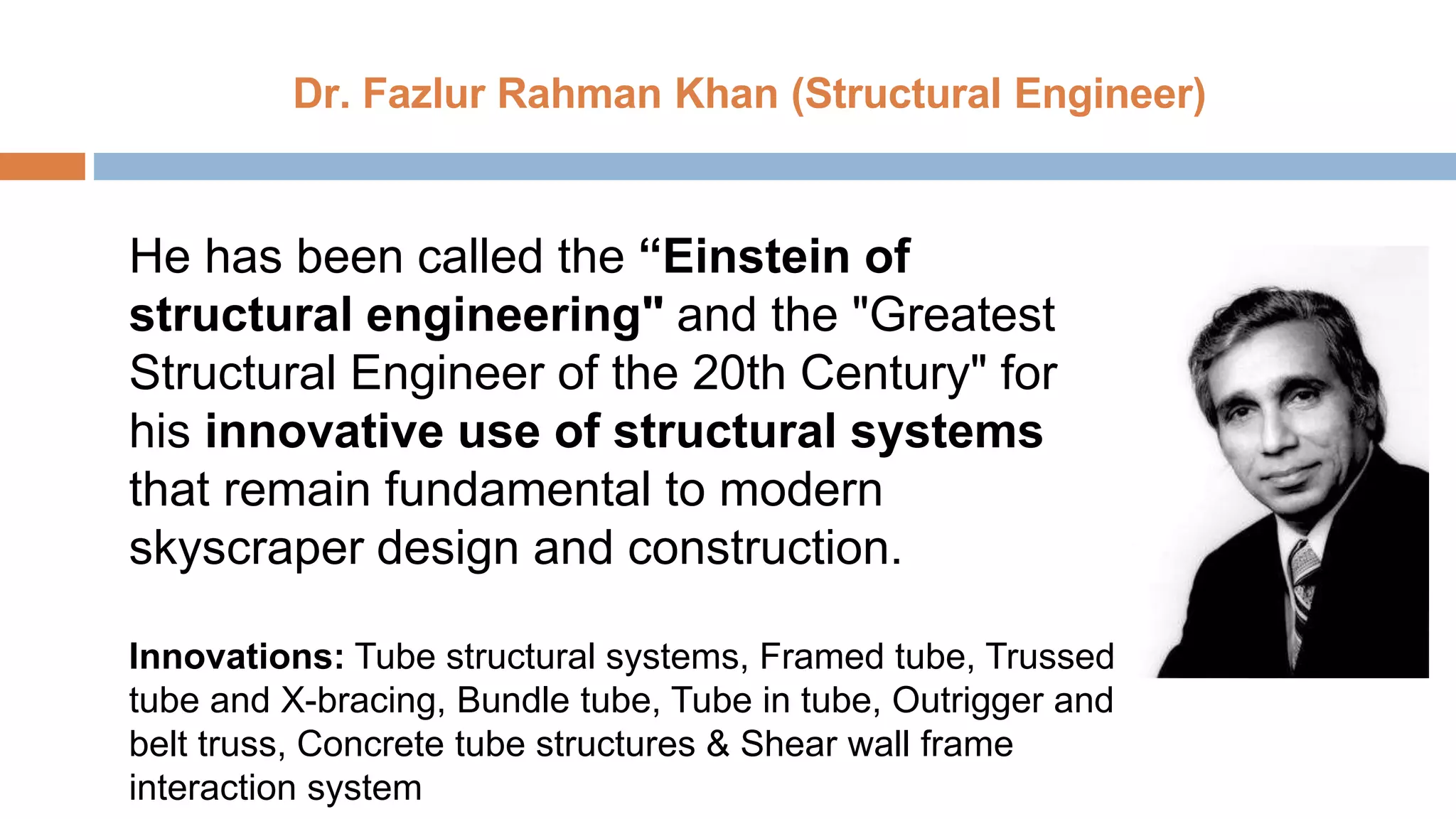
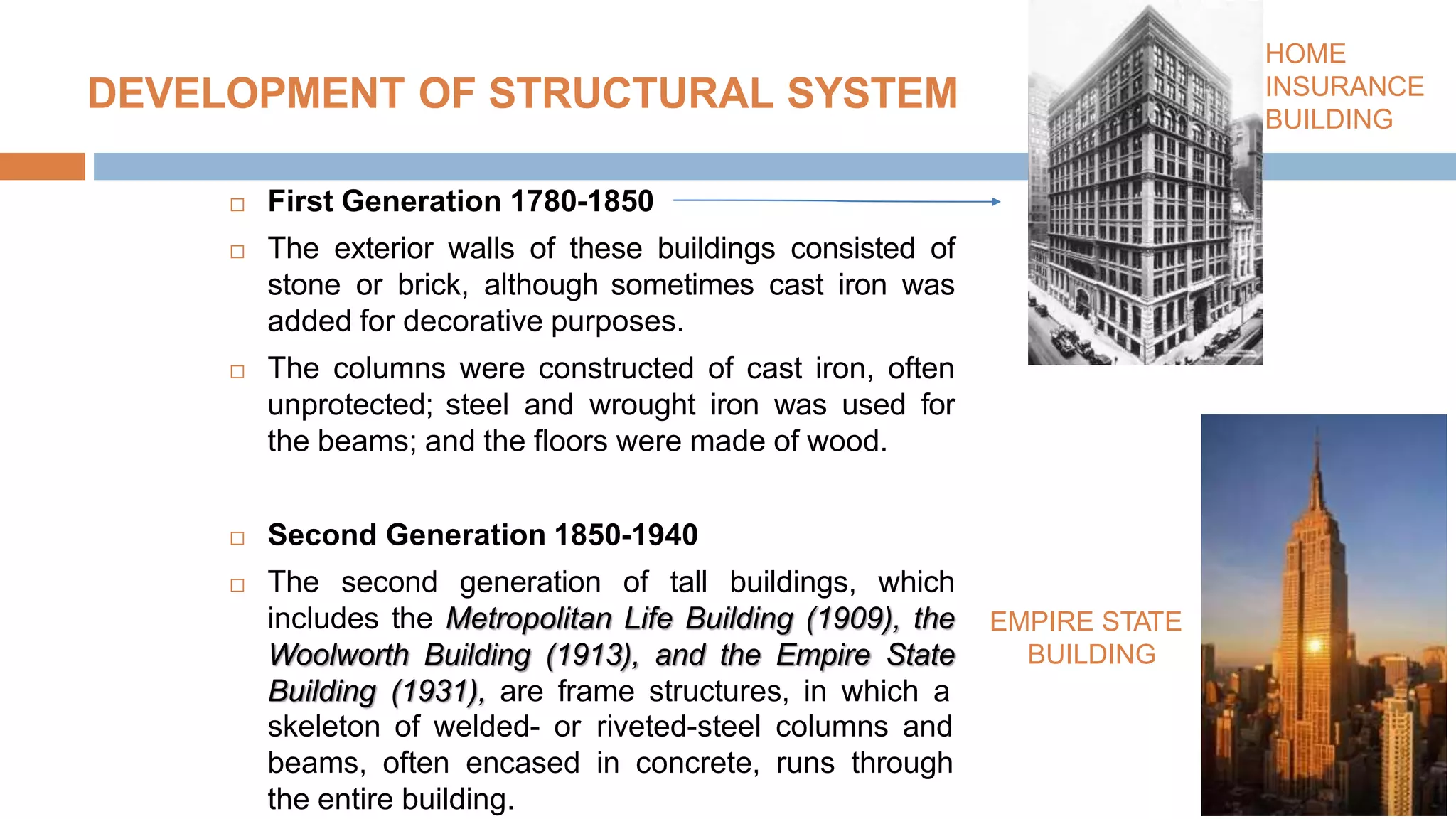
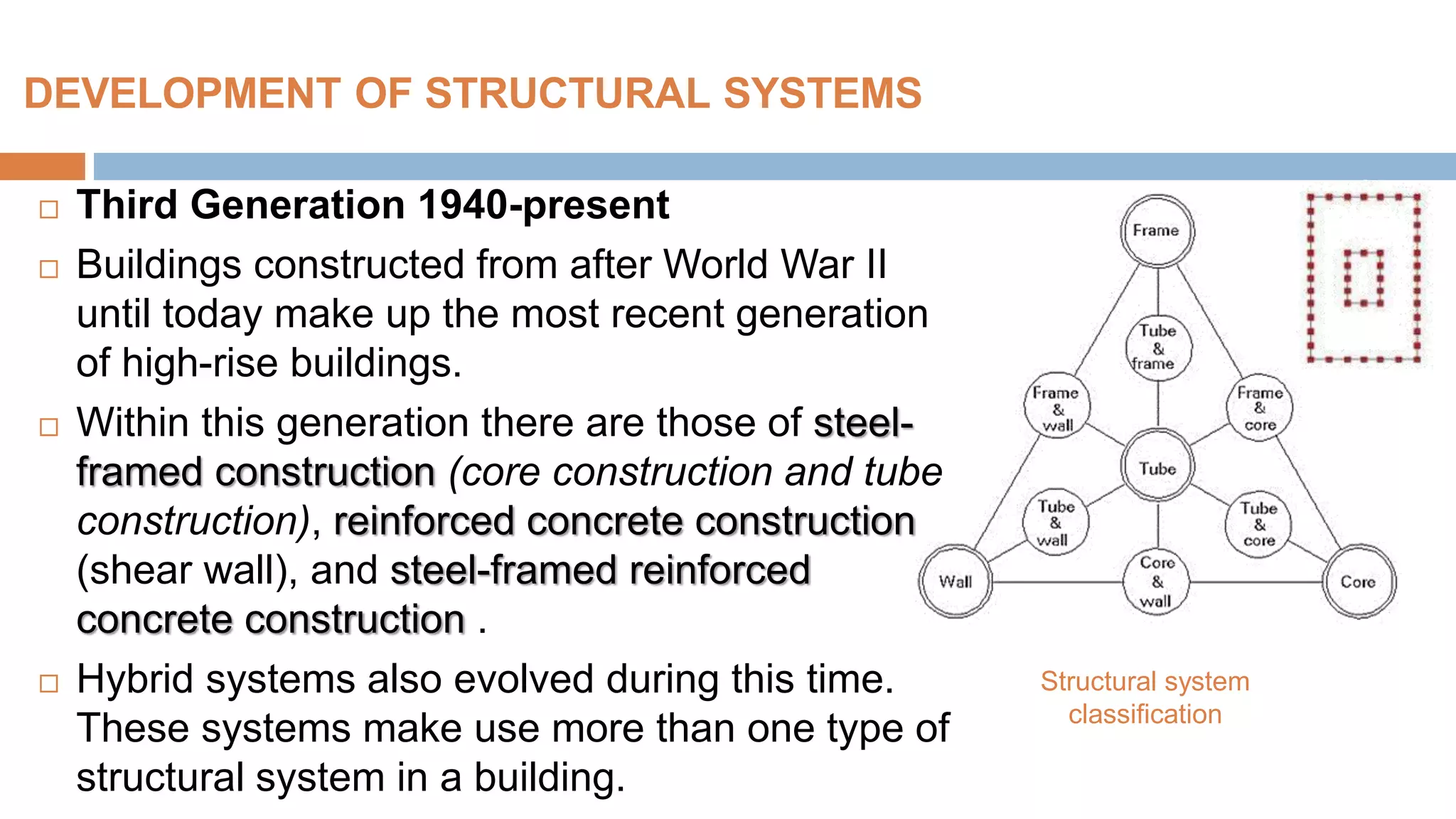
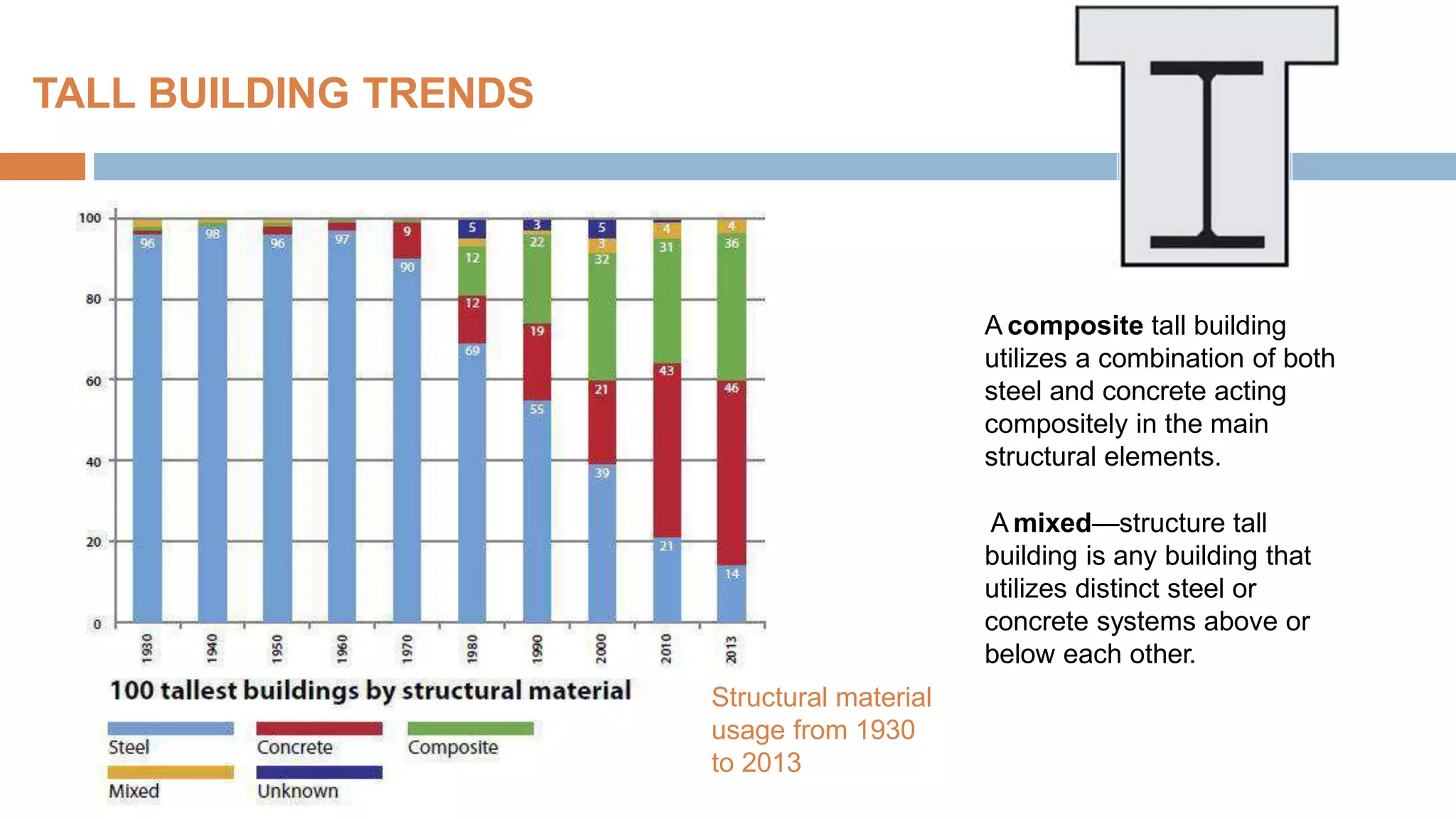
