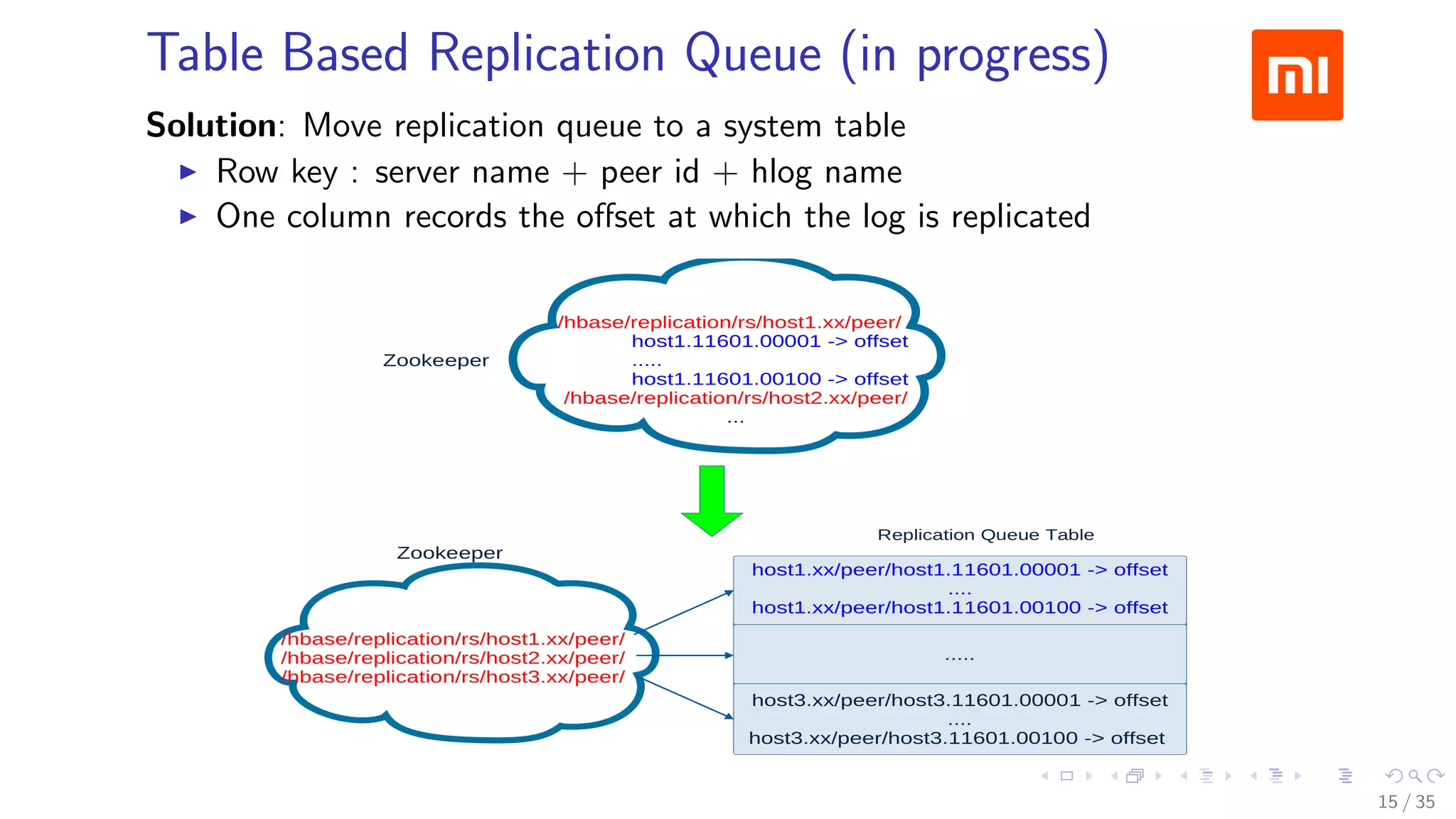
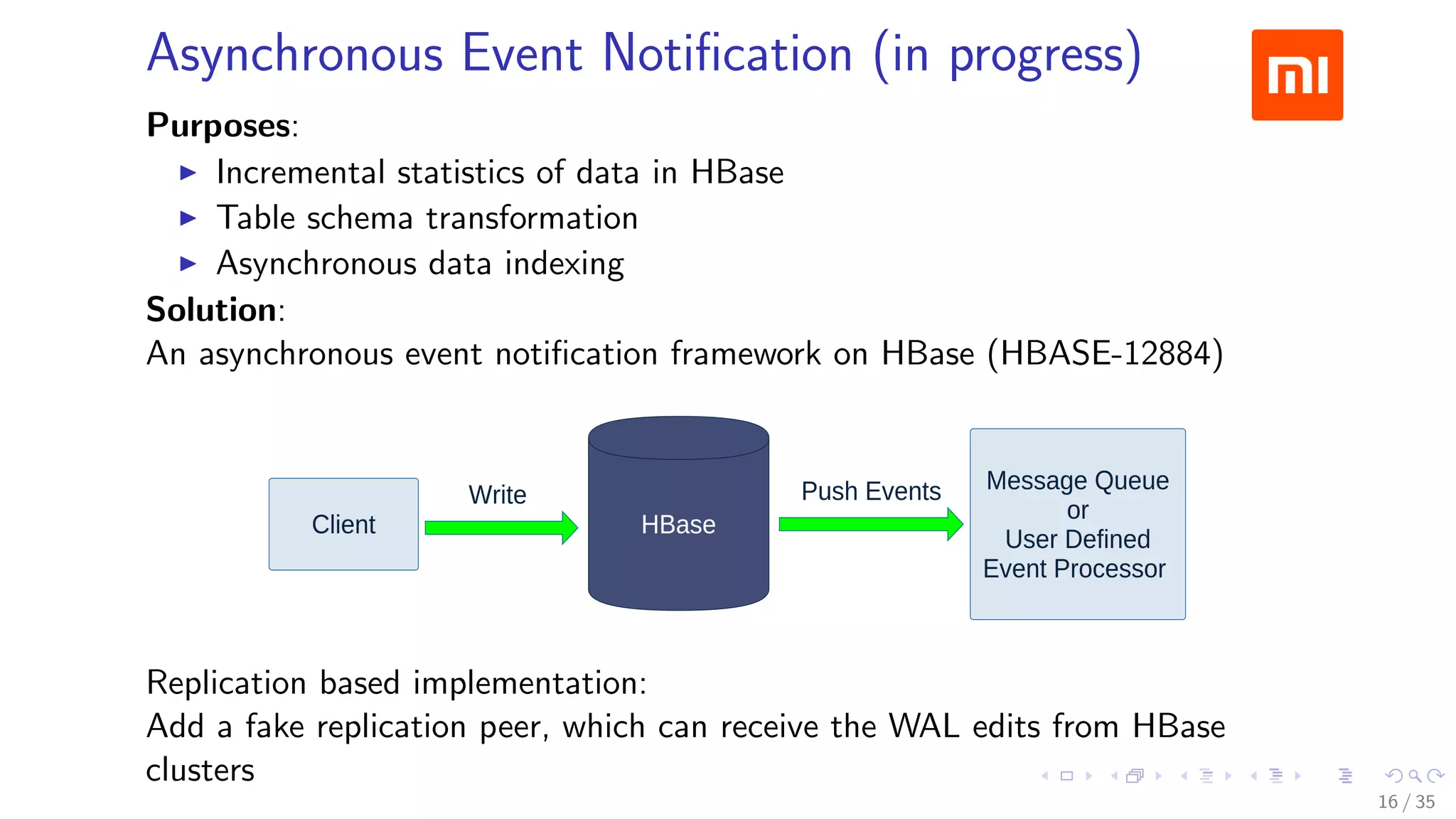
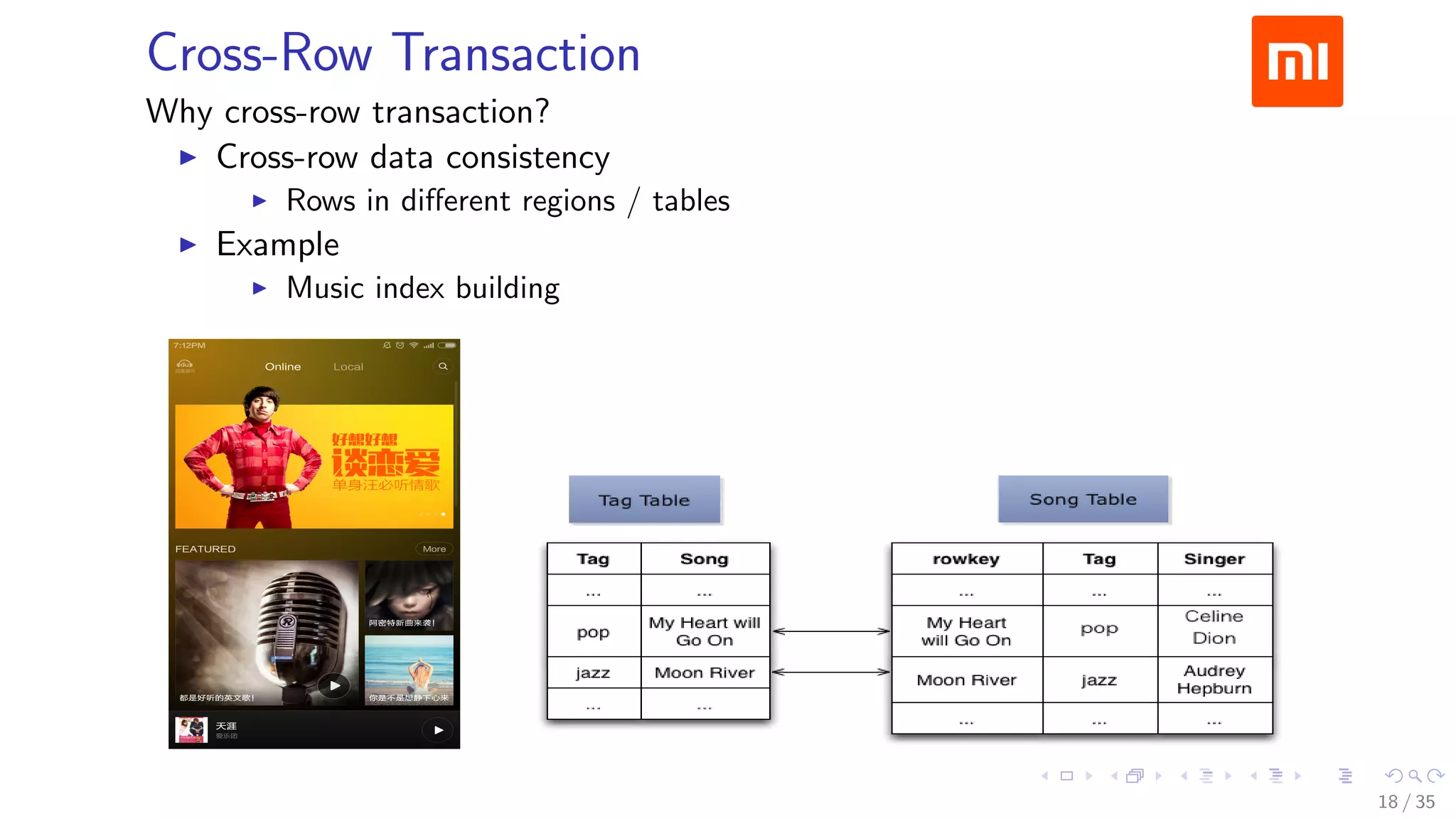
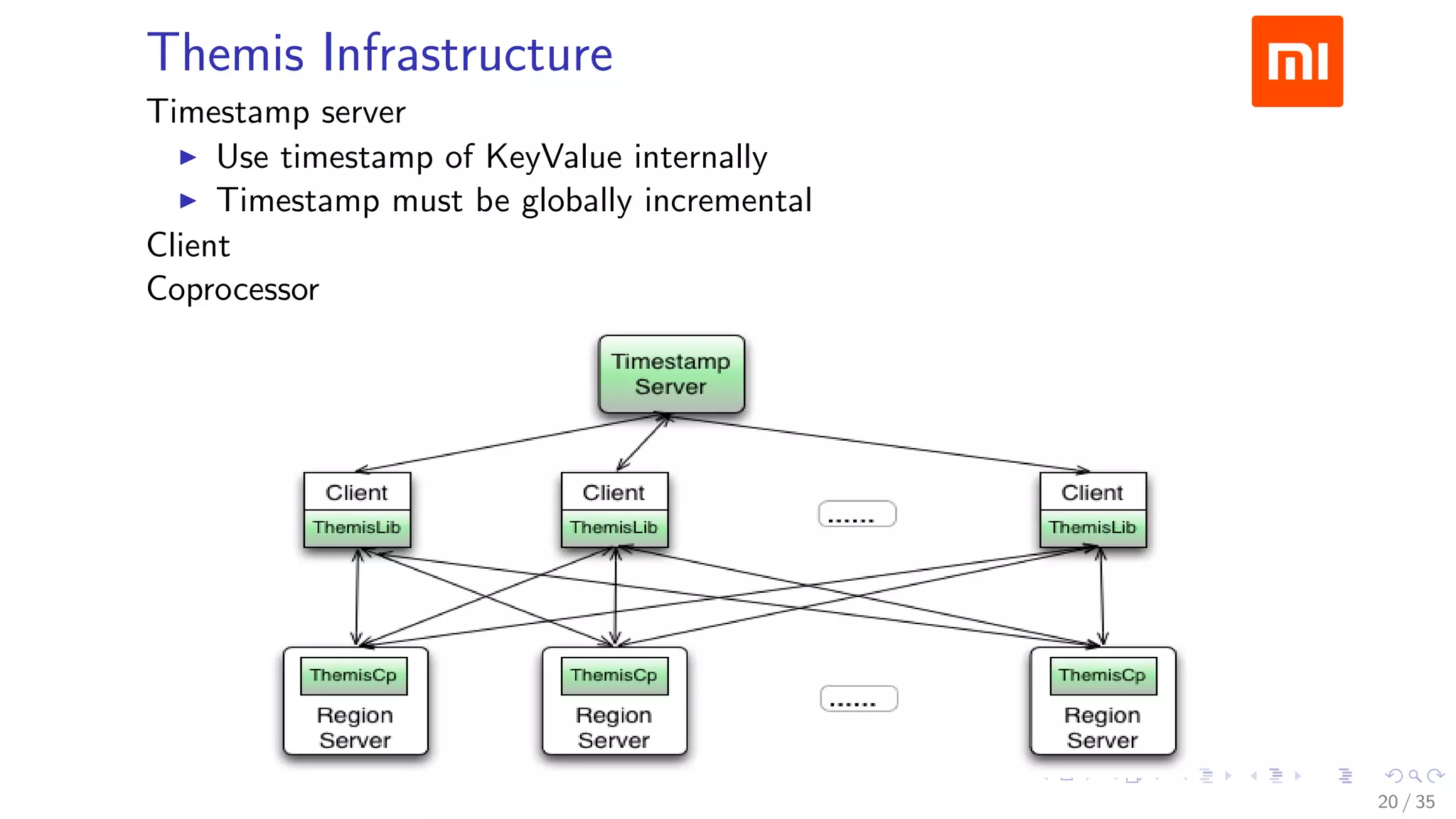
