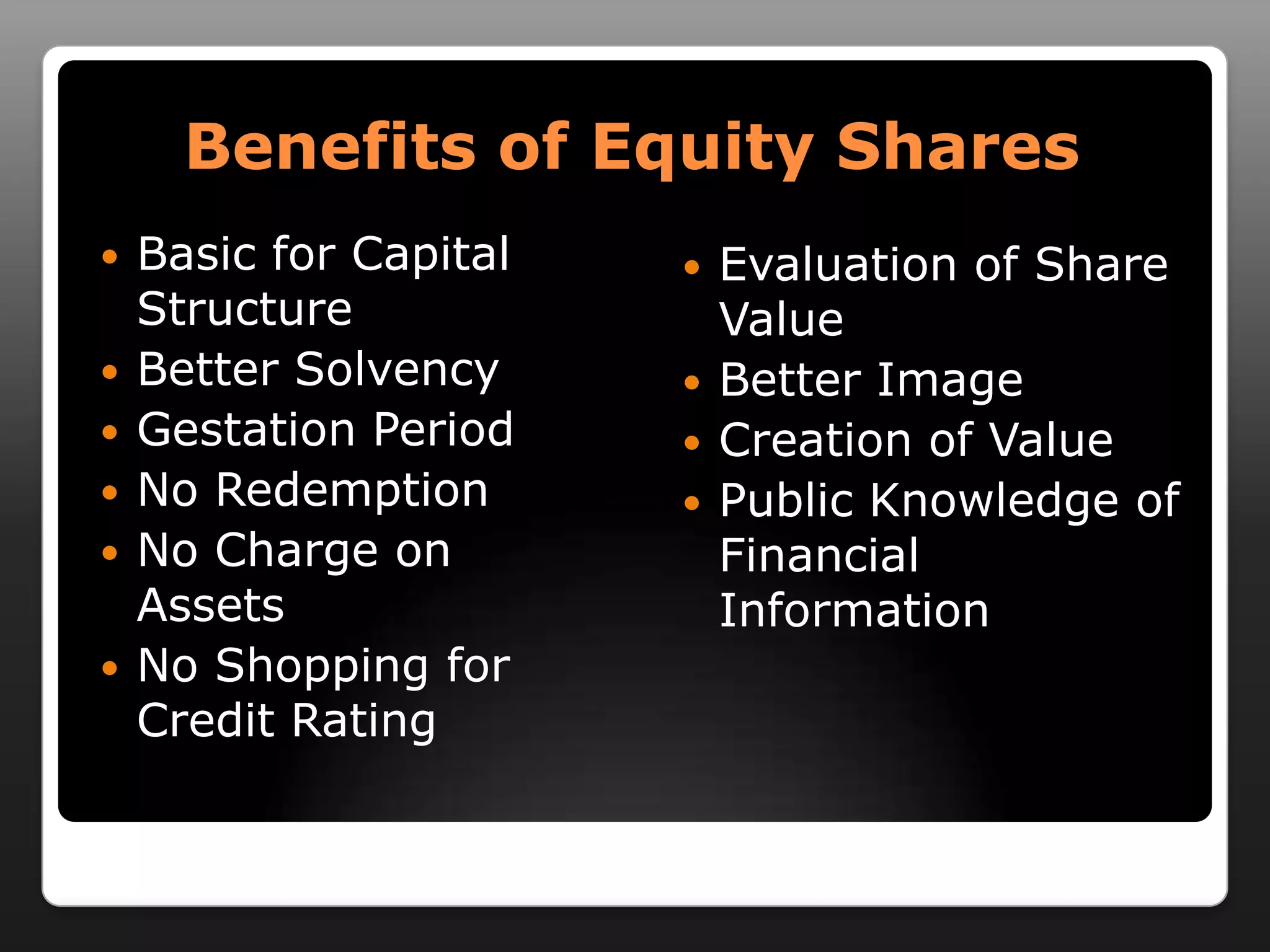
