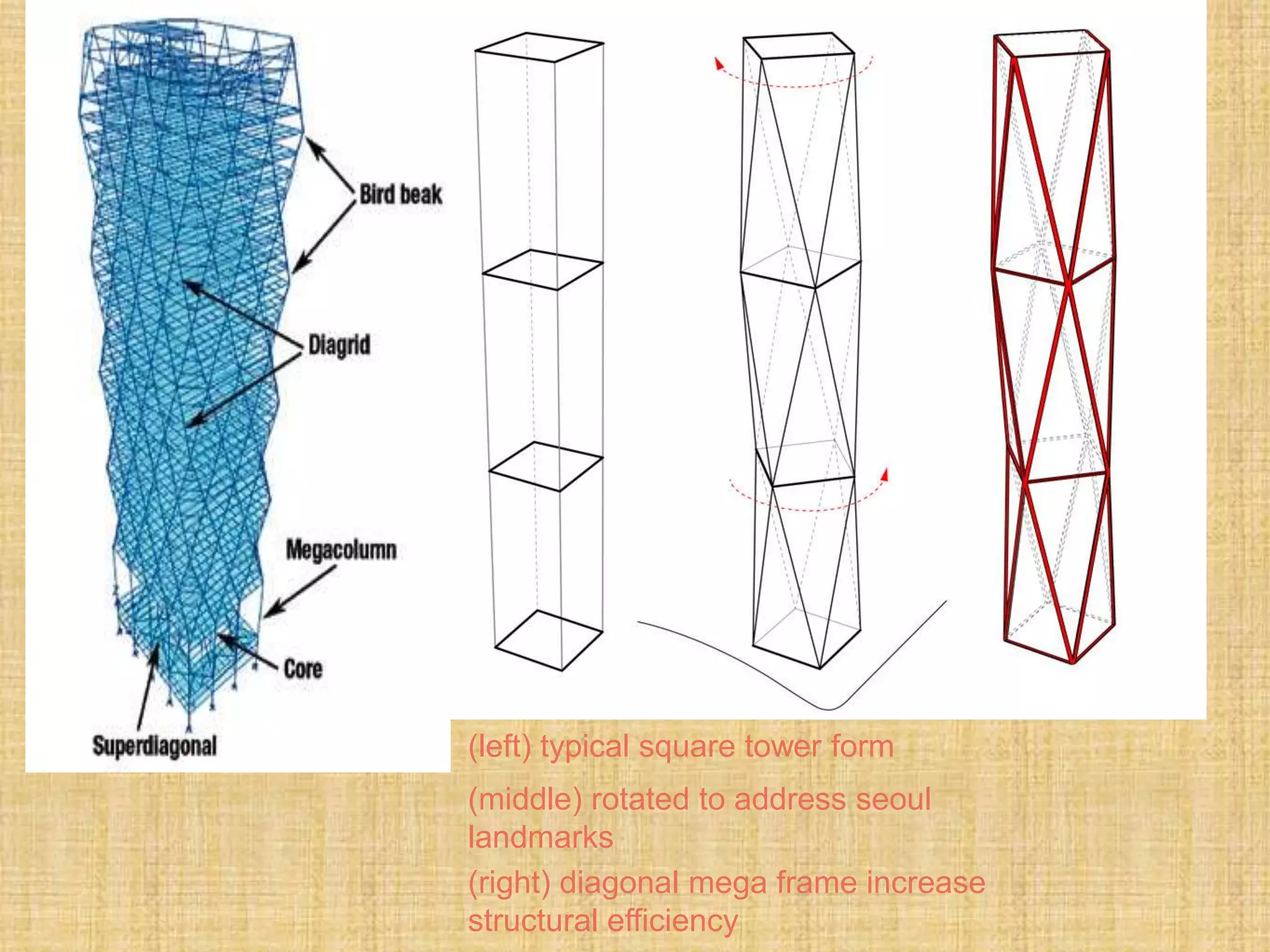
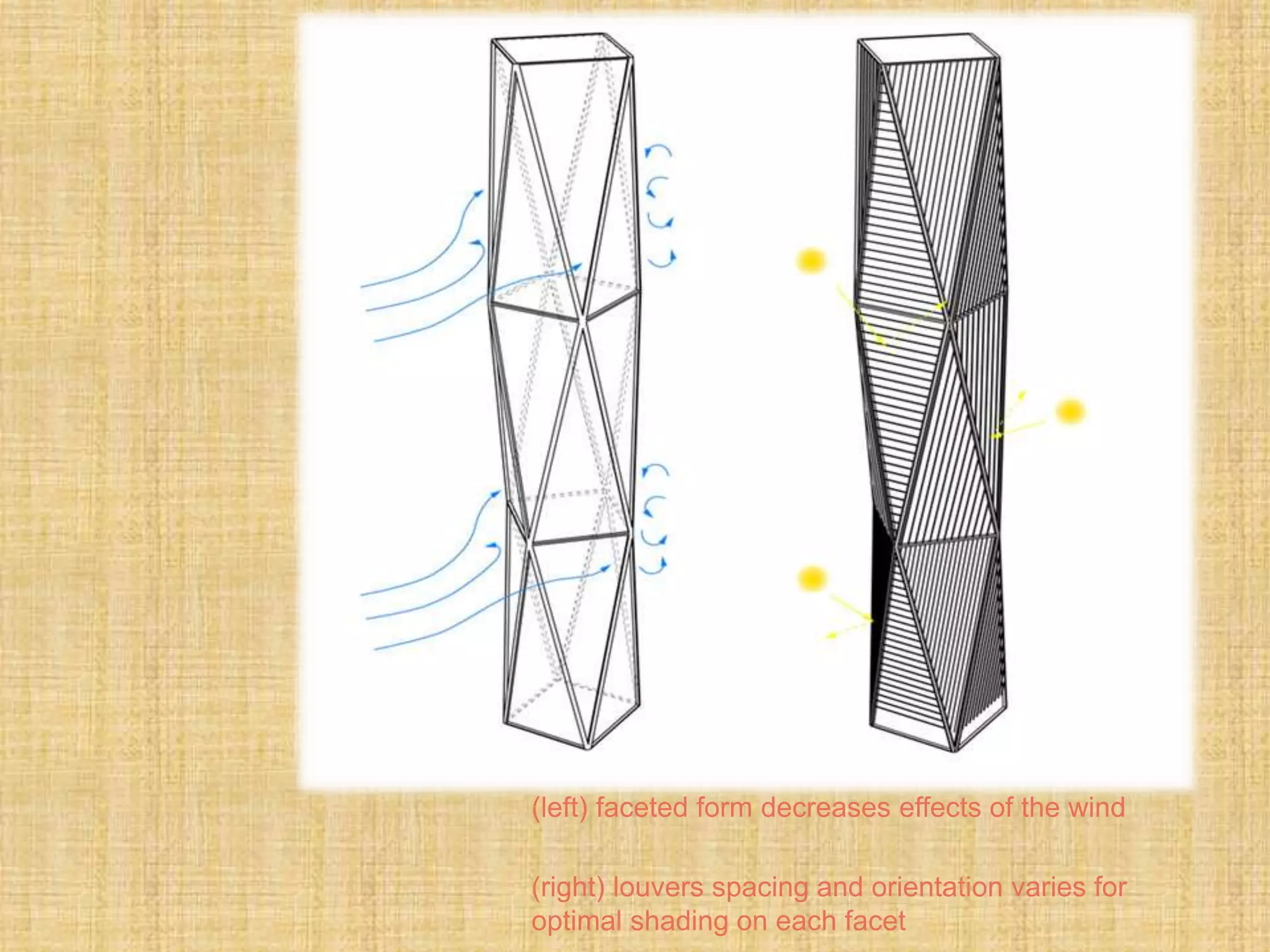
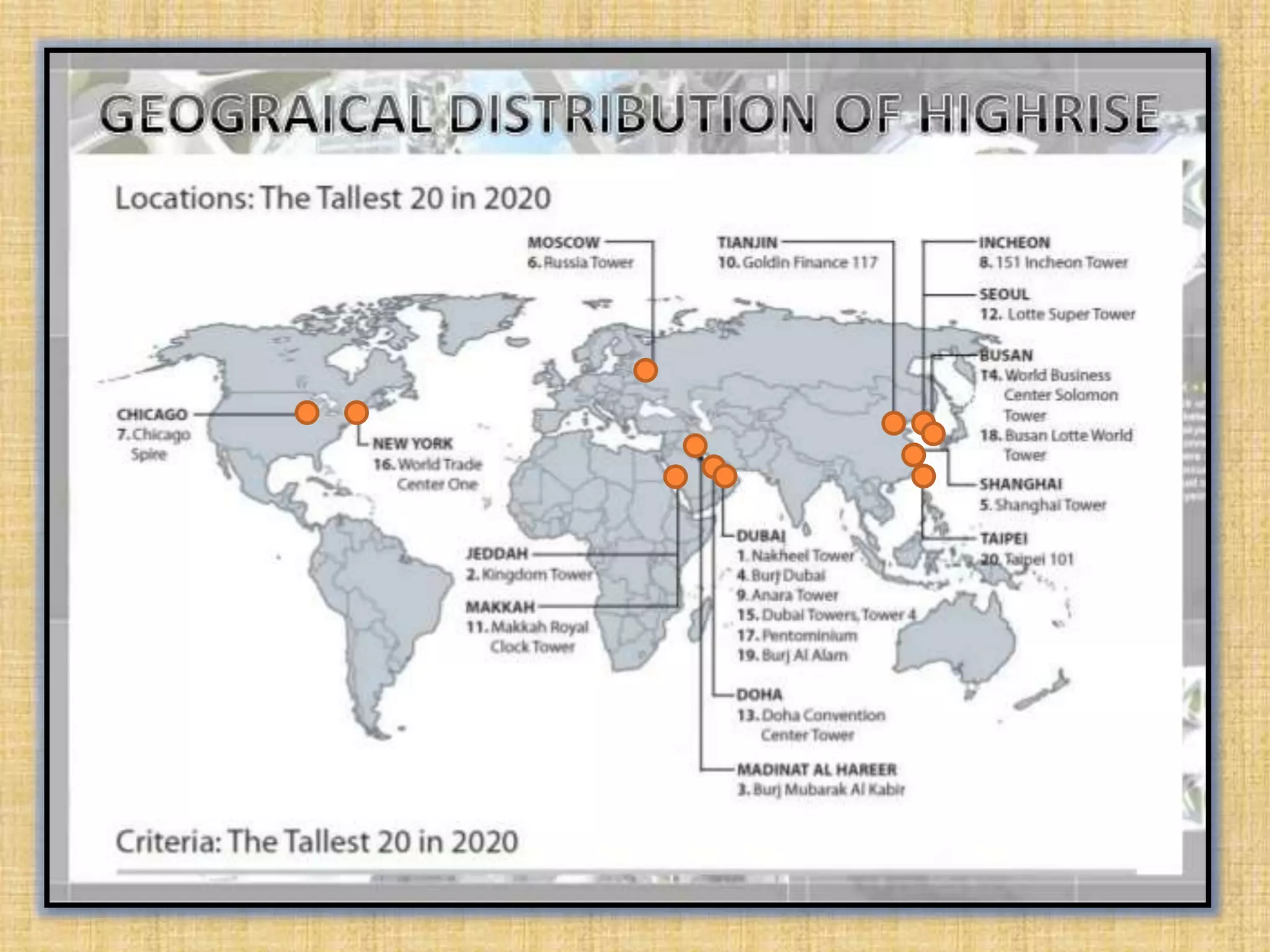
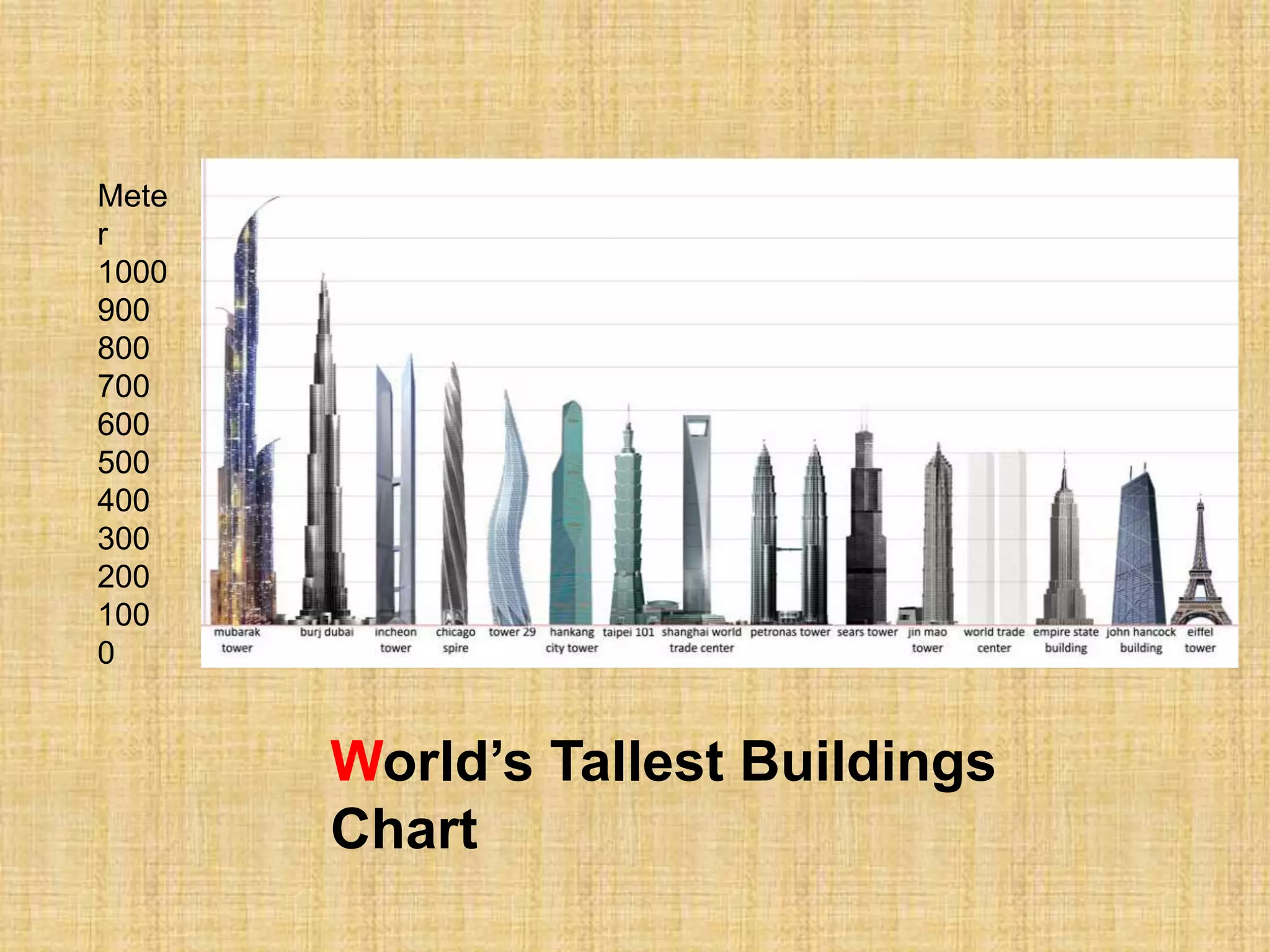
This document provides information about a study on the analysis and design of high-rise buildings. It defines what constitutes a high-rise building and explores the various factors driving demand for them. It examines the history of tall buildings and provides a chart showing increases in building heights over time. It also discusses structural systems and loads, including gravity, lateral and special loads. Core functions, parking considerations and case studies of high-rise projects are presented.