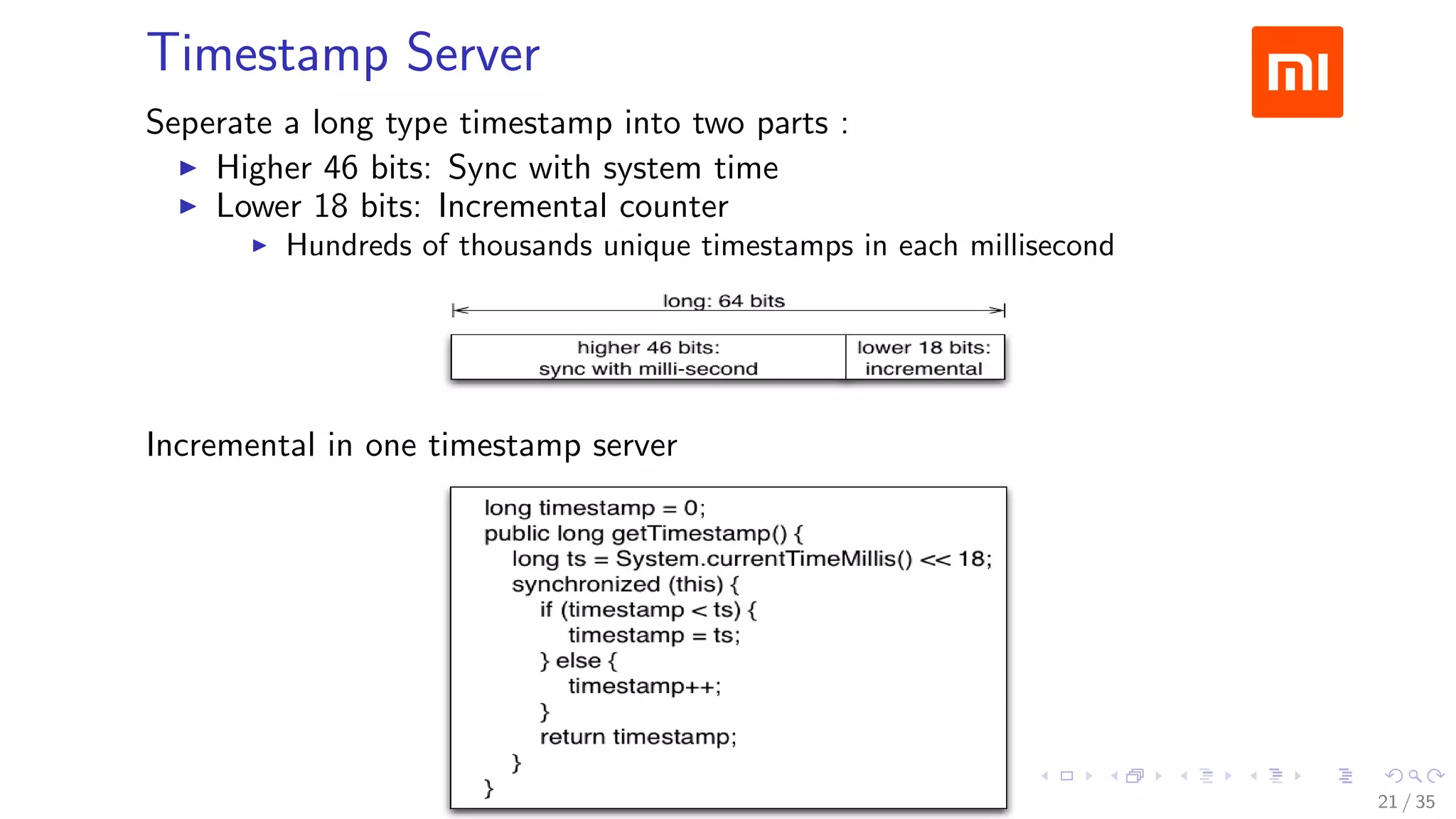
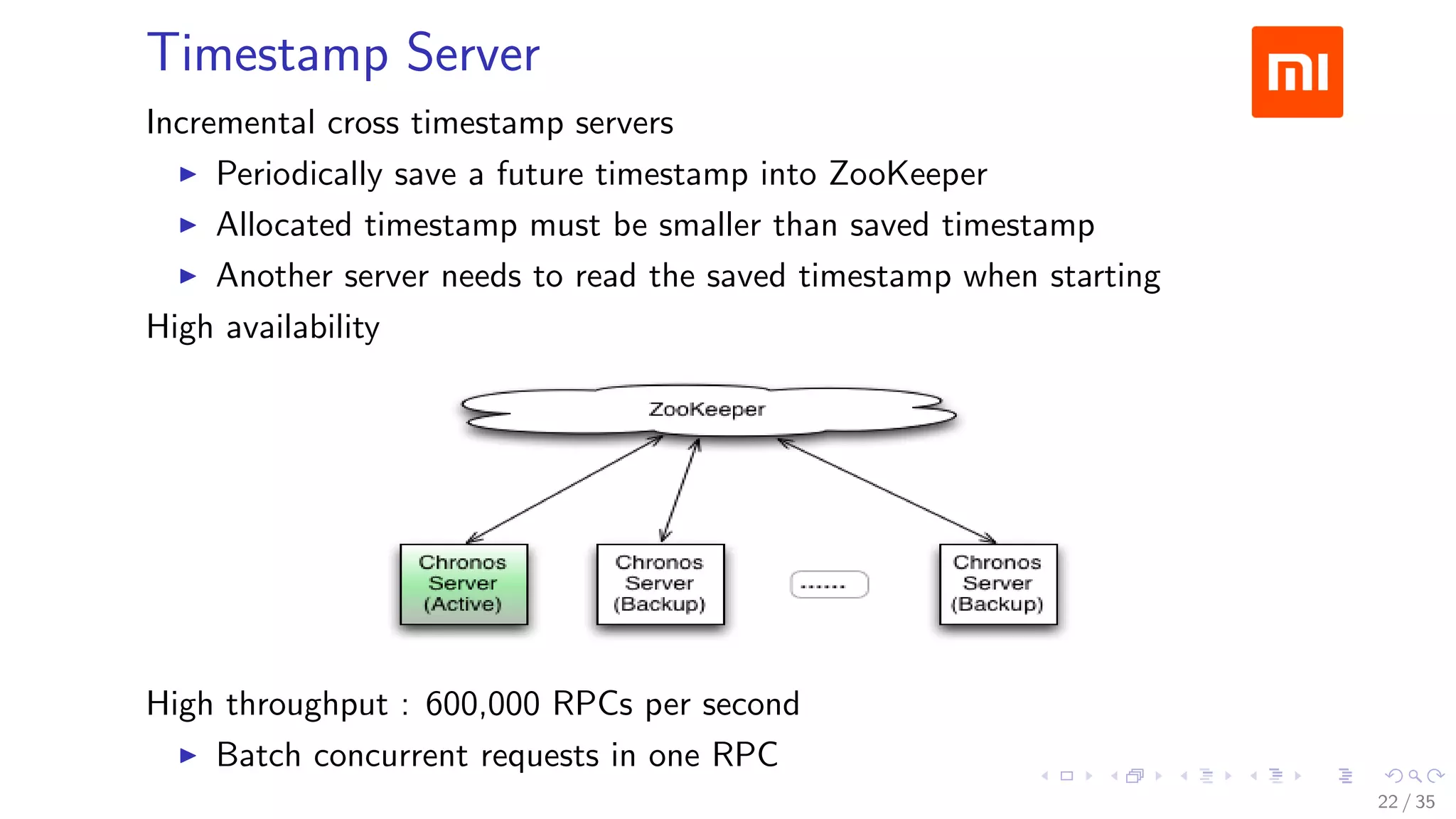
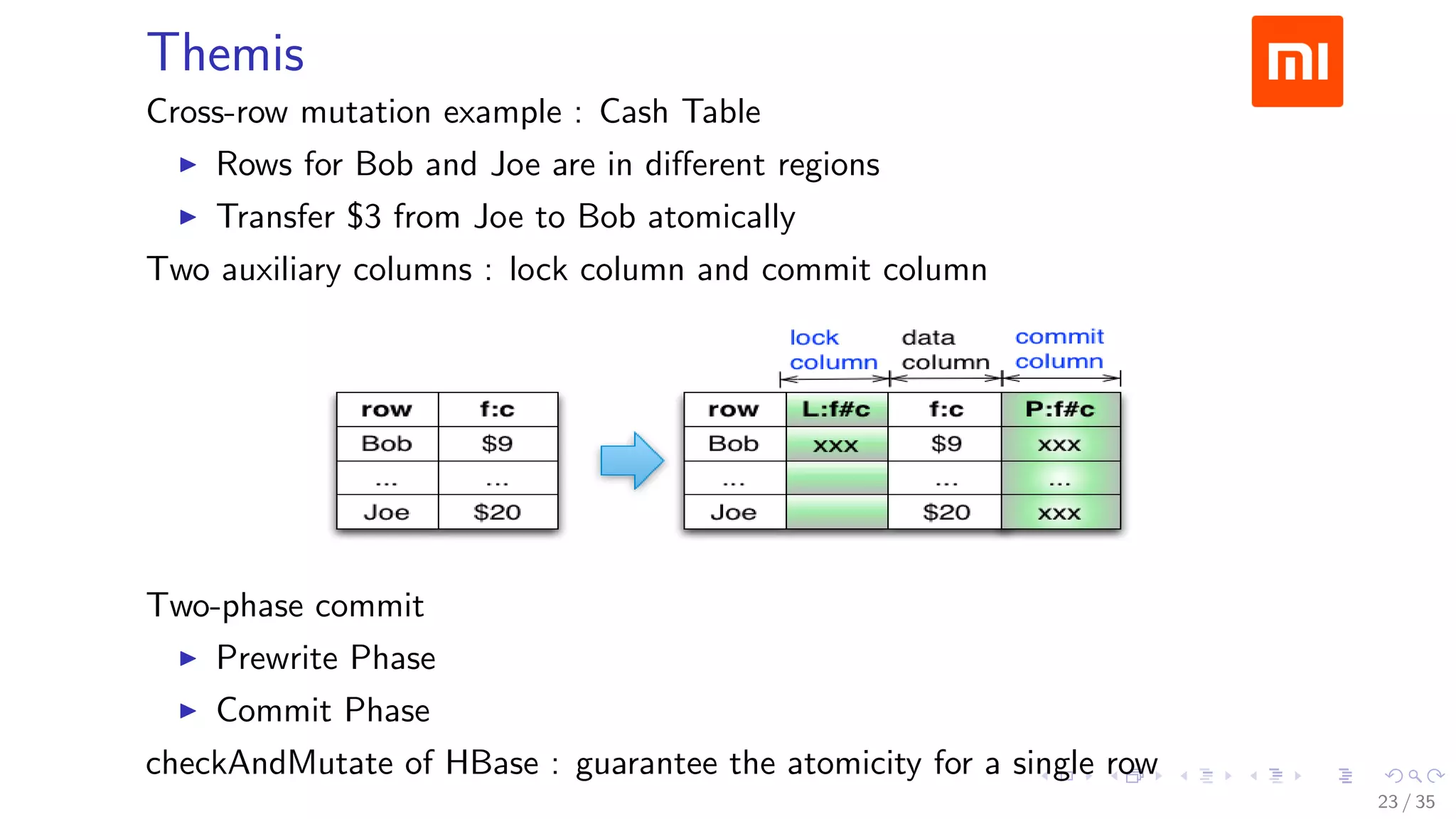
The document discusses Xiaomi's HBase implementation and highlights that in 2014, Xiaomi sold 60 million phones, with significant advancements in cloud services and offline processing. It also addresses challenges faced by HBase, such as long garbage collection pauses and hotspot issues, and introduces solutions like multi-region server instances and an asynchronous event notification framework. Additionally, it outlines the Themis framework developed for cross-row transactions on HBase, aiding in data consistency and optimization.