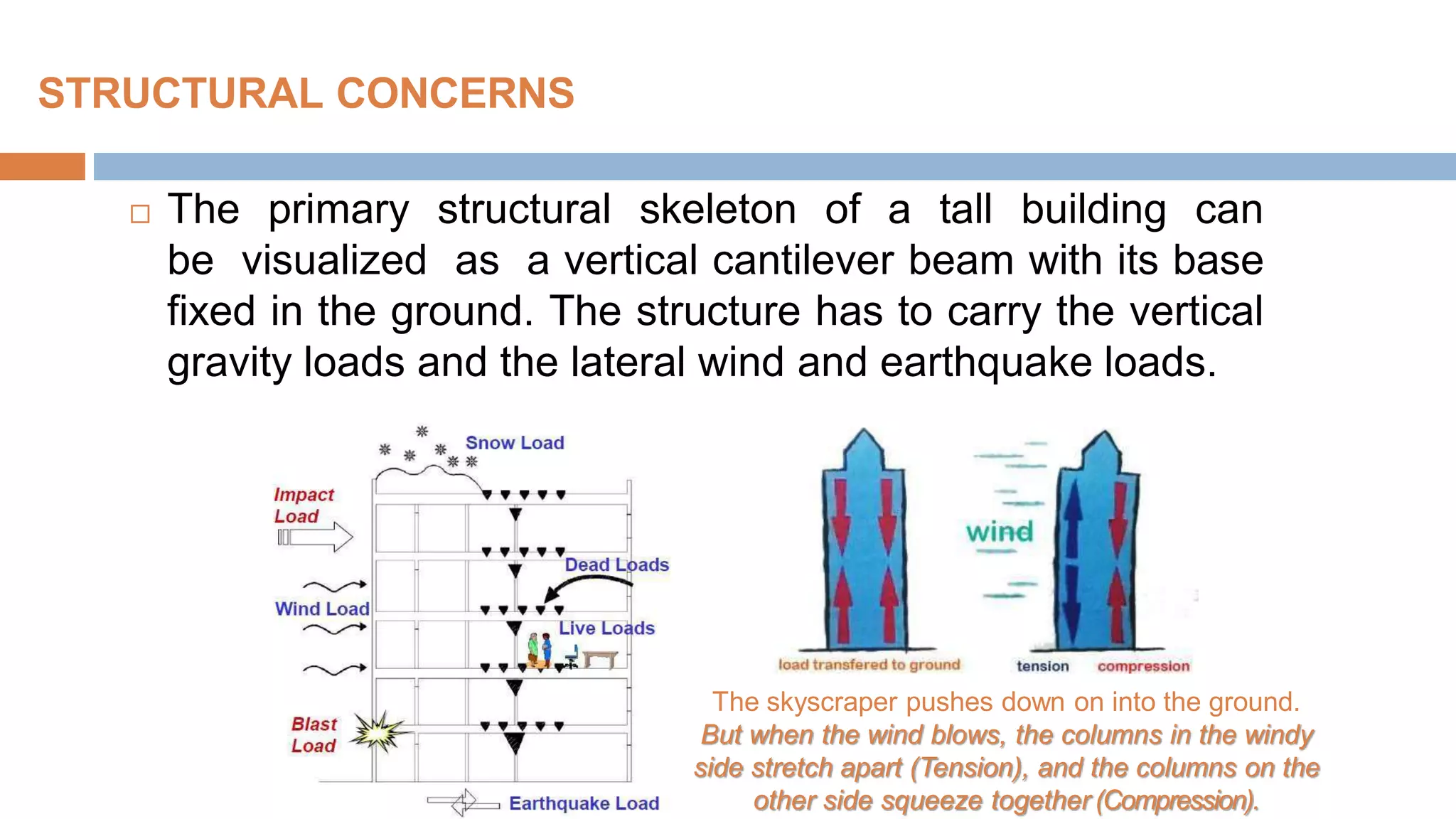
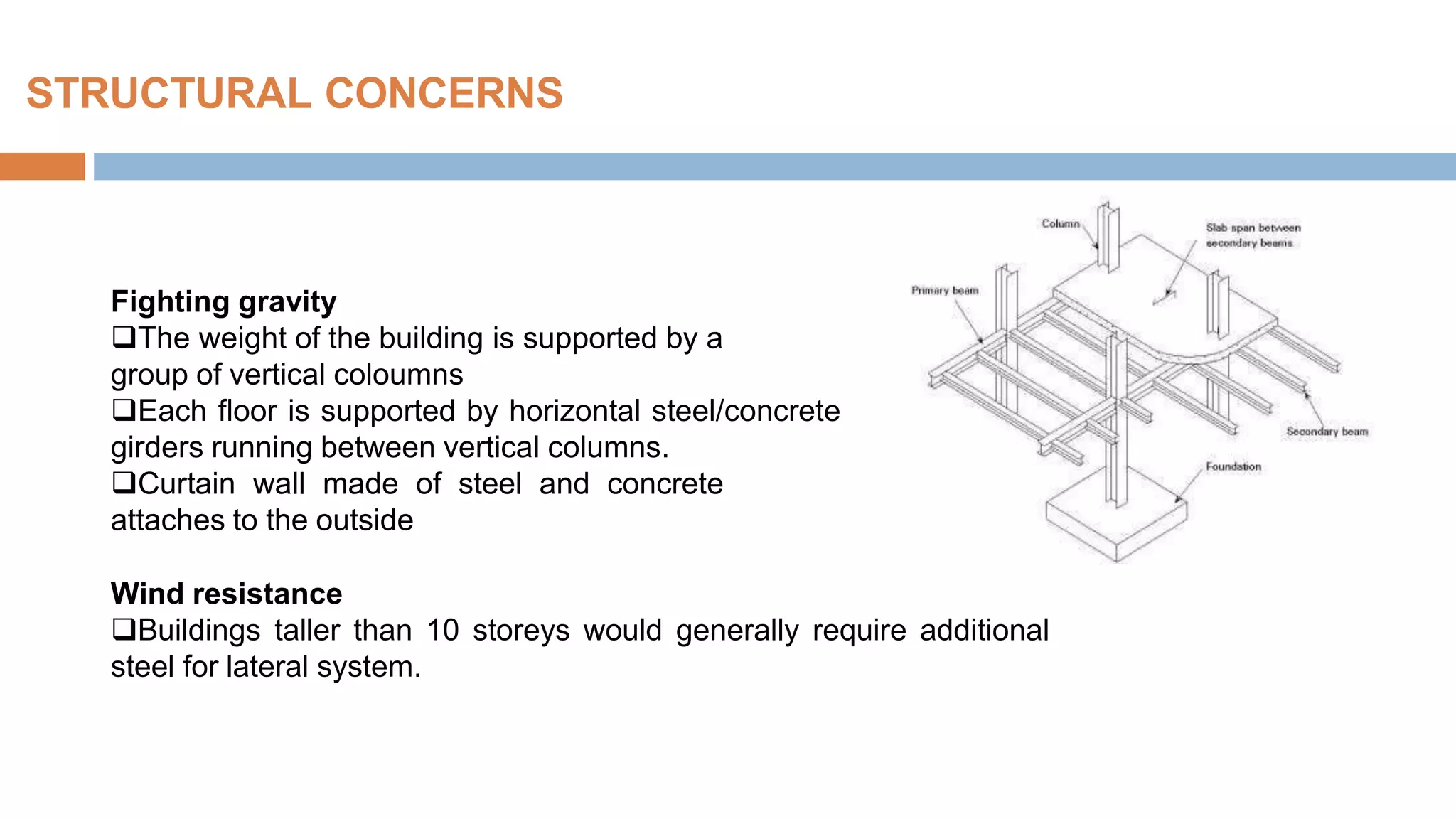
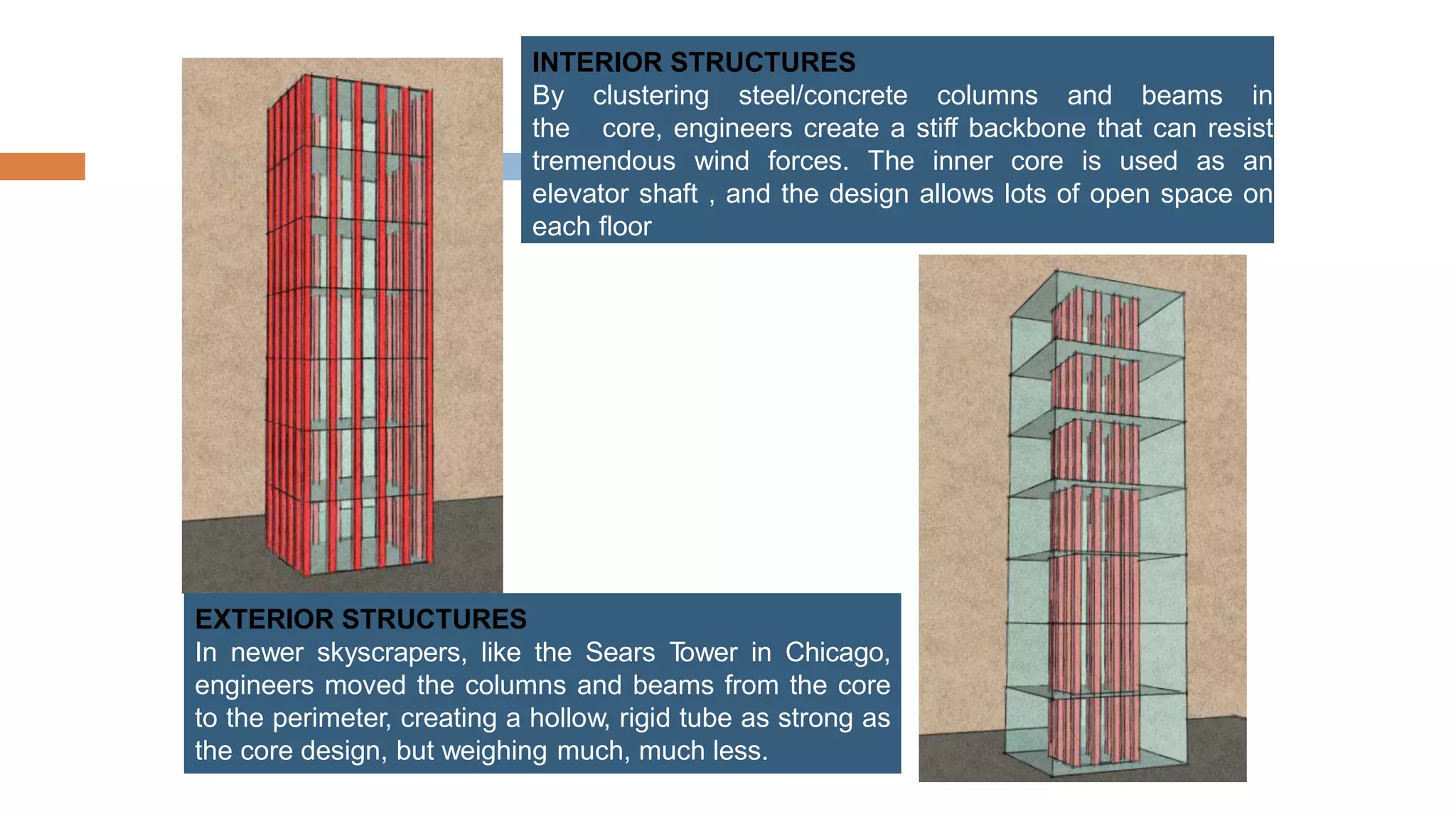
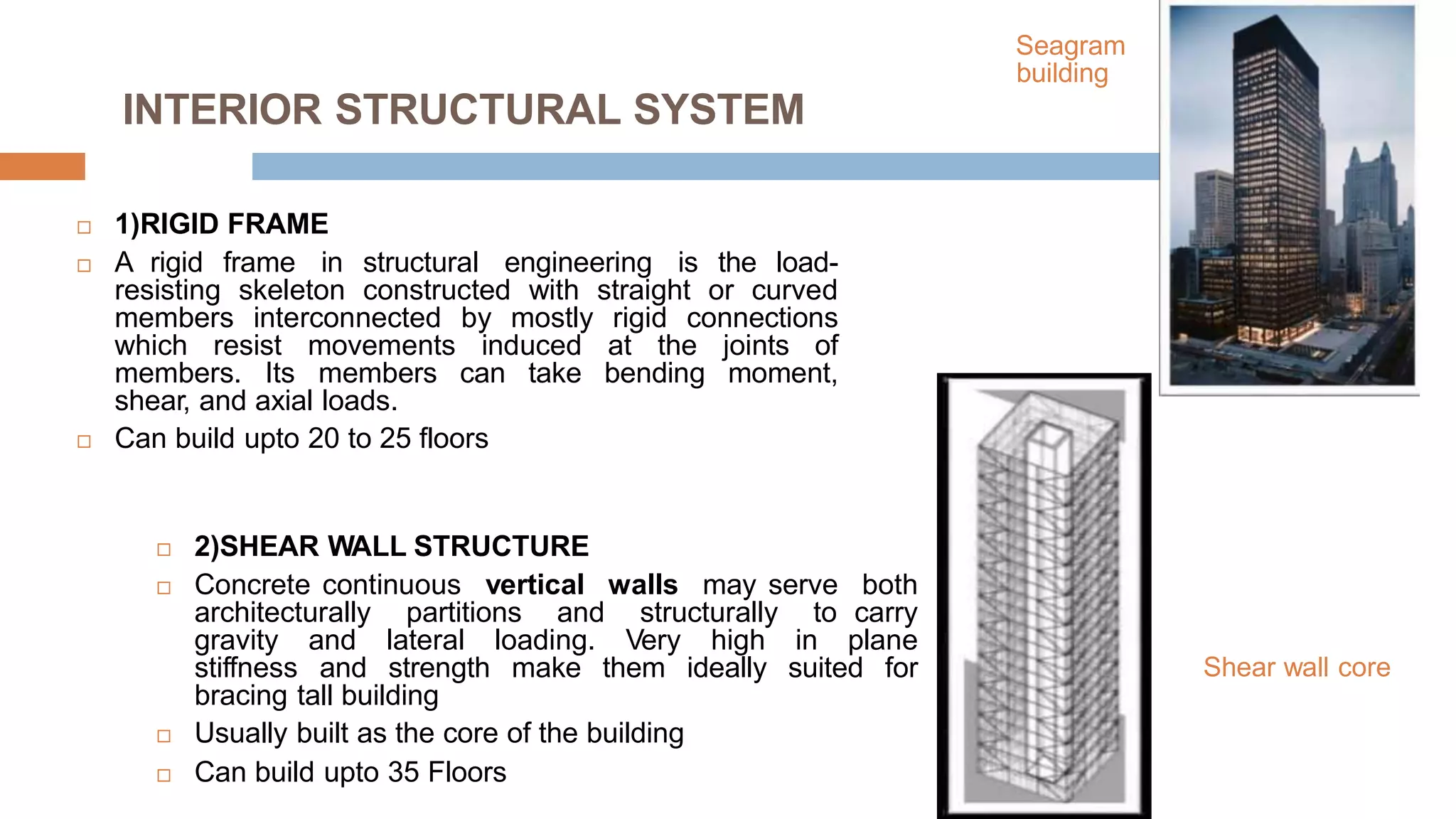