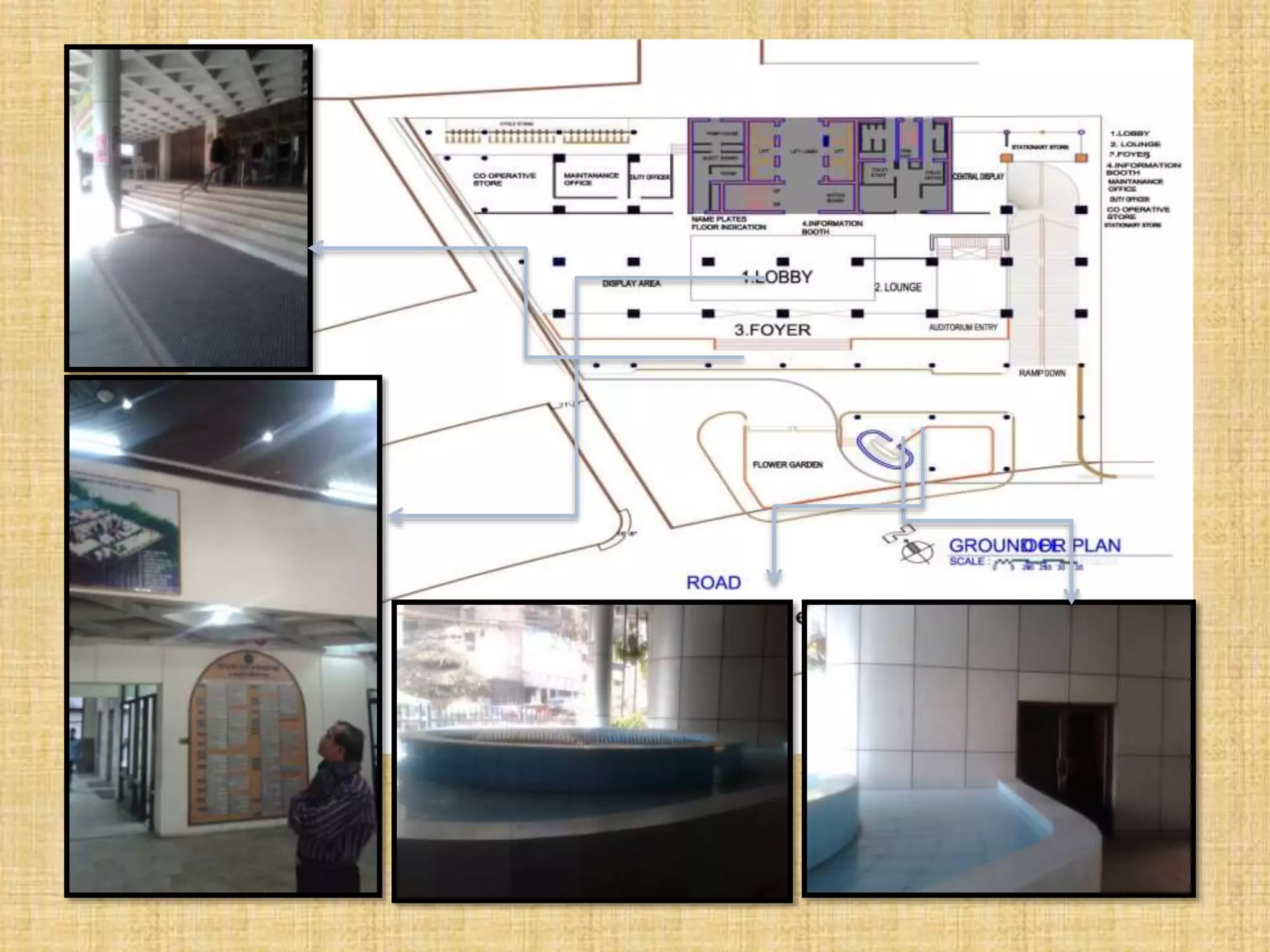
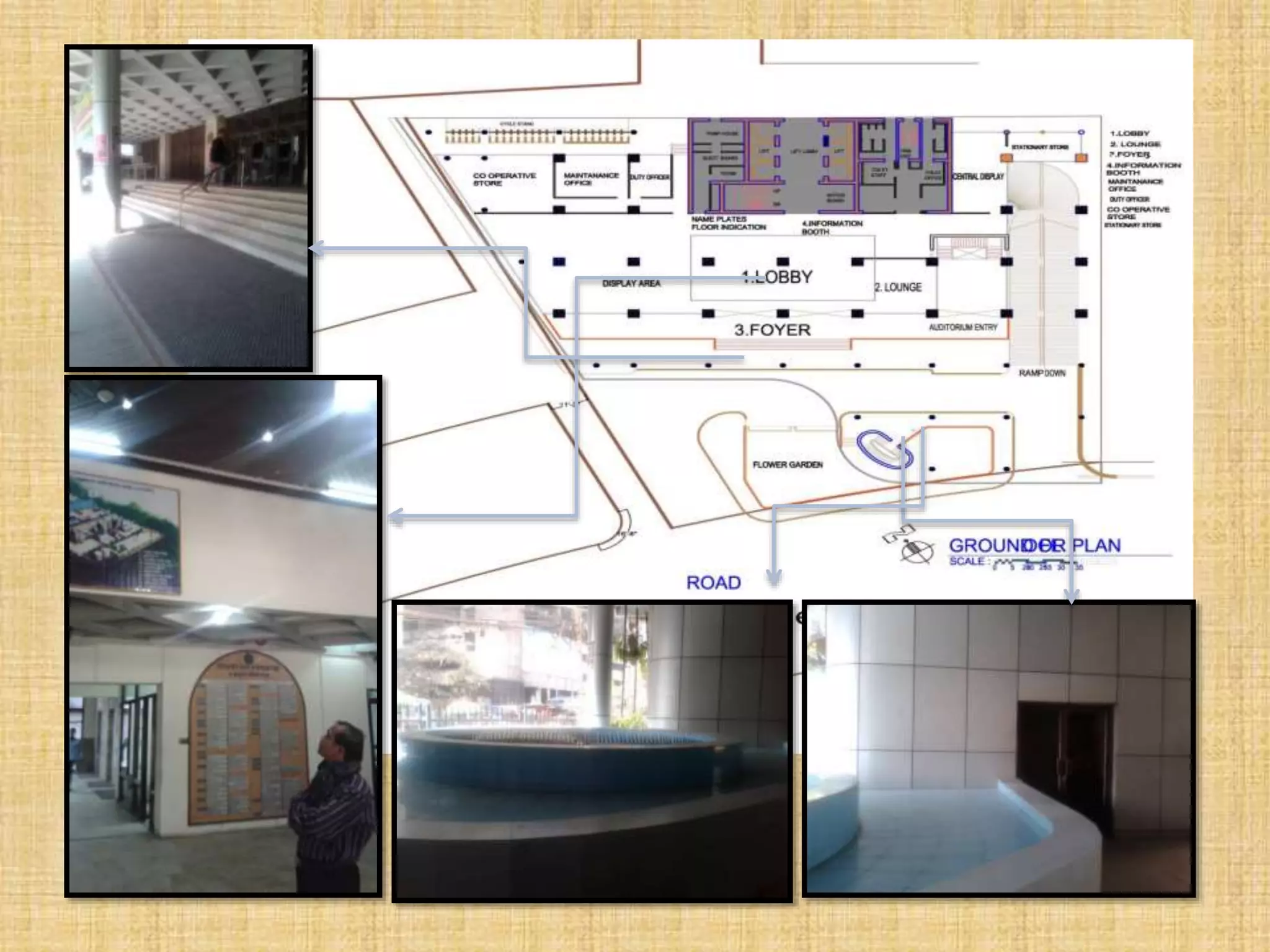
![1. Reception for 3 person 40 sft
2. Lobby for 50 person 300 sft
3. Waiting room for 30 person 200 sft
4. Auditorium for 200 person 4000 sft
Green room, Toilet, Stage, Stair
5. Prayer room for 50 person 300 sft
6. Café for 80 person 1700 sft
7. Storage room 500 sft
8. Substation room 1000 sft
