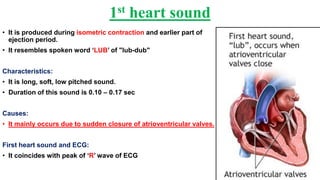
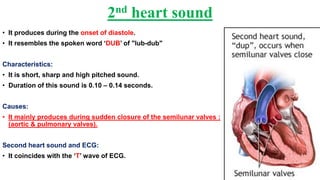
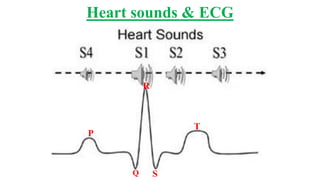
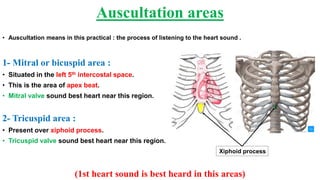
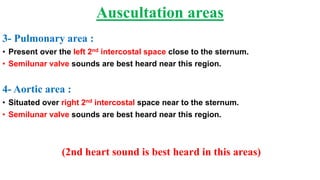
This document describes the four main heart sounds and how to auscultate them using a stethoscope. It explains that the first heart sound corresponds to closure of the atrioventricular valves and the R wave of an ECG. The second heart sound corresponds to closure of the semilunar valves and the T wave of an ECG. The third heart sound occurs during rapid ventricular filling between the T and P waves. The fourth heart sound corresponds to atrial contraction between the P and Q waves. It identifies the best areas over the heart to auscultate each sound using a stethoscope.