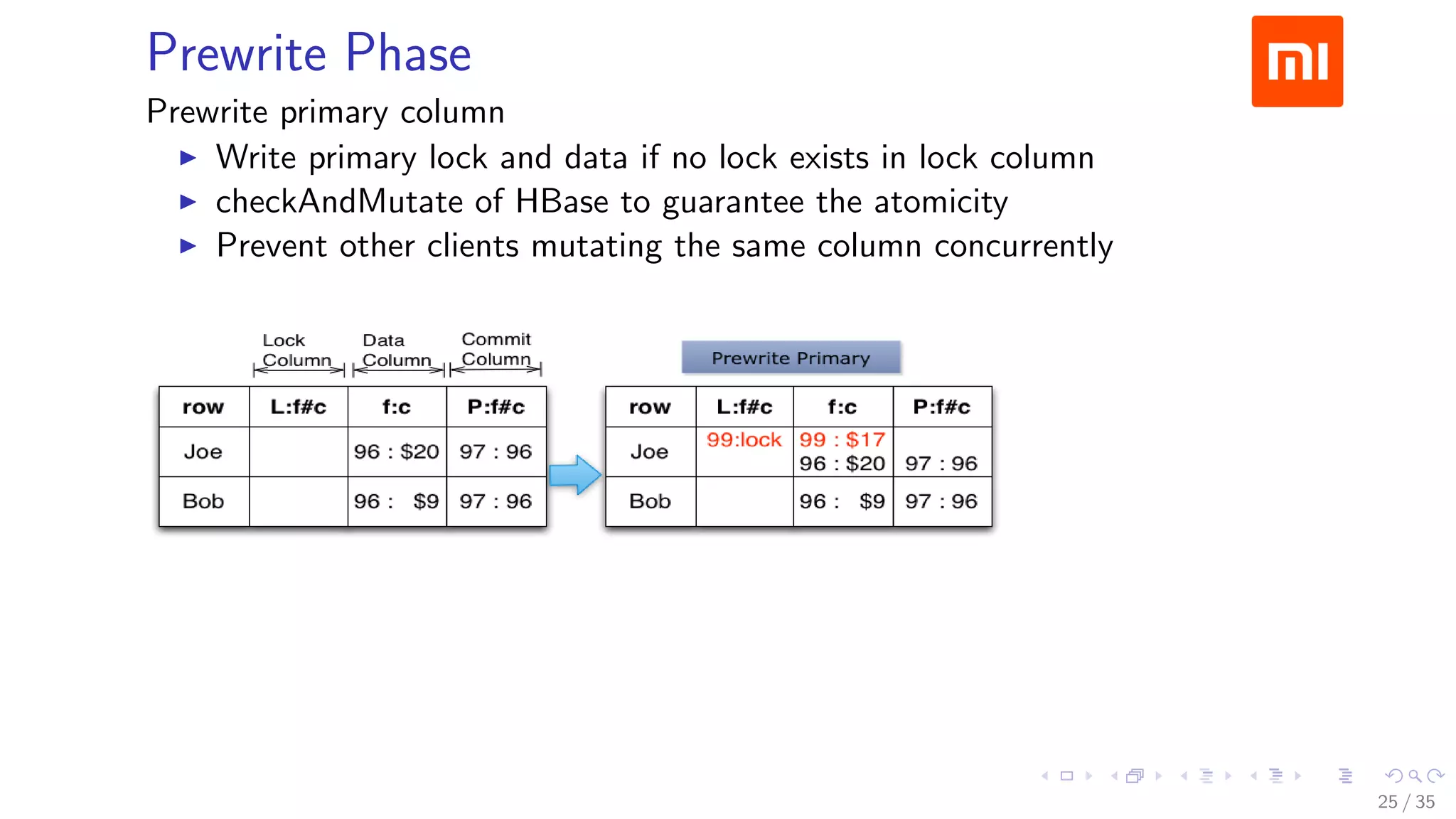
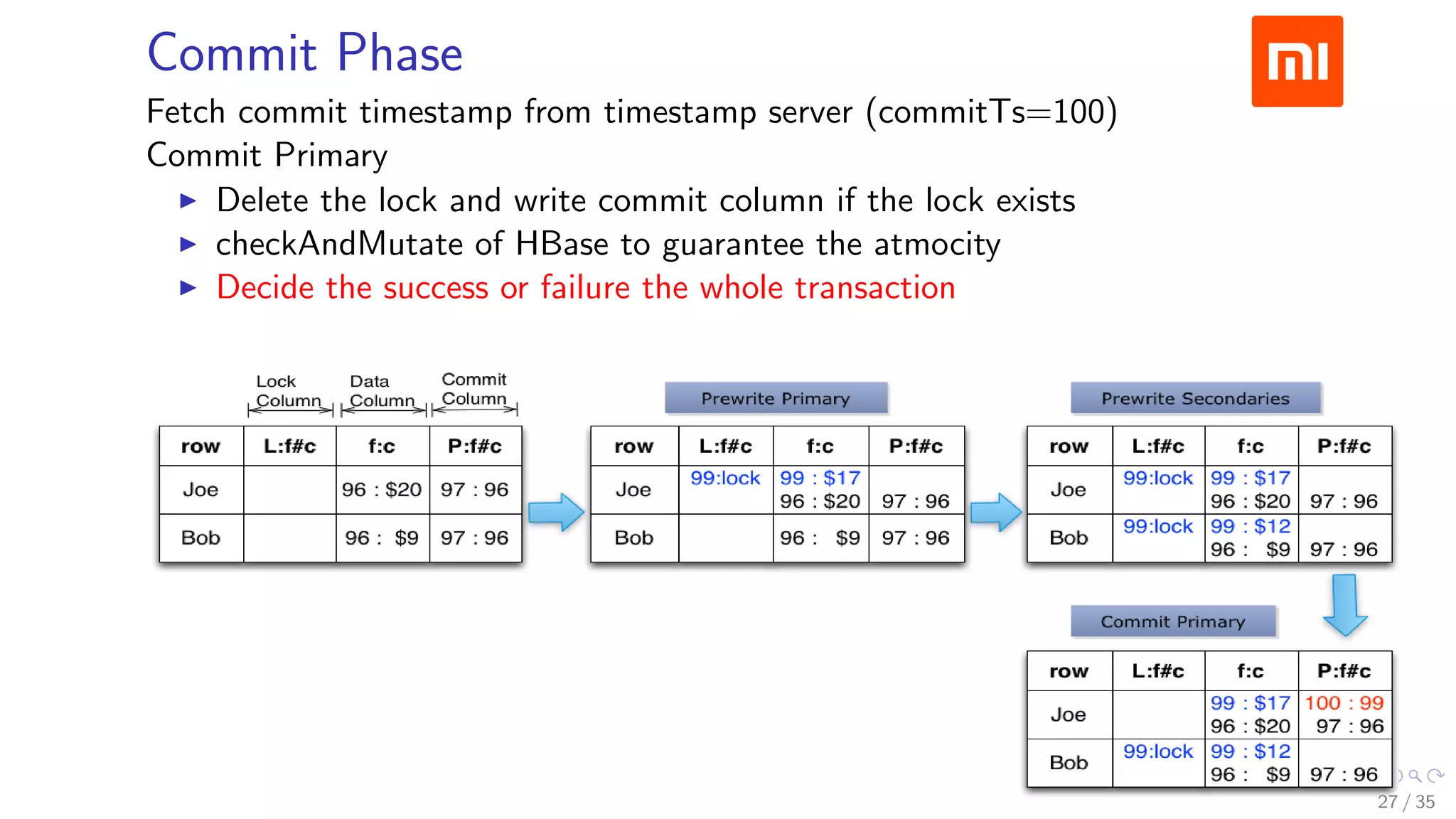
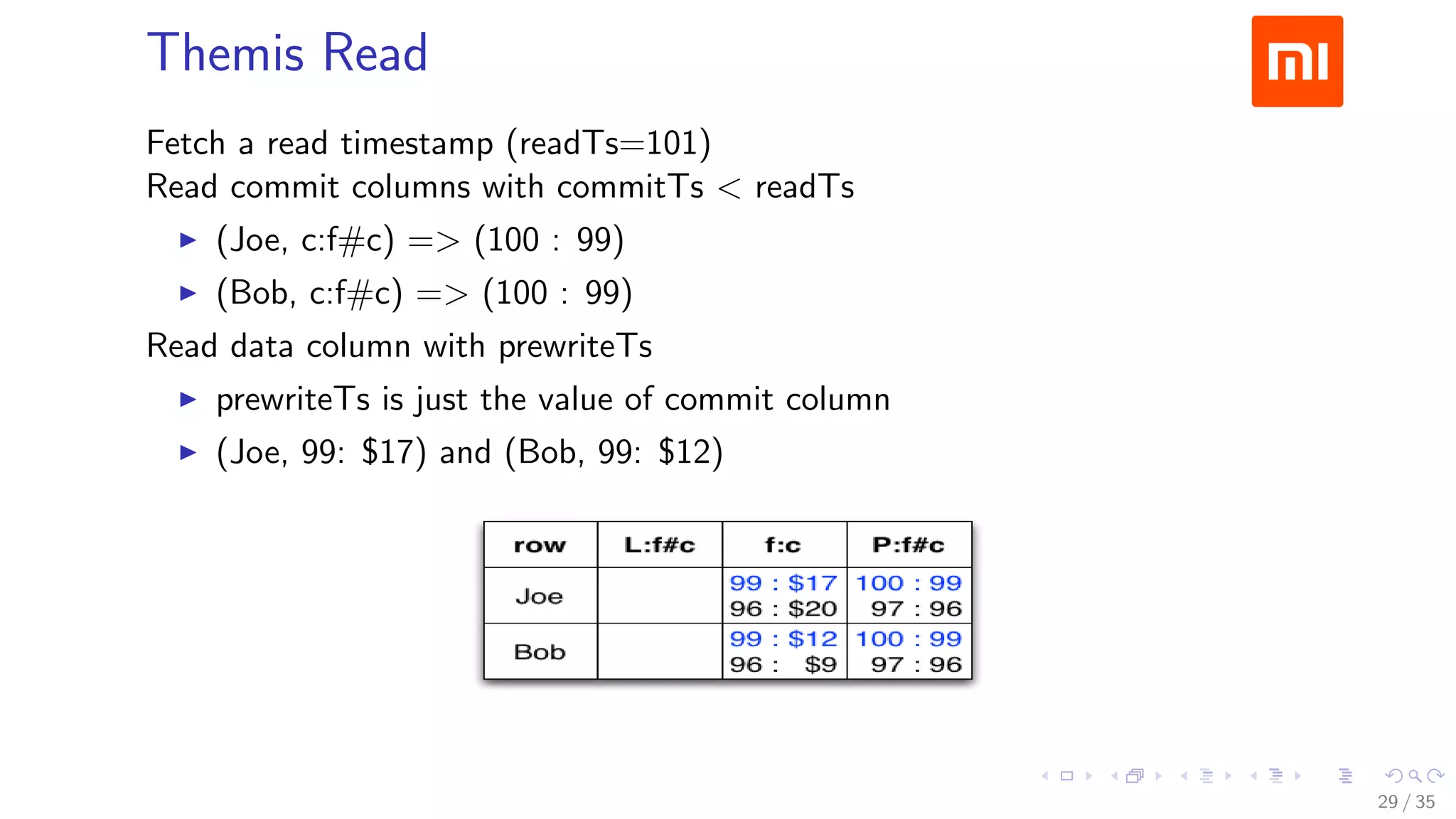
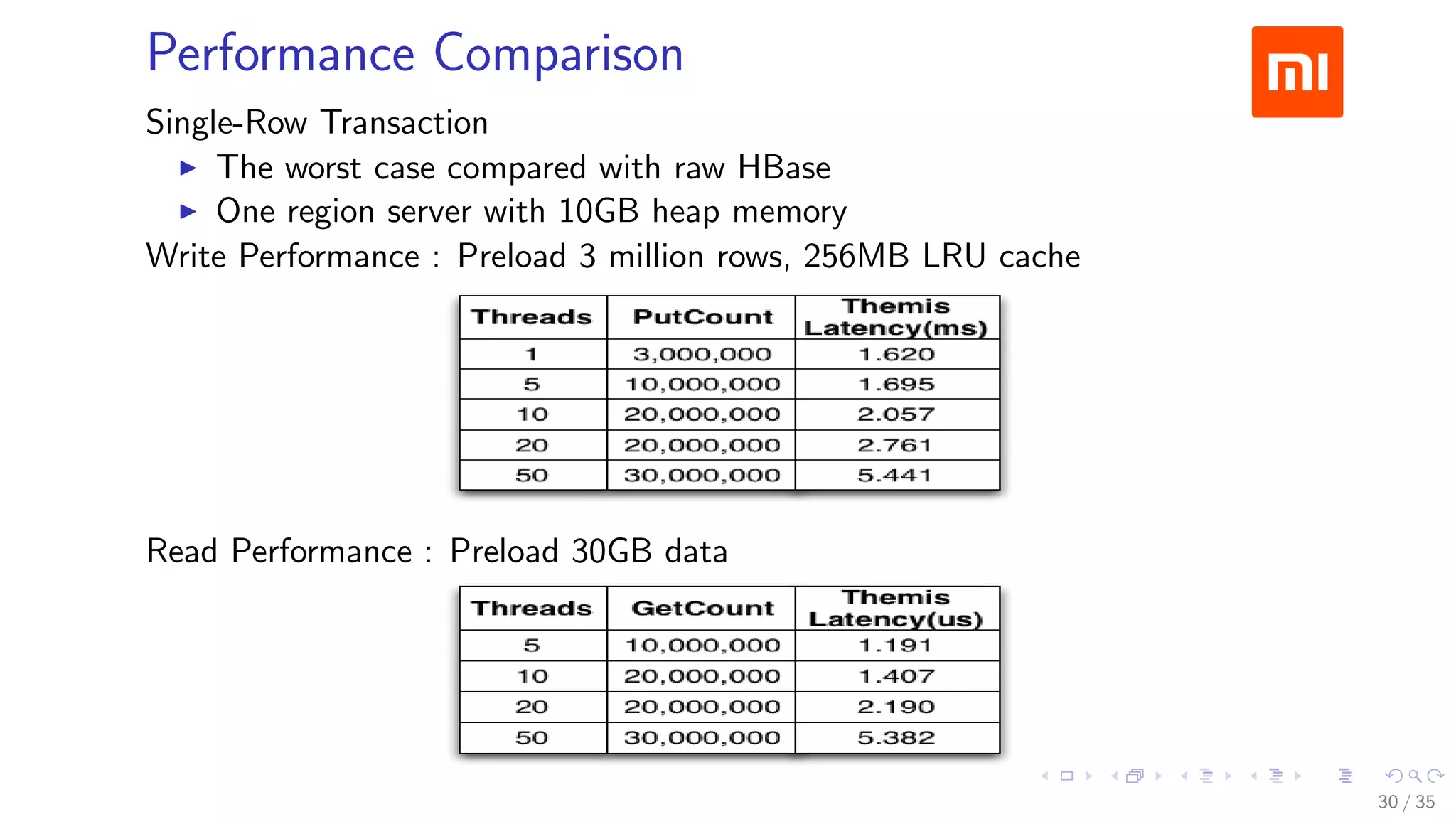
![Prewrite Phase
Fetch a prewrite timestamp from timestamp server (prewriteTs=99)
Select primary and secondary columns
Primary
Column : (Joe, f:c)
PrimaryLock: {secondaries : [(Bob, f:c)]}
Secondaries
Column : (Bob, f:c)
SecondaryLock: {primary : (Joe, f:c)}
24 / 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operations-session6-150605170216-lva1-app6891/75/HBaseCon-2015-HBase-Operations-at-Xiaomi-24-2048.jpg)