9. Guard room 120 sft
10. Bank space 4500 sft
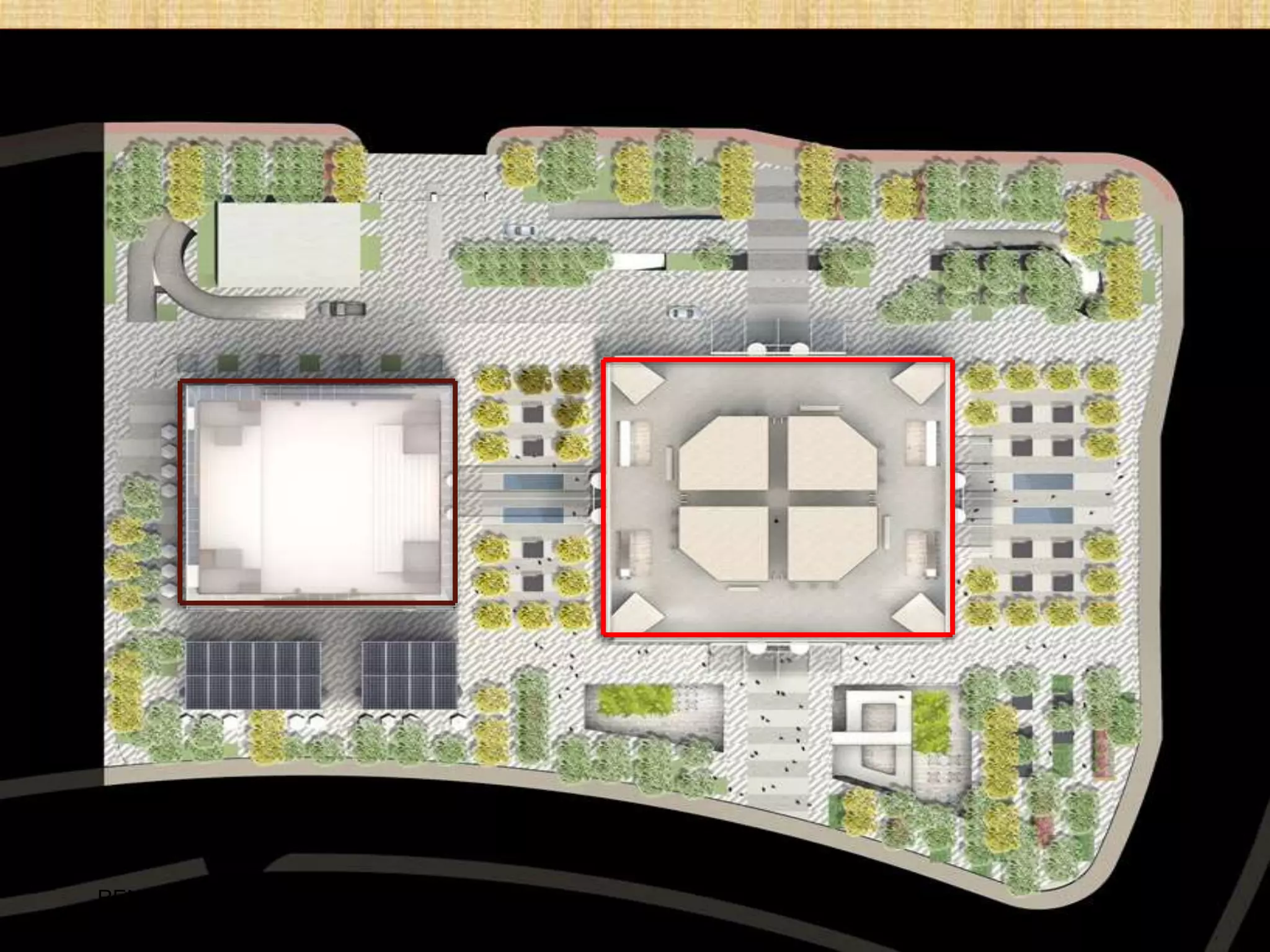
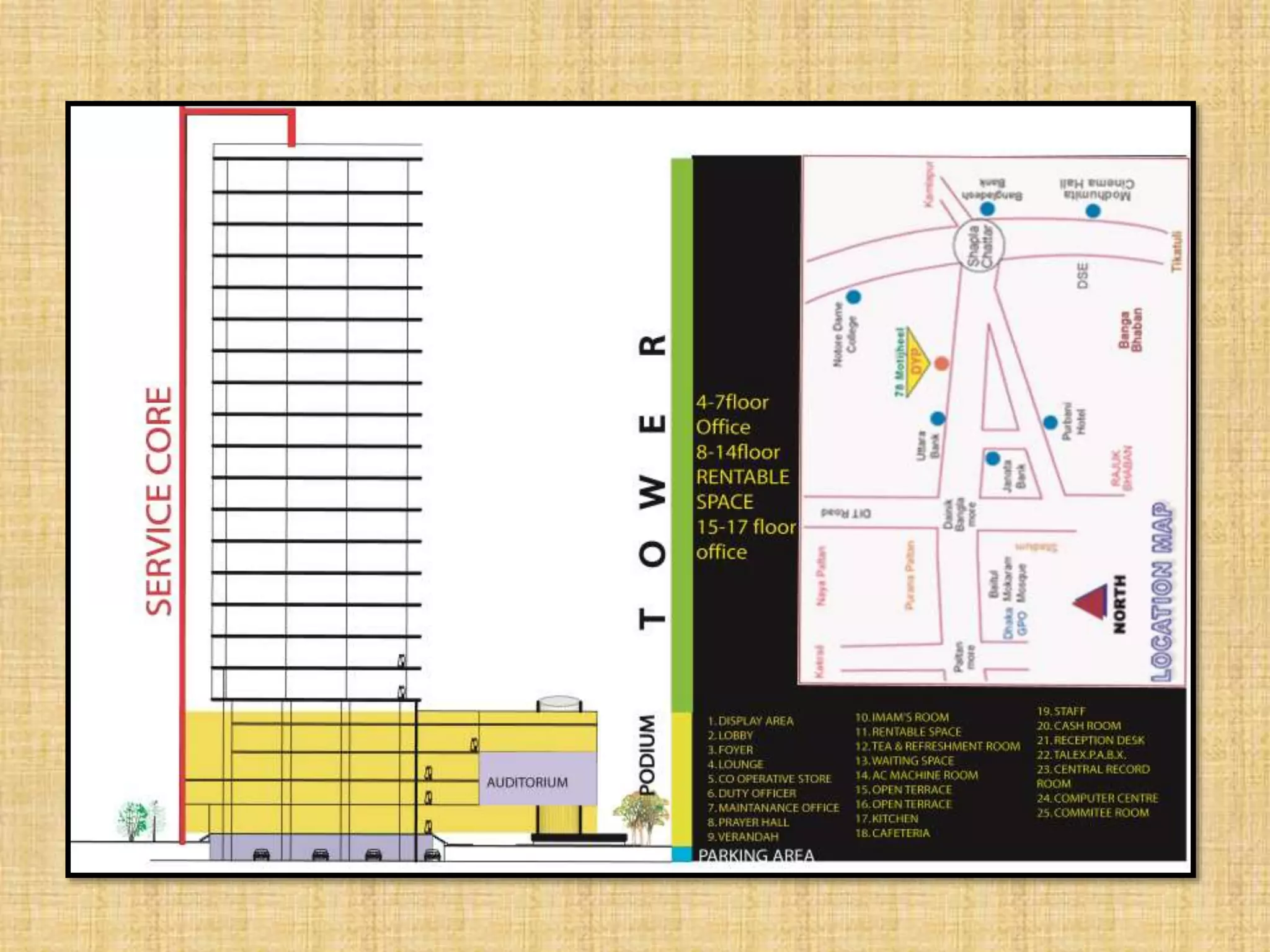
TOWER FUNCTION
1. official space, (5000-6000sft)
service core per floor
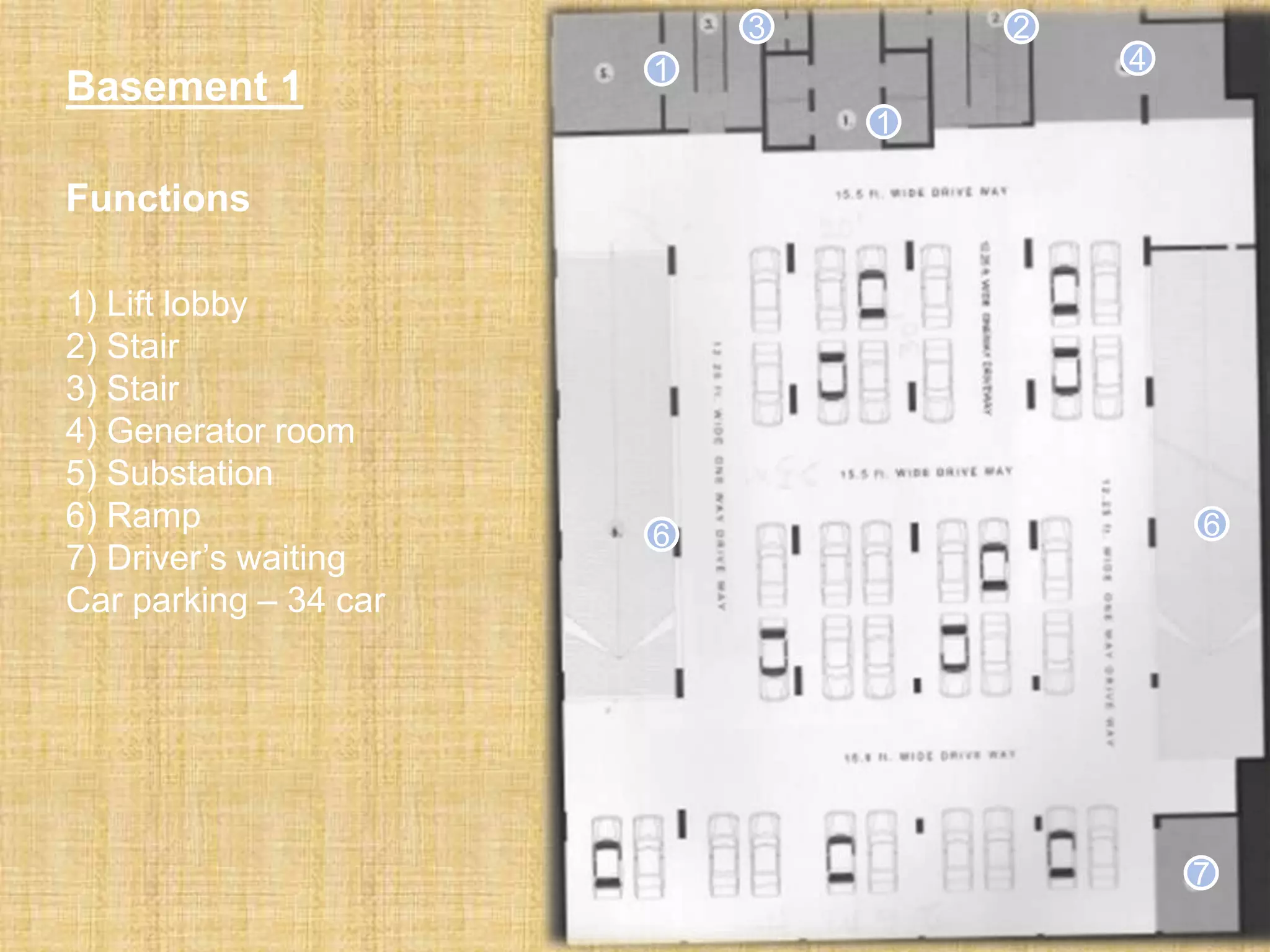
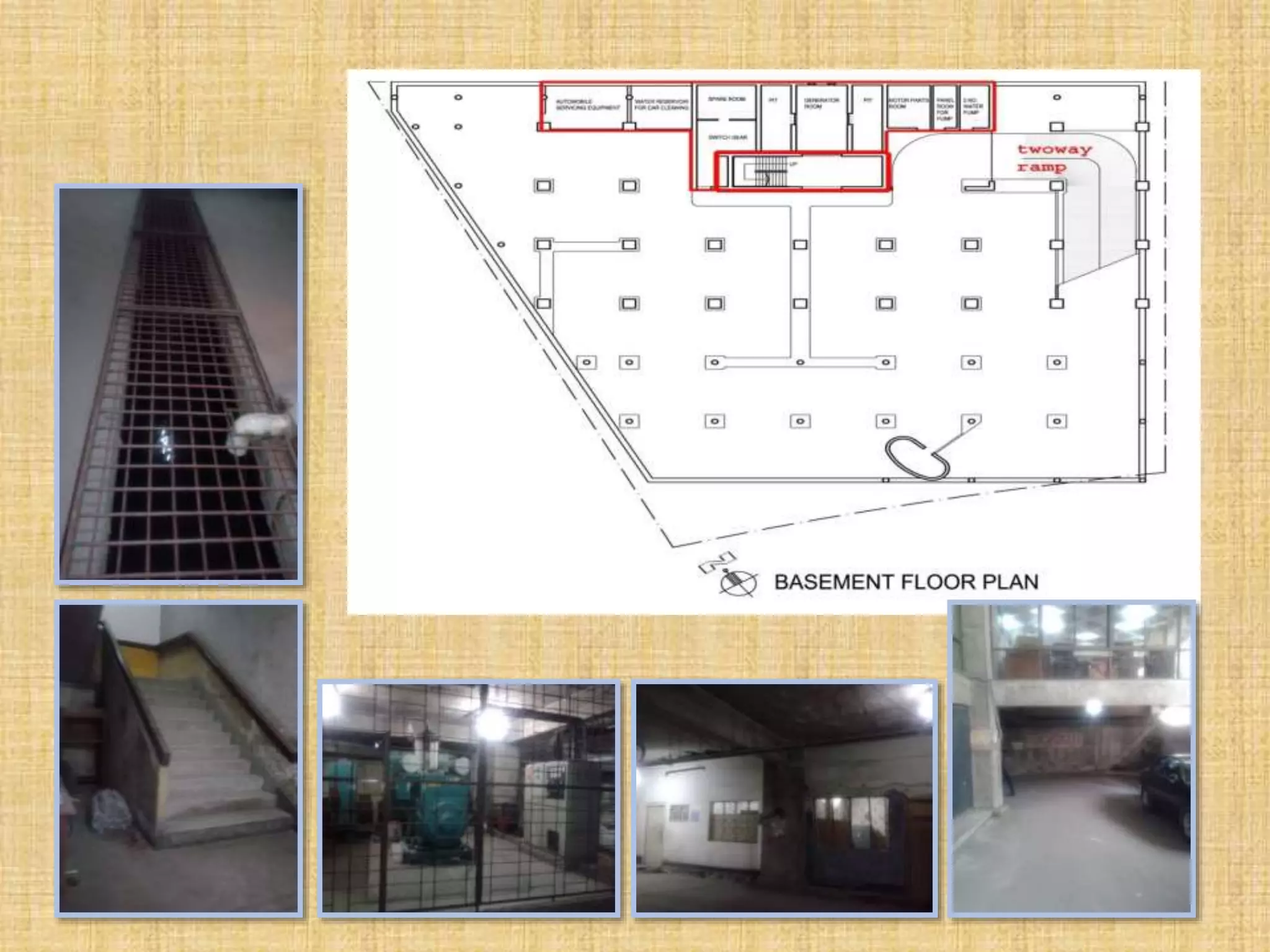
BASEMENT FUNCTION
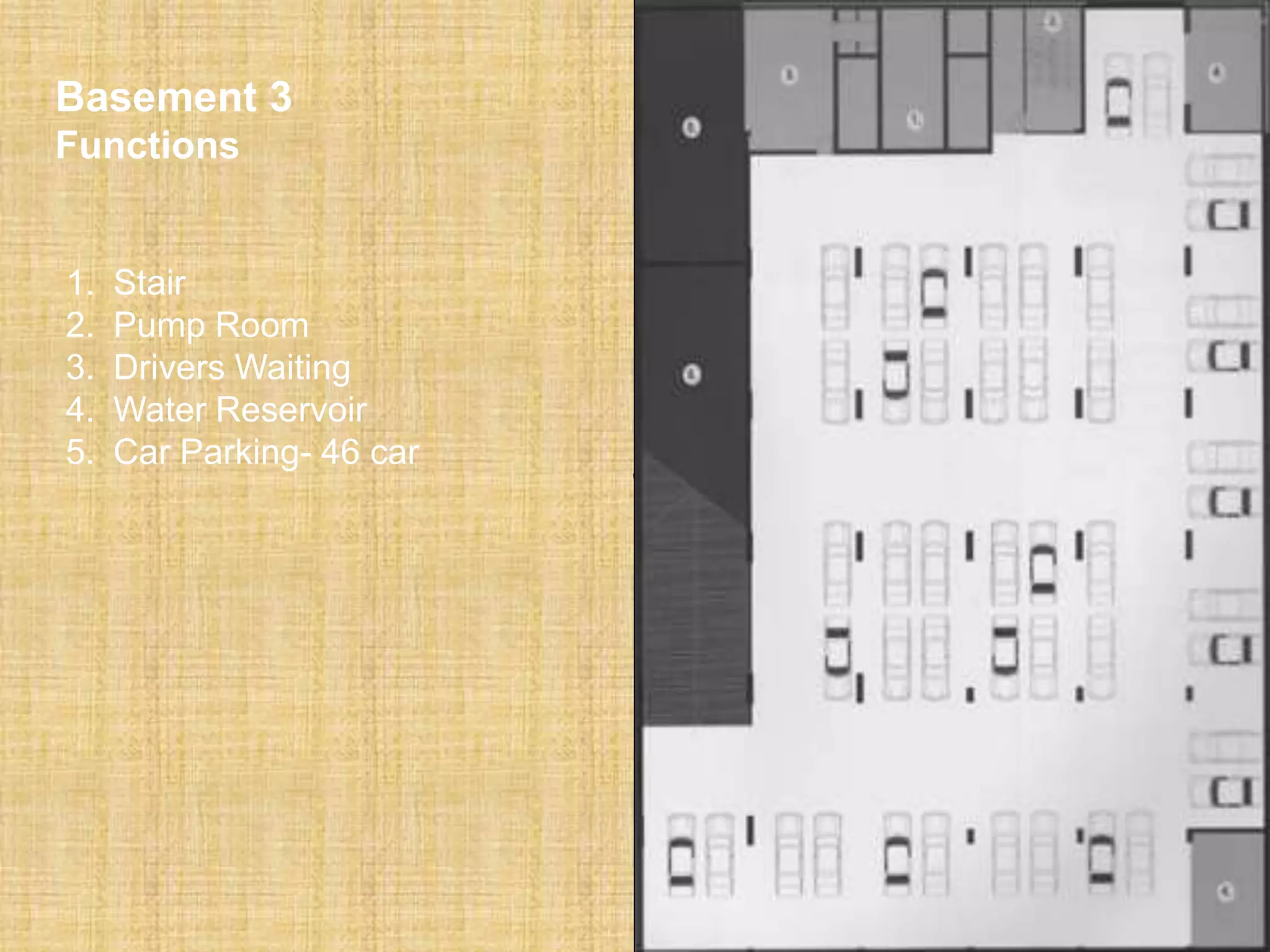