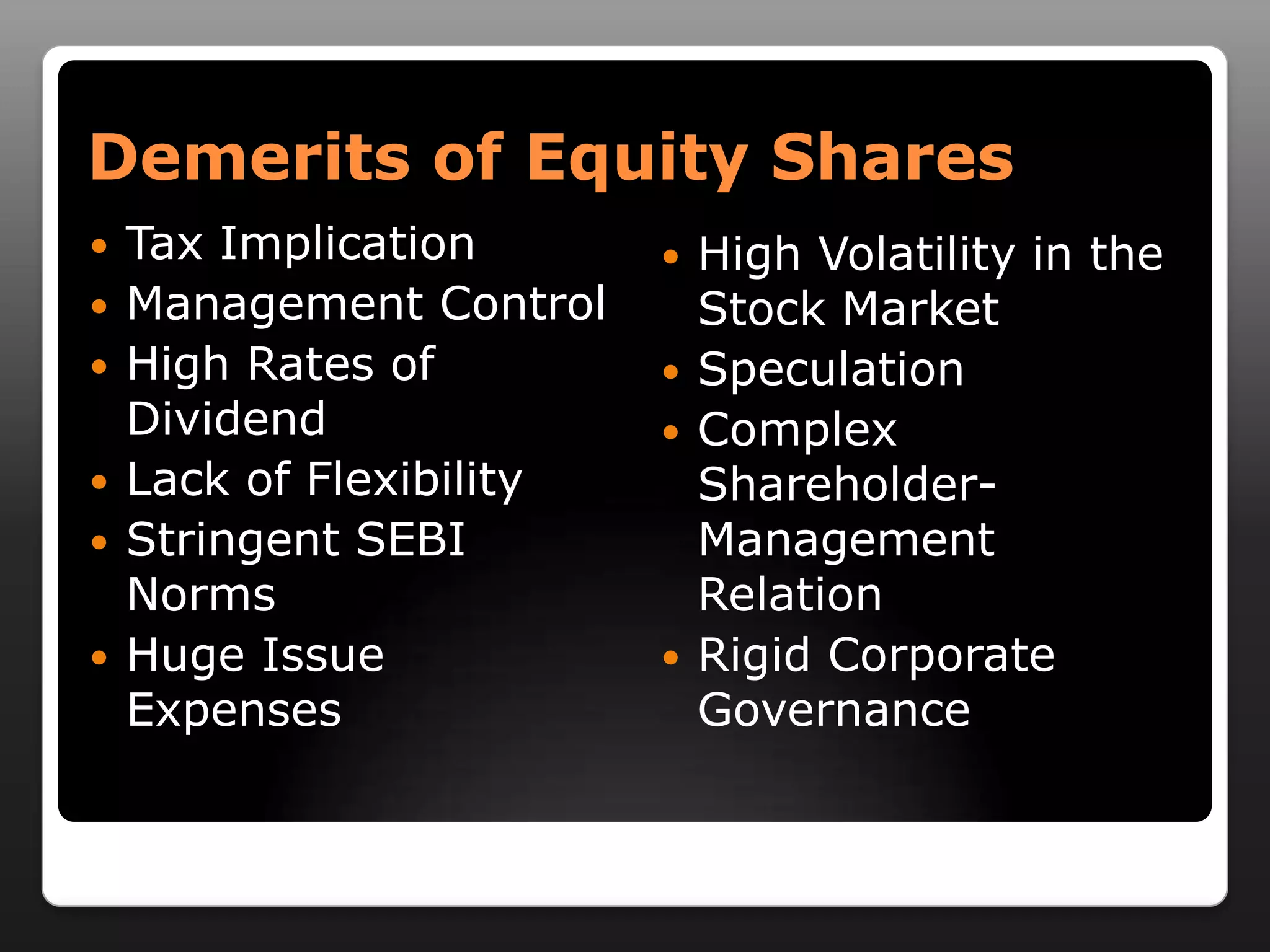
