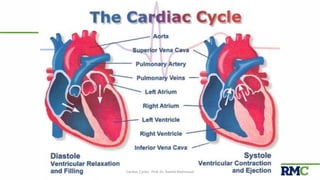
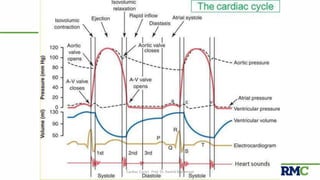
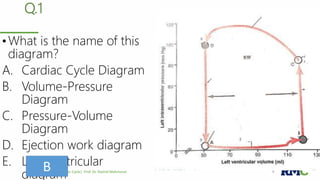
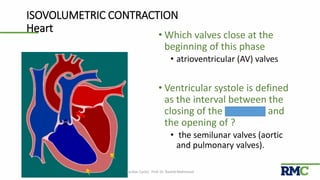
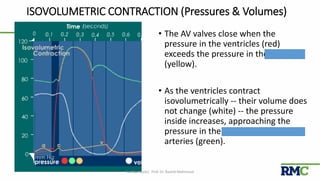
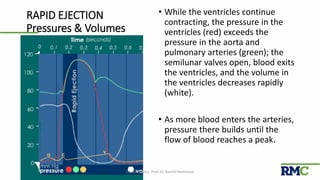
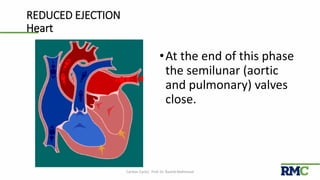
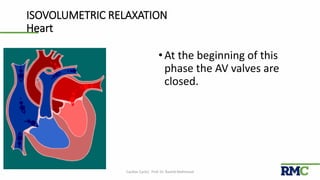
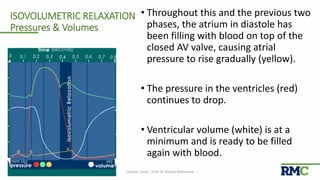
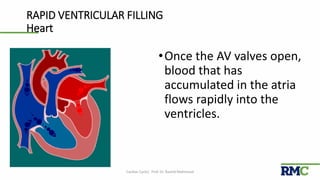
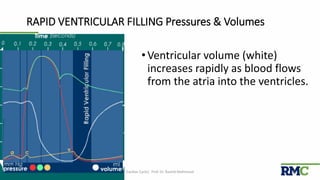
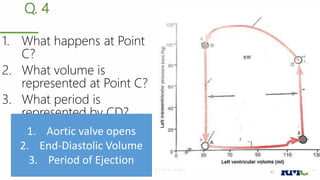
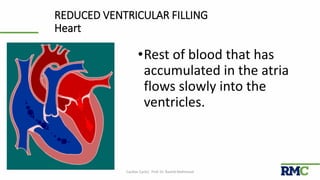
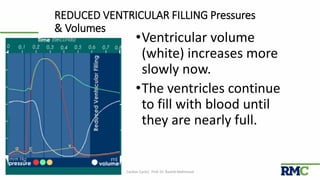
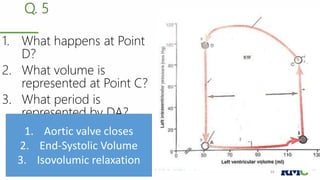
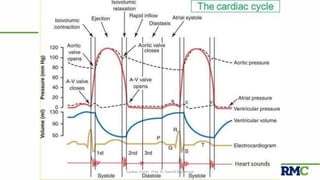
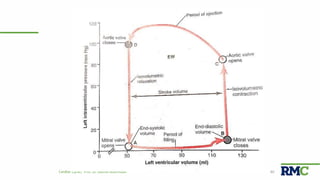
The cardiac cycle refers to the repeating sequence of events in the heart from one heartbeat to the next. It consists of systole, the contraction phase, followed by diastole, the relaxation phase. Systole includes isovolumic contraction, rapid ejection, and slow ejection as the ventricles contract and pump blood out. Diastole includes isovolumic relaxation, rapid filling, slow filling, and atrial systole as the ventricles relax and fill with blood. Key measurements of heart function include end-diastolic volume, end-systolic volume, stroke volume, and ejection fraction. The aortic and pulmonary valves close more forcefully than the atrioventricular valves.