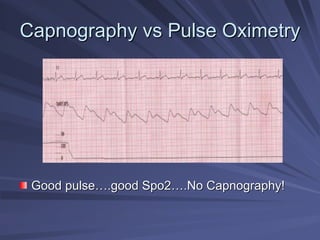
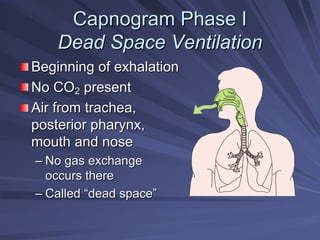
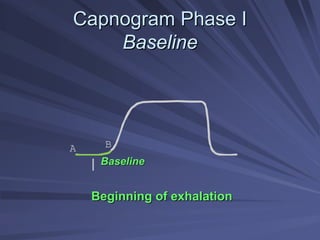
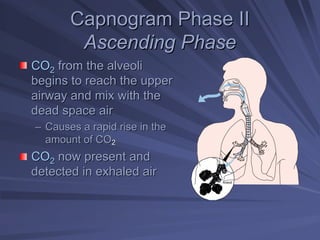
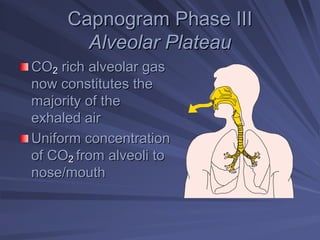
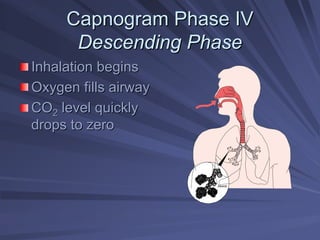
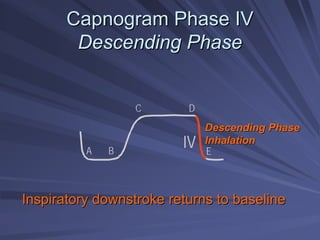
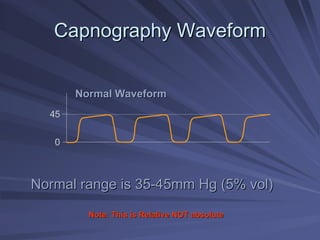
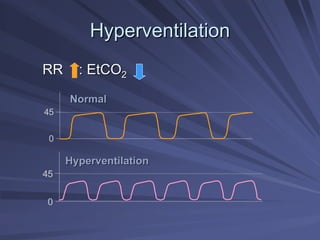
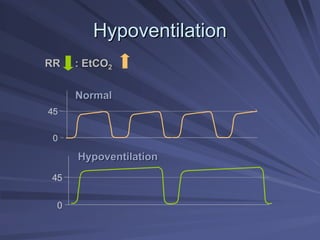
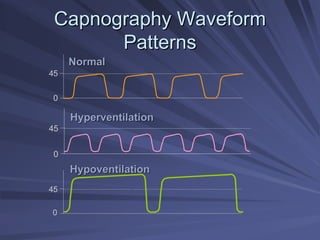
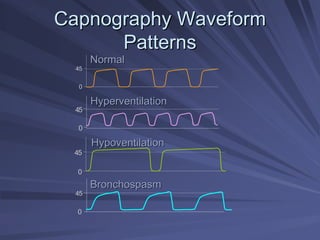
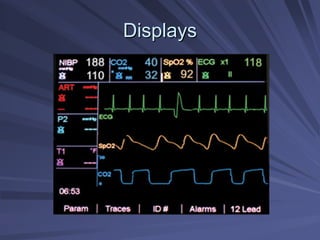
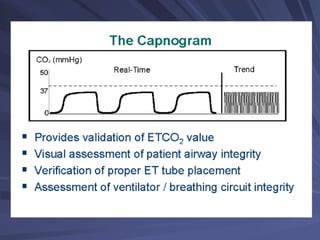
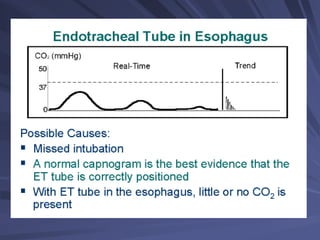
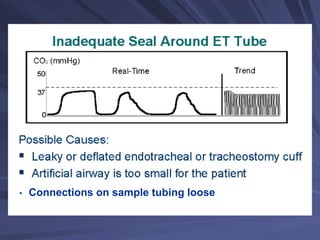
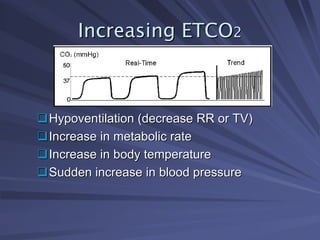
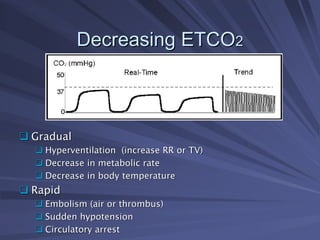
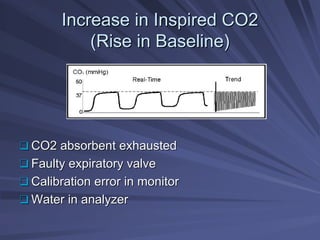
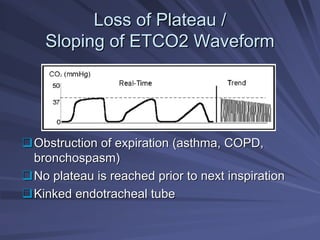
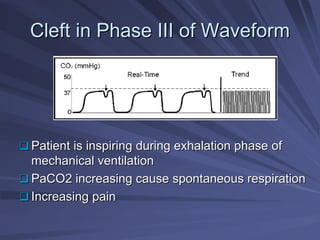
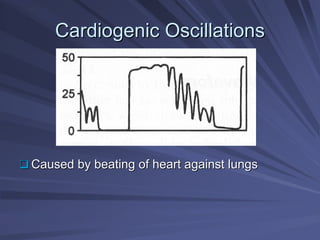
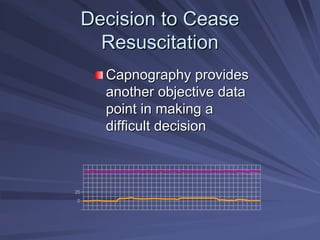
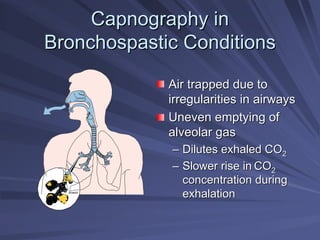
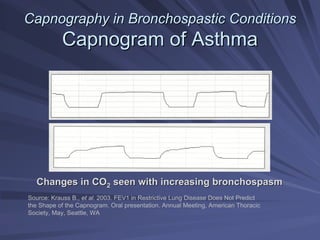
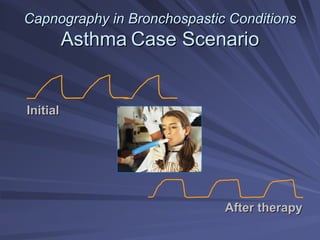