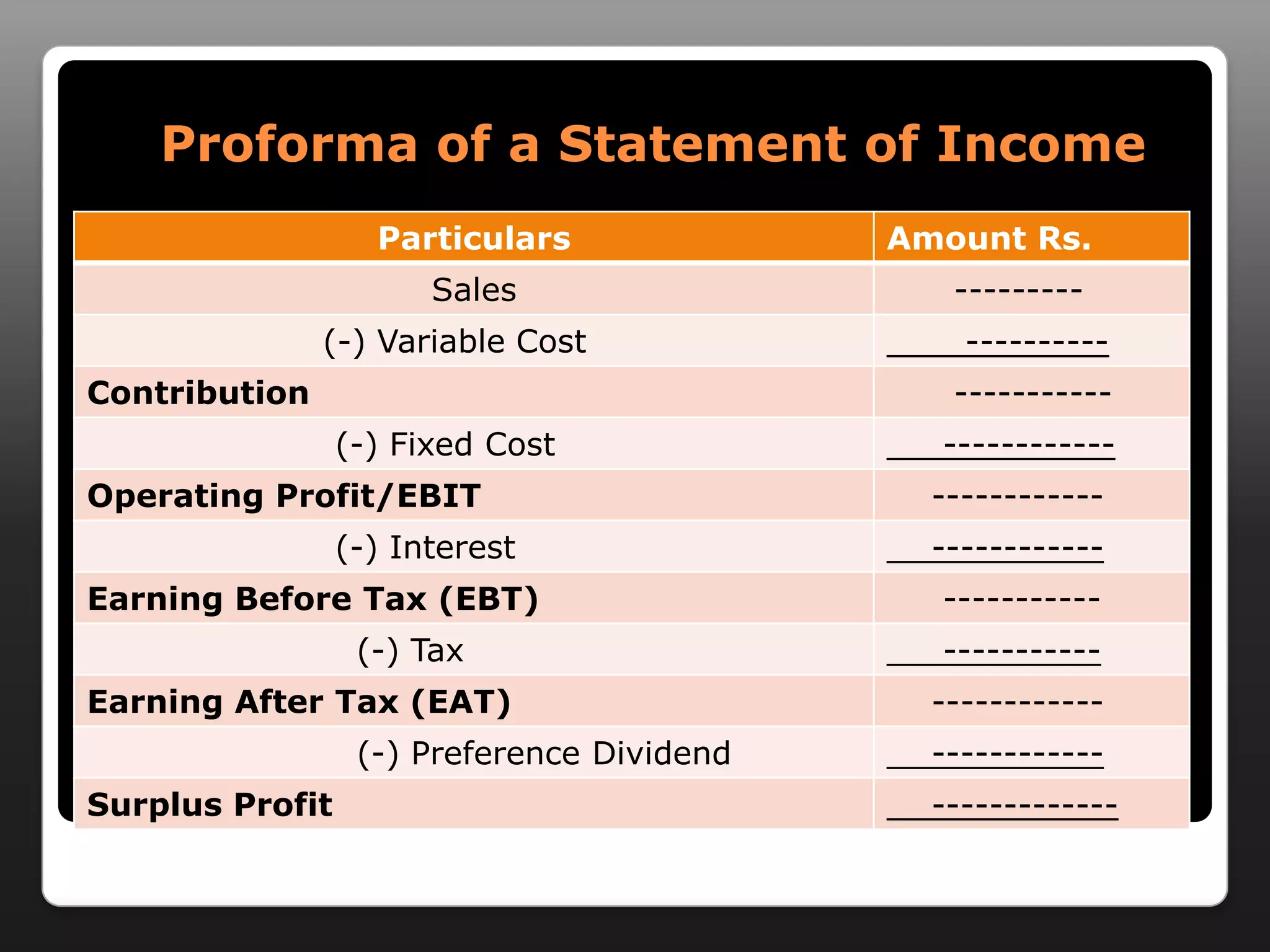
