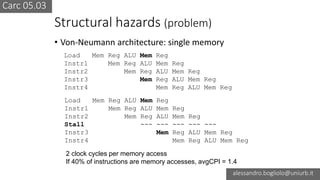
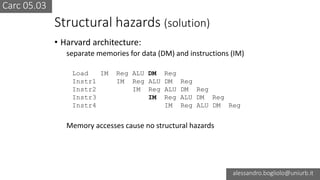
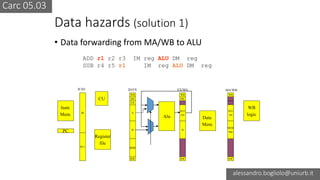
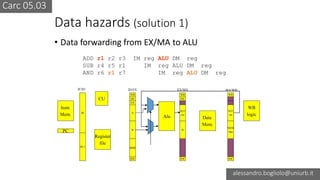
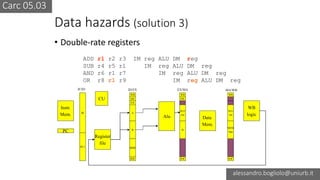
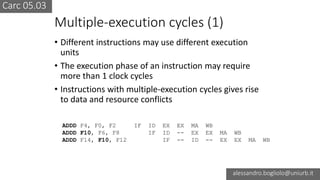
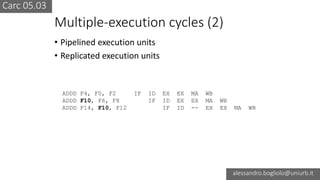
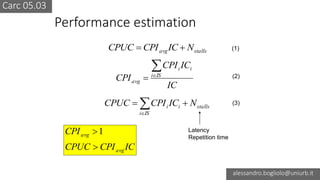
The document discusses various types of CPU pipeline hazards, including structural, data, and control-flow hazards, while proposing solutions for each. It explains structural hazards due to shared memory access and suggests the use of Harvard architecture to prevent them, alongside various techniques for addressing data hazards through methods such as data forwarding and utilizing multiple execution cycles. Additionally, it covers control-flow hazards and their solutions, including branch prediction techniques and delayed branches to enhance CPU performance.