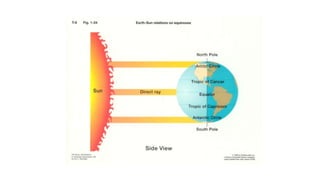
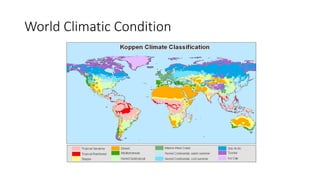
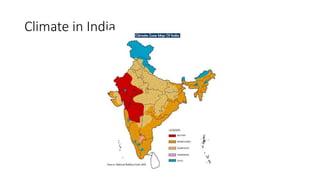
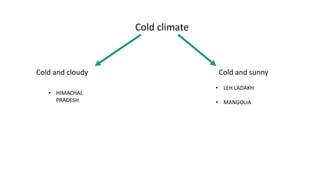
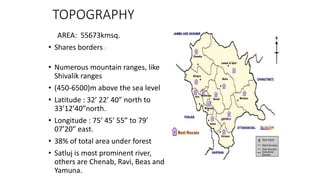
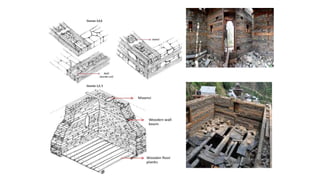
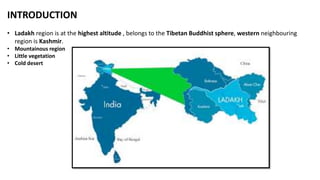
The document discusses climatic conditions and architectural features of cold regions. It describes the climates of Himachal Pradesh, Ladakh, and Mongolia. For Himachal Pradesh, it notes temperature variations by altitude and common building materials like timber. In Ladakh, the dry, sunny climate and hilly terrain influence the compact, solar-oriented settlement patterns. Traditional houses have thick mud walls, flat roofs, and courtyards. Mongolian architecture features portable yurts made of a wooden frame and felt covering. All three regions employ natural, insulating materials and passive solar design strategies to cope with cold weather.