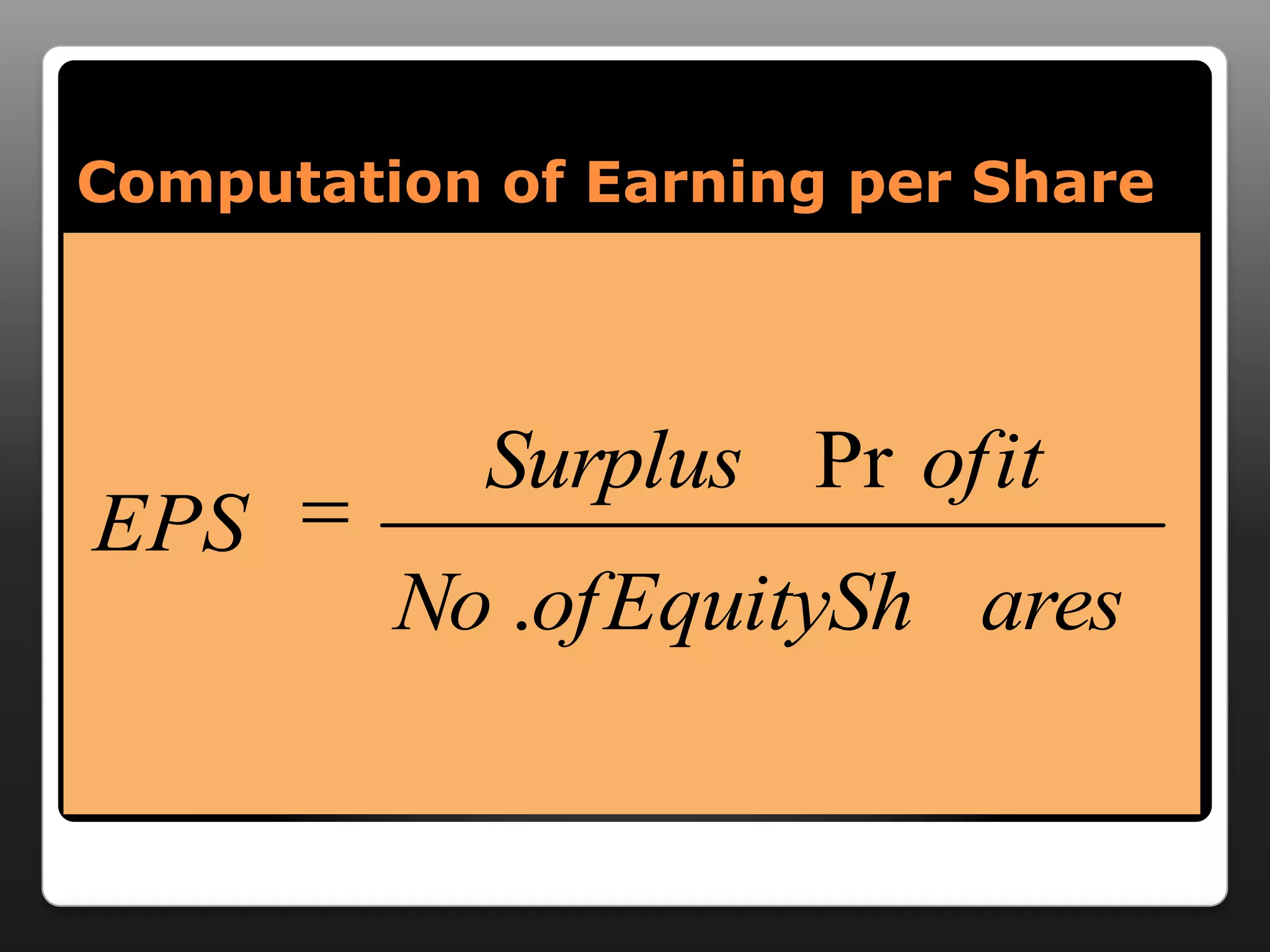