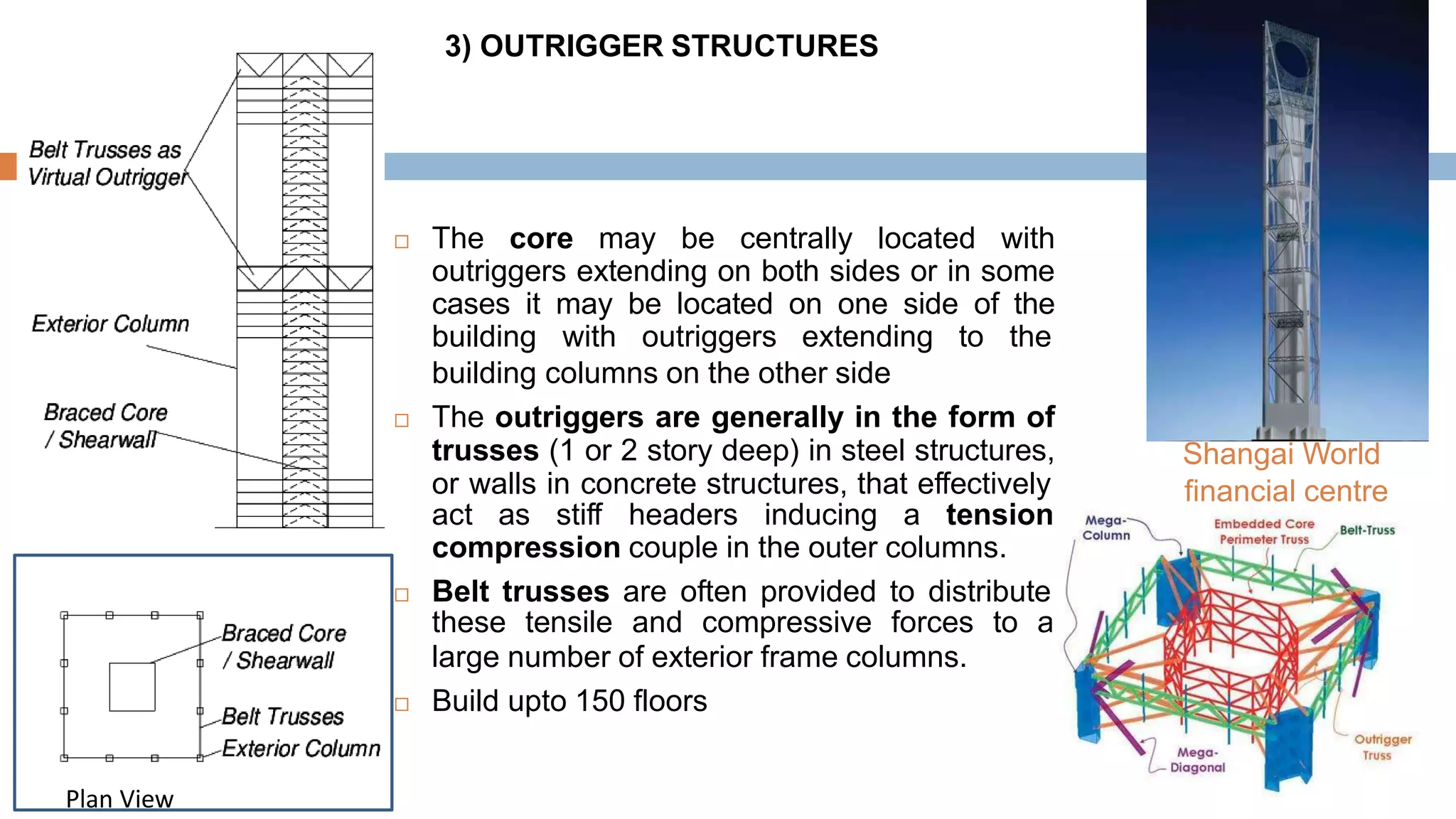
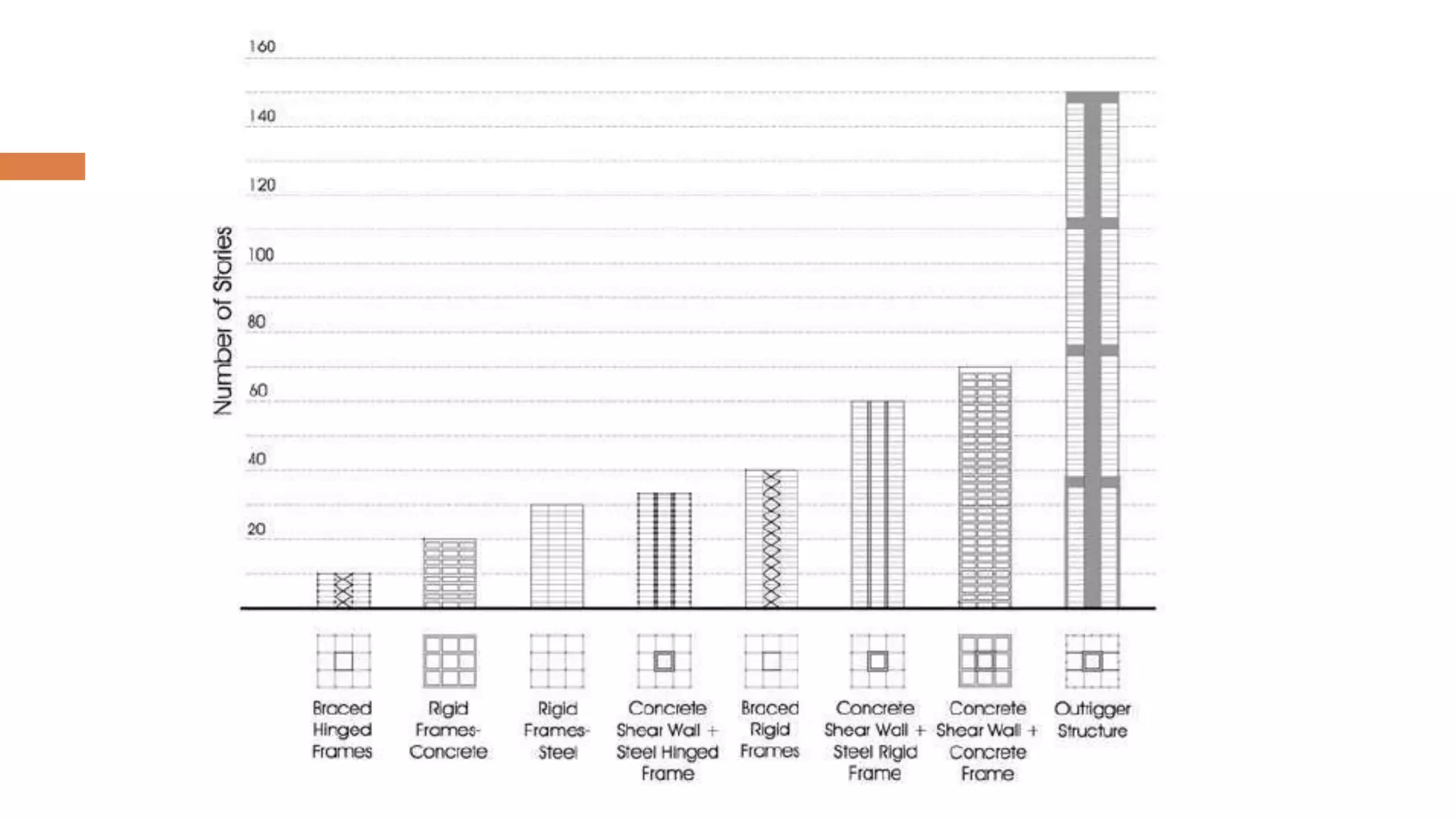
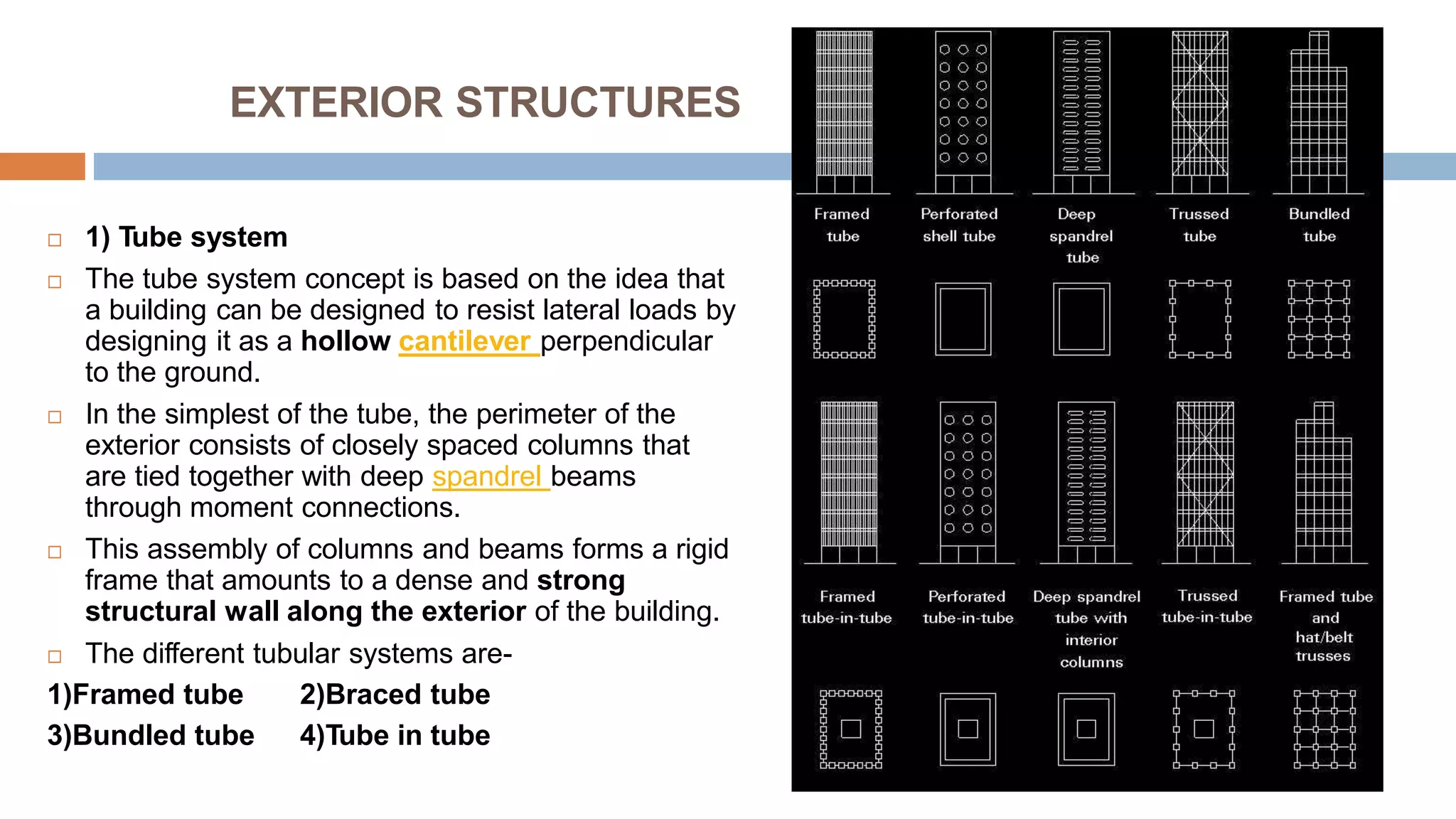
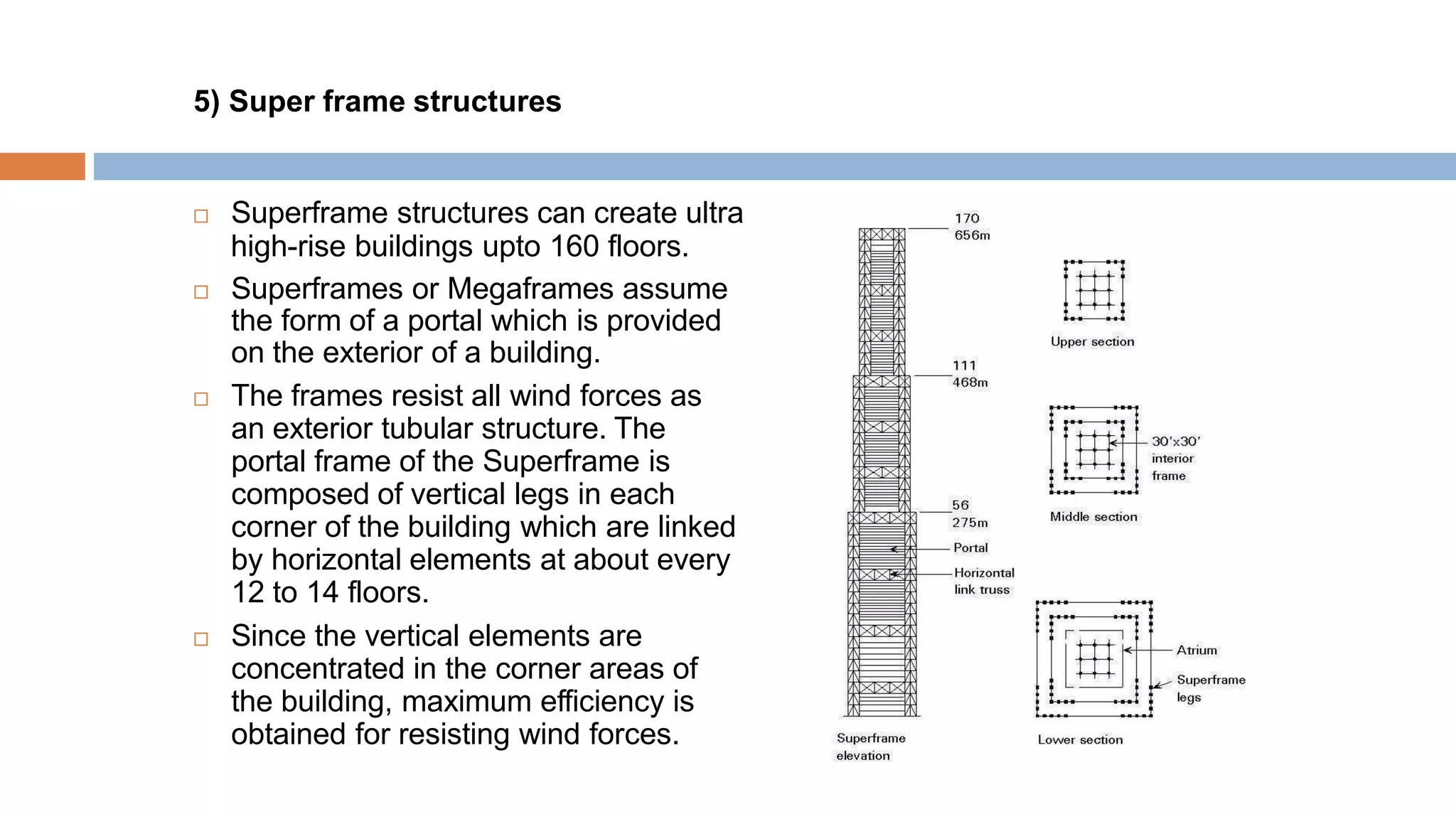
