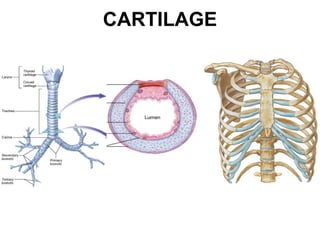
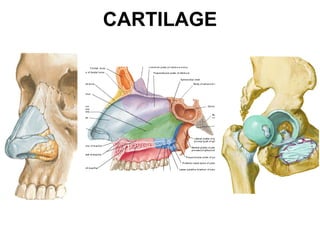
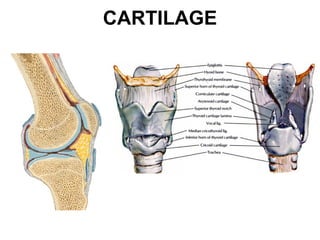
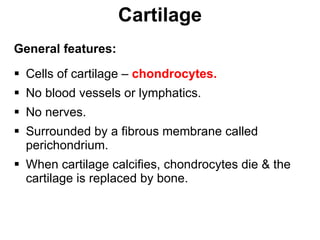
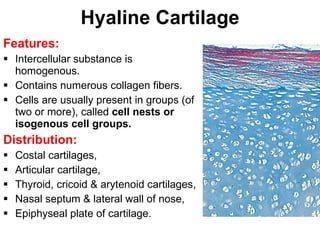
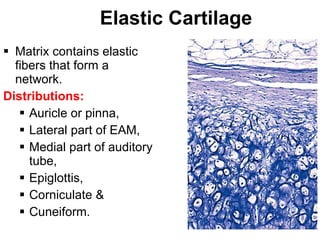
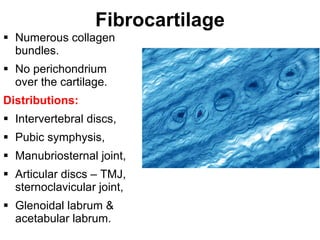
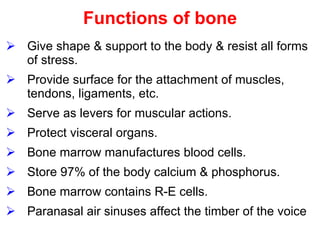
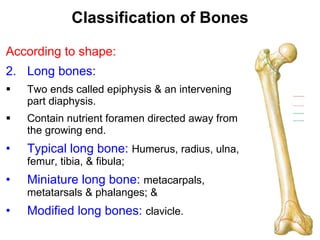
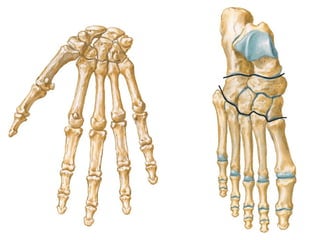
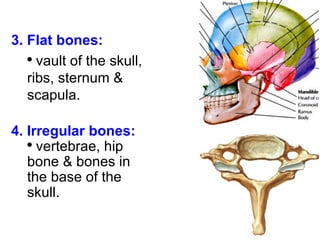
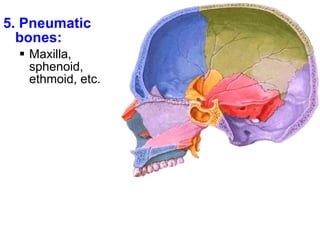
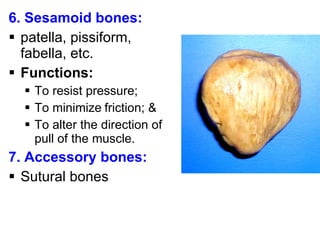
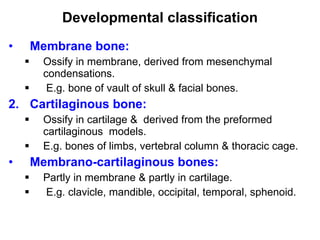
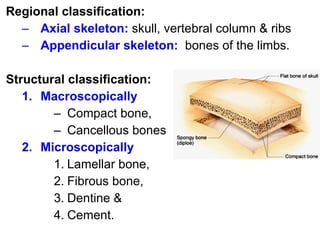
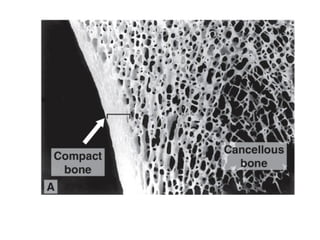
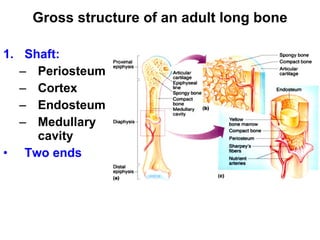
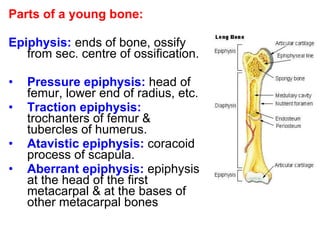
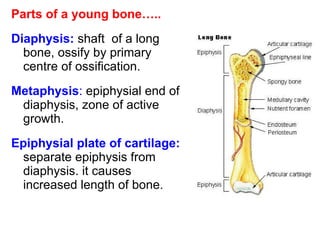
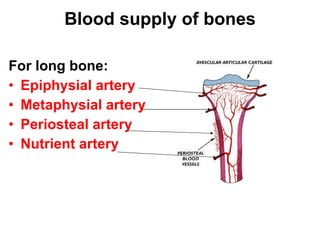
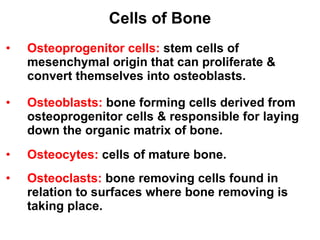
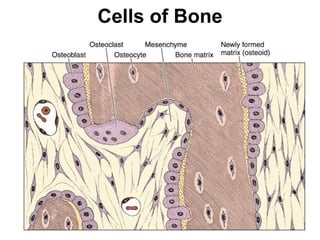
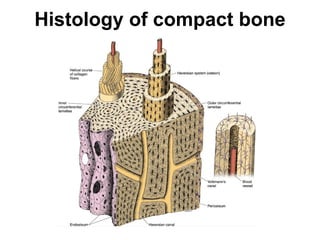
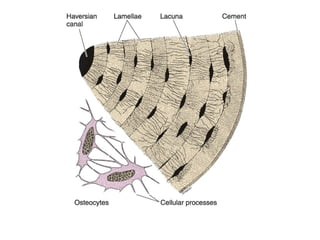
Cartilage and bone are composed of different types of cells and matrices. Cartilage includes hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage which are distinguished by their matrix composition and distributions in different parts of the body. Bone provides structure, protection and acts as a calcium reservoir. Bones are classified based on their shape, development, and location in the body. The histology of long bones includes a periosteum, cortex, endosteum, marrow cavity, and epiphyses at each end. Bone cells include osteoprogenitors, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts which play different roles in bone formation and resorption.