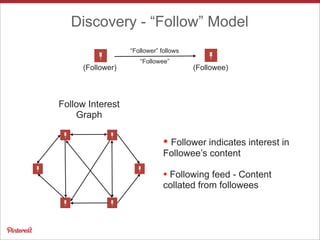
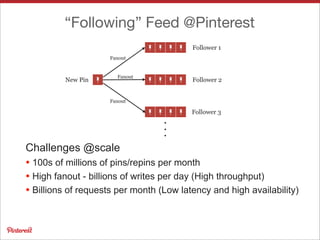
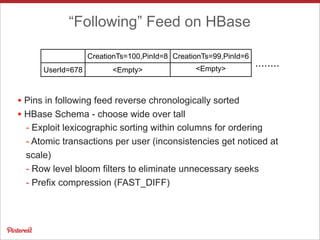
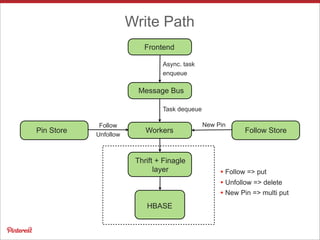
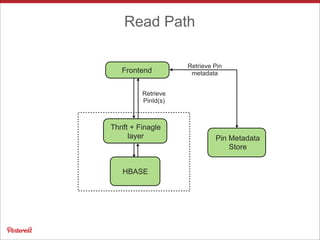
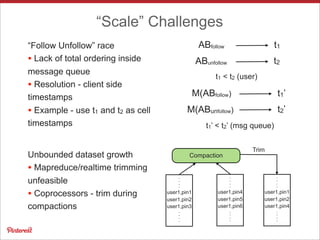
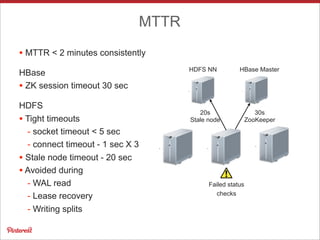
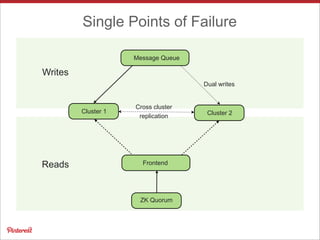
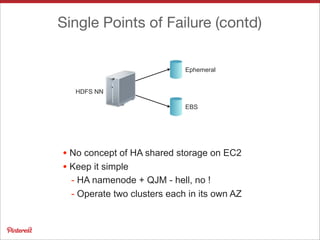
Pinterest uses Apache HBase to store data for users' personalized "following feeds" at scale. This involves storing billions of pins and updates per day. Some key challenges addressed are handling high throughput writes from fanouts, providing low latency reads, and resolving potential data inconsistencies from race conditions. Optimizations to HBase include increased memstore size, block cache tuning, and prefix compression. Maintaining high availability involves writing to dual clusters, tight Zookeeper timeouts, and automated repairs.