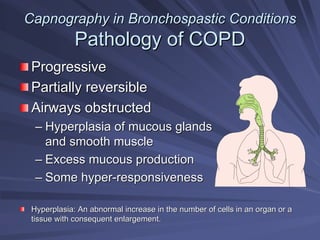
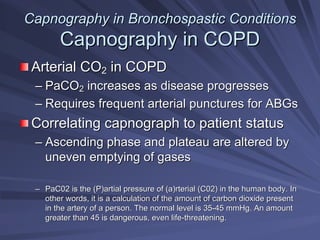
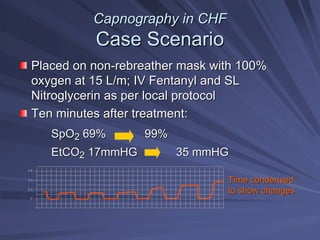
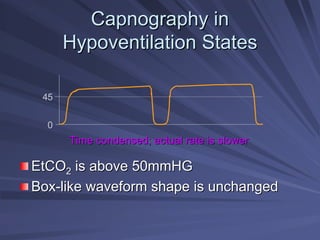
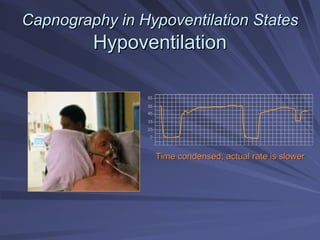
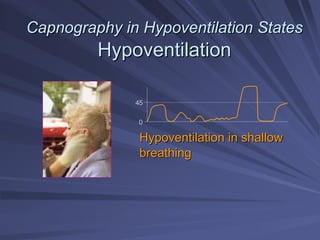
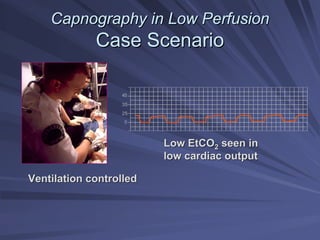
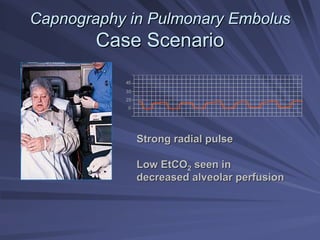
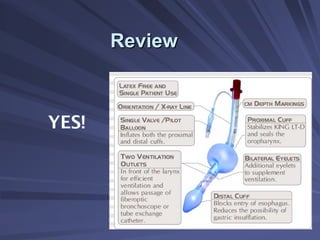
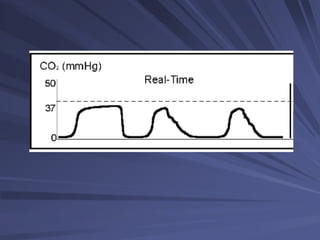
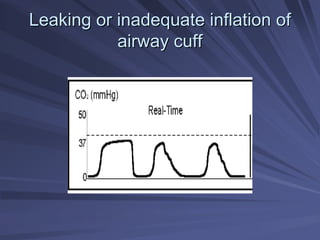
Capnography measures exhaled carbon dioxide (CO2) levels to assess ventilation and predict patient outcomes. It can assist with endotracheal tube placement confirmation and evaluation of CPR effectiveness. The capnographic waveform has four phases: phase I shows dead space ventilation with no CO2; phase II is the ascending phase as CO2 reaches the airway; phase III is the alveolar plateau with uniform CO2 concentration; phase IV is the descending phase as inhalation begins and CO2 levels drop. Conditions like hypoventilation and hyperventilation impact the waveform's frequency, duration, height and shape.