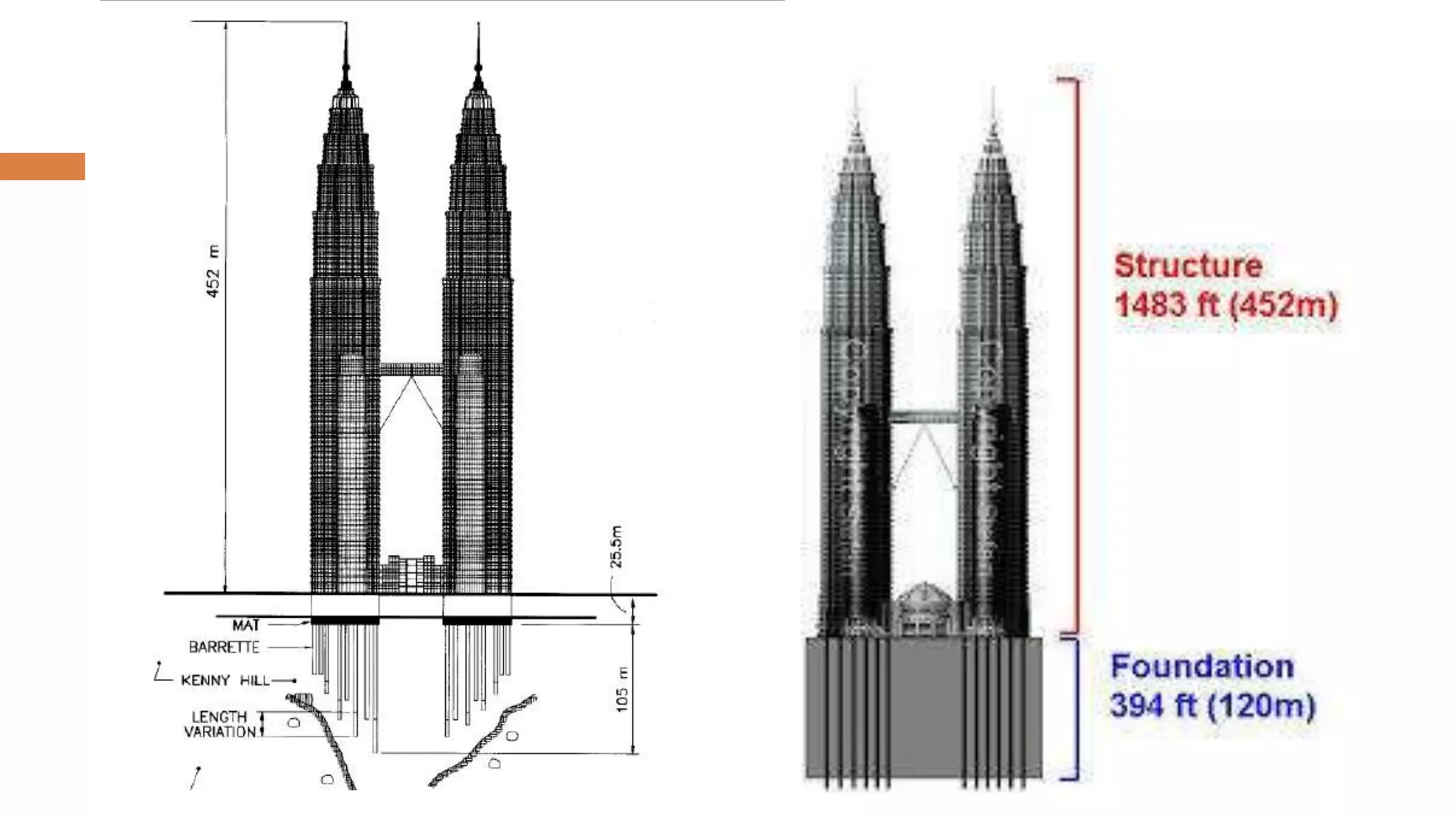
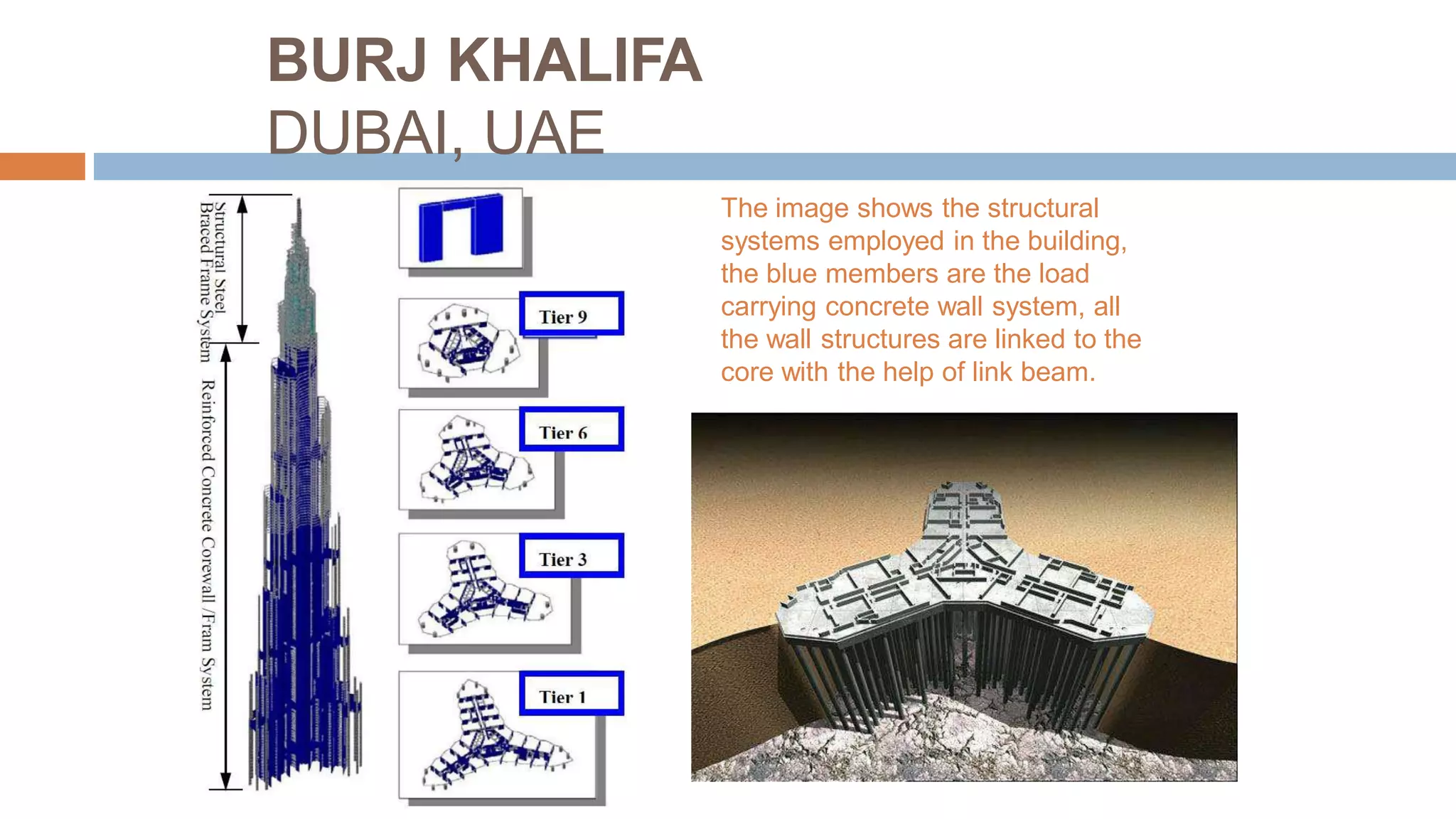
Structural systems in high-rise buildings have evolved over three generations from the late 18th century to present. Early systems used stone, brick, cast iron and wood. Later systems in the 1850-1940 period used steel frames with concrete. Modern systems from 1940 on use steel cores, outriggers, tube designs, diagrids, and superframes to resist gravity and lateral wind loads. Definitions of high-rise vary but are generally above 35 meters. Drivers for tall buildings include land scarcity, demand for space, and prestige. Innovators like Fazlur Rahman Khan pioneered new efficient systems. Future trends may include taller megatalls over 600 meters using new composite systems and materials.