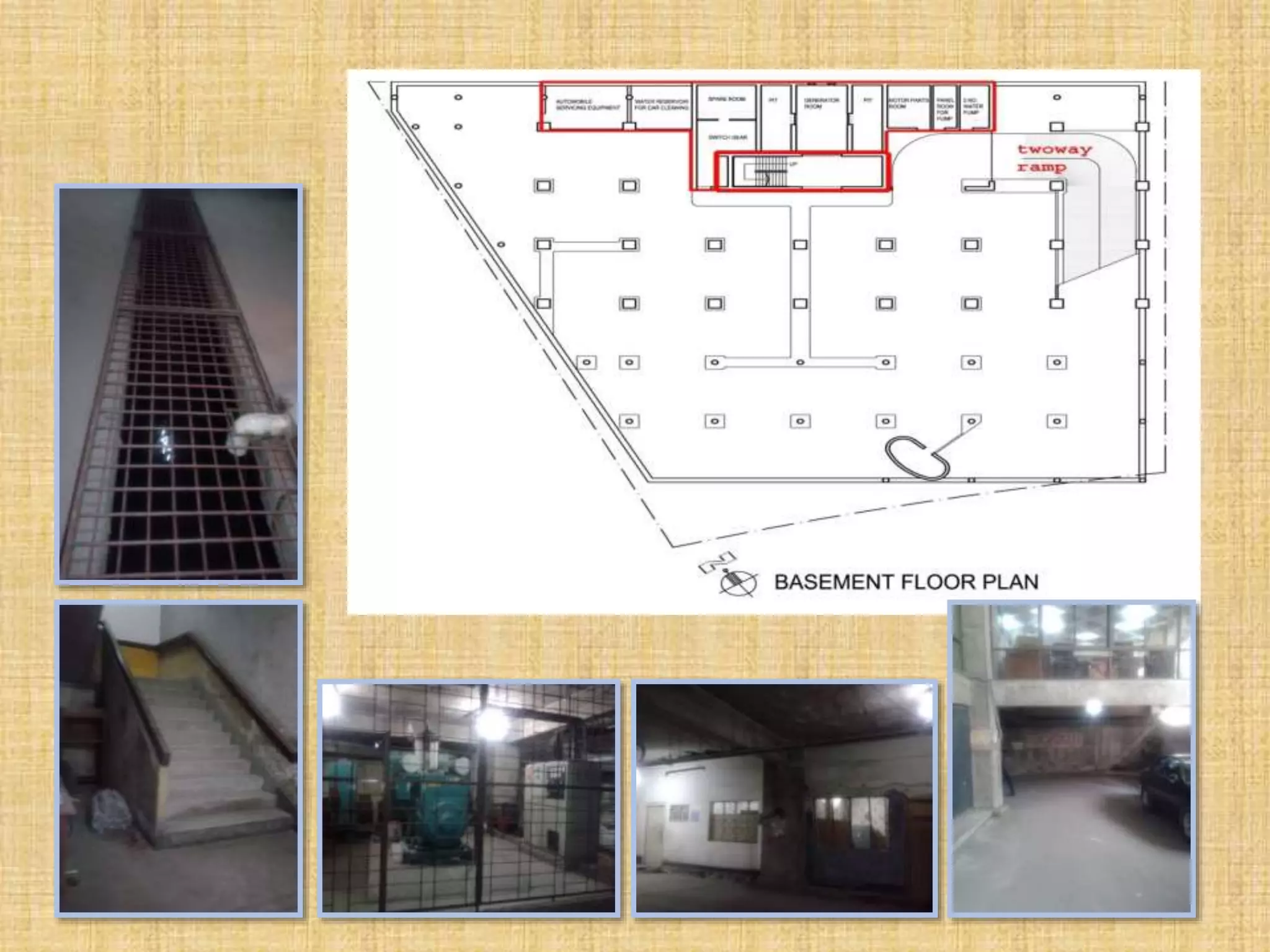
1. 3 floor
2. Parking car, Parking bike
3. Generator room 300 sft
4. Water machine room 400 sft
5. Chiller room 250 sft
6. Control room 80 sqft
7. Security room 120 sqft
8. Drivers waiting room 150 sft
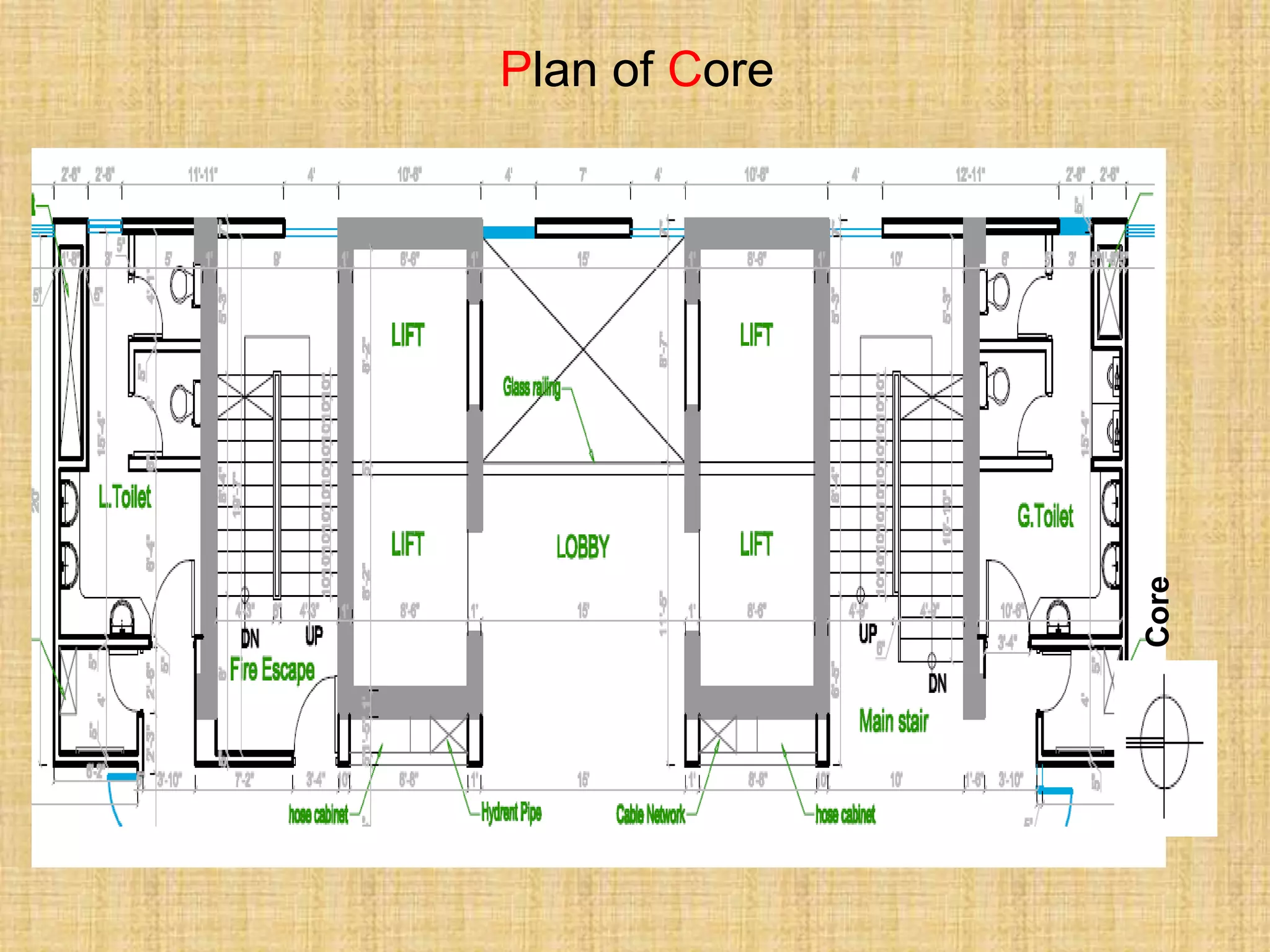
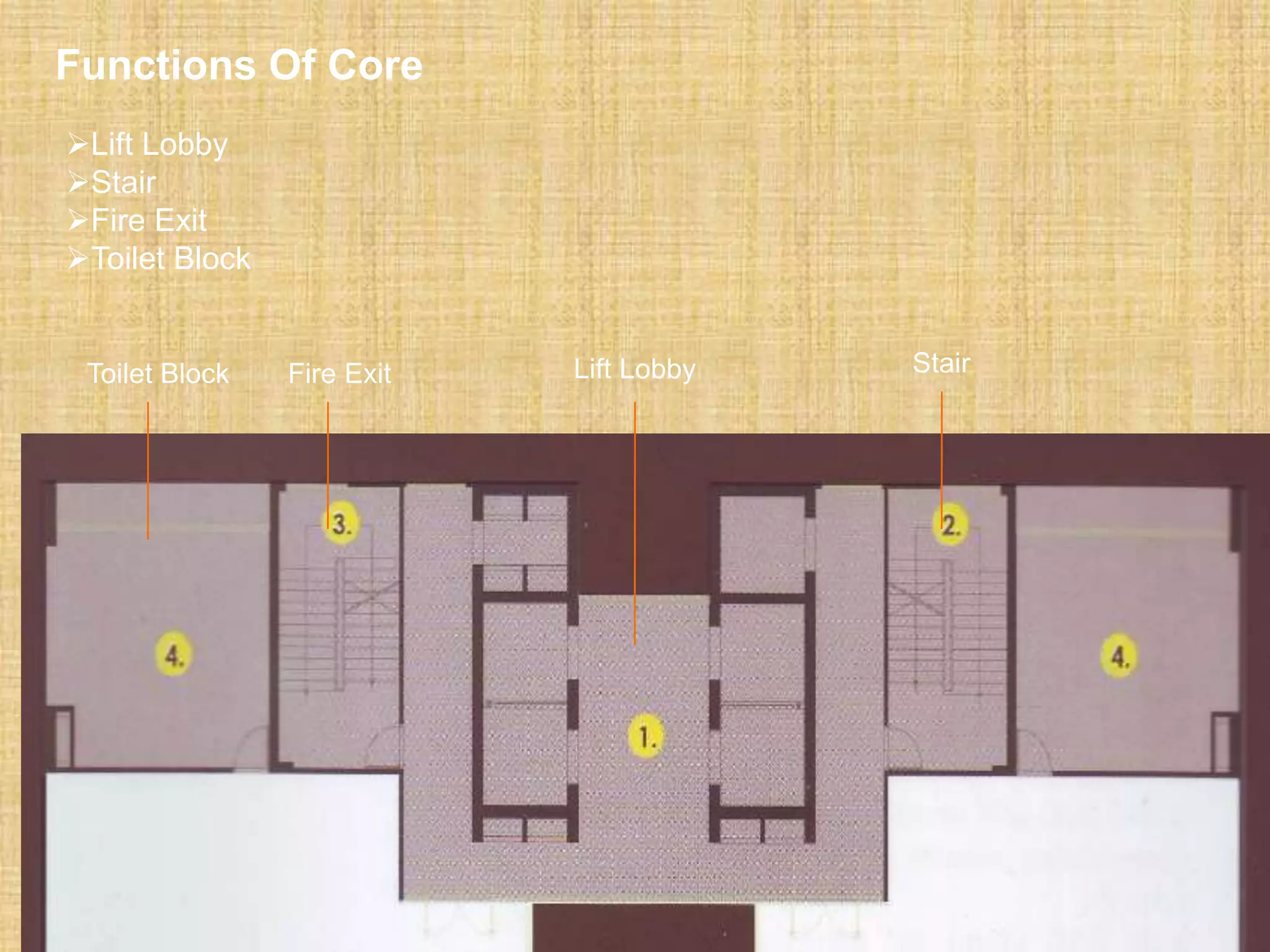
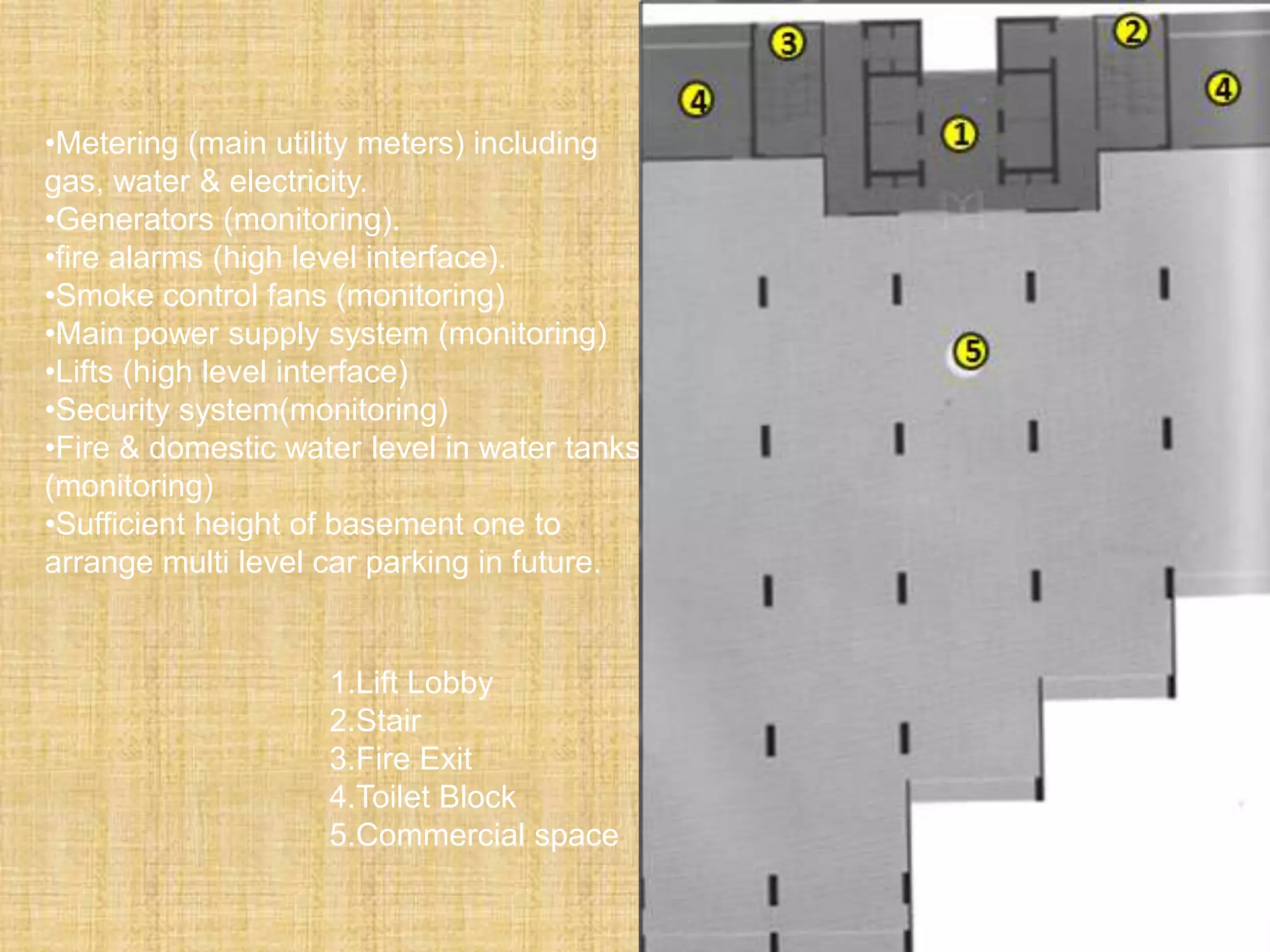
SERVICE CORE/ FLOOR
1. Lift
2. Stair
3. Fire exit
4. Toilet zone 500 sft
5. Kitchen room 80sft
6. Ac duct 100 sft
7. Electrical room 150 sft
PODIUM FUNCTION 1- 3 FLOOR
Top of the Tower
Machine room [chiller & aver ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150219080508-conversion-gate02/75/Final-presentation-by-Akramul-masum-from-southeast-university-bangladesh-37-2048.jpg)



















![Diagonal Tower
Structure in General
skyscraperBuilding type
Building status planned [approved]
Facade material glass
Usage
Main usage commercial office
Side usage shop(s)
Location
Address as text Yongsan International
Business District
City Seoul
Province Seoul Metropolitan City
Country South Korea
Technical Data
Height
(architectural)
343.00 m
Floors (above
ground)
64
Construction end 2016
Involved Companies
Architect:
Skidmore, Owings & Merrill LLP
Features & Amenities
Sky lobby is present
Identification
Name Diagonal Tower
Daniel libeskindArchitect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150219080508-conversion-gate02/75/Final-presentation-by-Akramul-masum-from-southeast-university-bangladesh-76-2048.jpg)