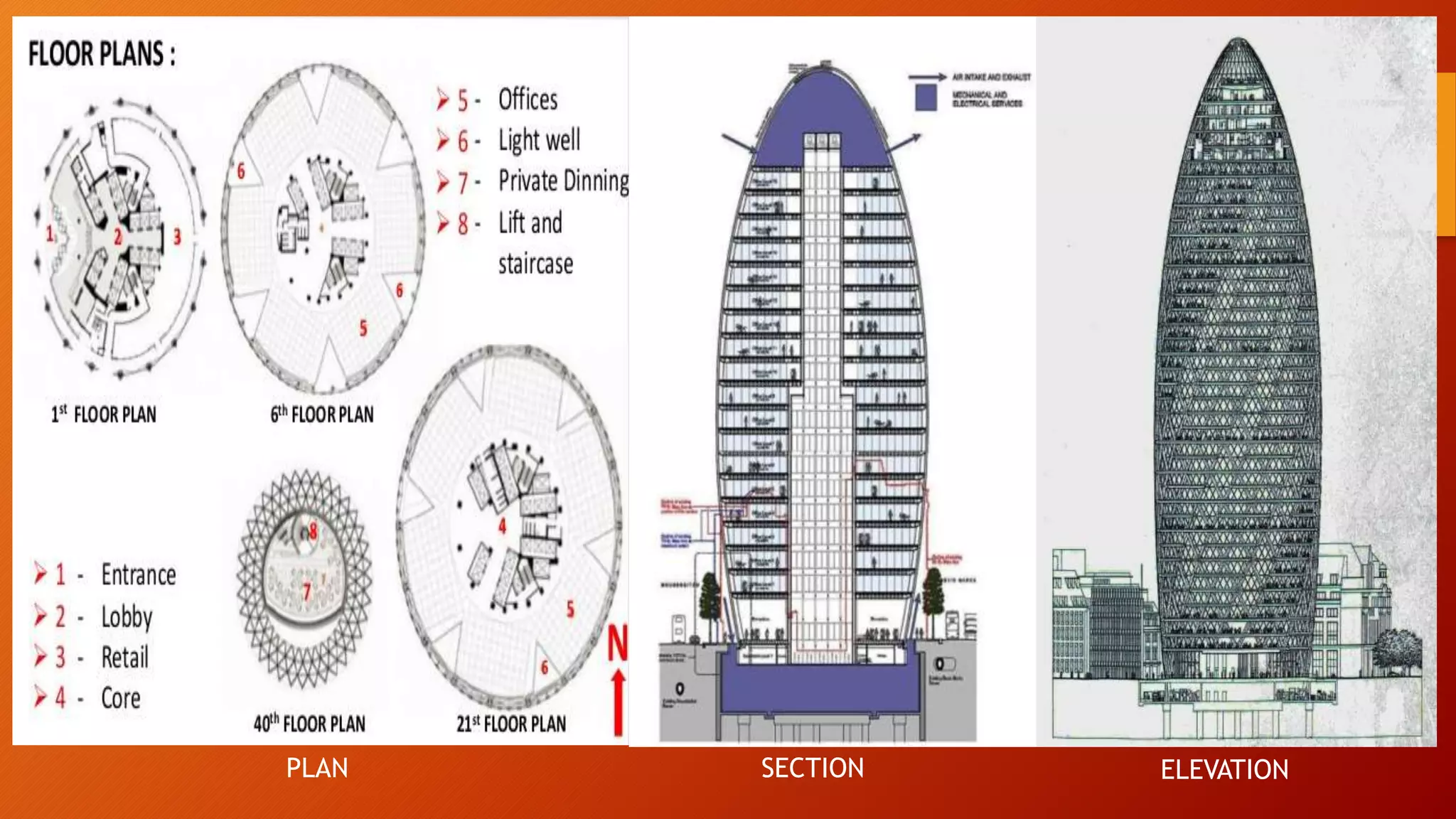
- Case studies highlight the Hearst Tower in New York, the Gherkin building in London, and the LIC Jeewan Bharti building in India, all of which utilize innovative steel designs like diagrids and space frames.