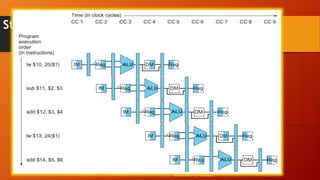
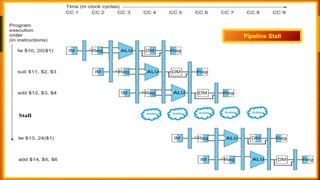
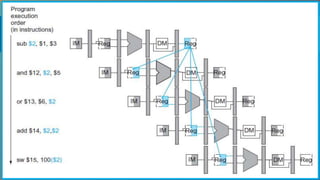
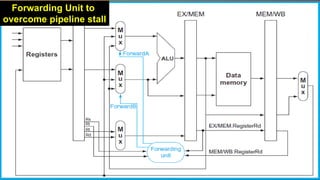
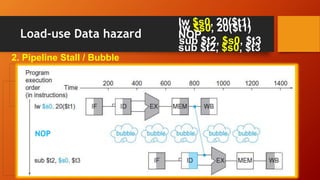
The document discusses different types of pipeline hazards including structural hazards, data hazards, and control hazards. It describes data hazards that occur due to dependencies between instructions as read after write, write after read, and write after write hazards. Methods to overcome data hazards include forwarding, stalling, and reordering instructions. Control hazards occur due to branches, and can be addressed through stalling, prediction, or delayed branching. Dynamic branch prediction uses 1-bit or 2-bit prediction schemes stored in a branch history table to more accurately predict branches.