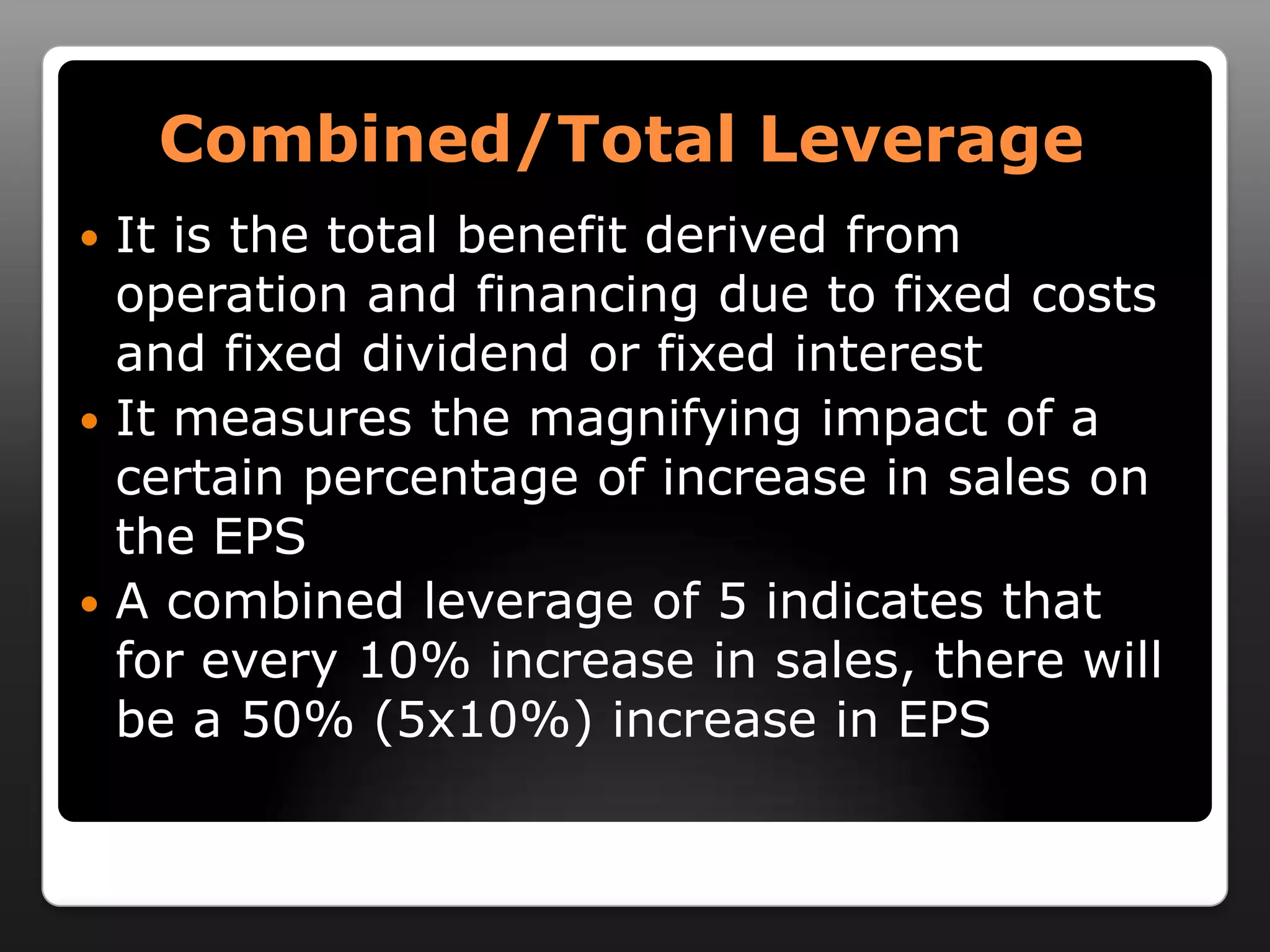
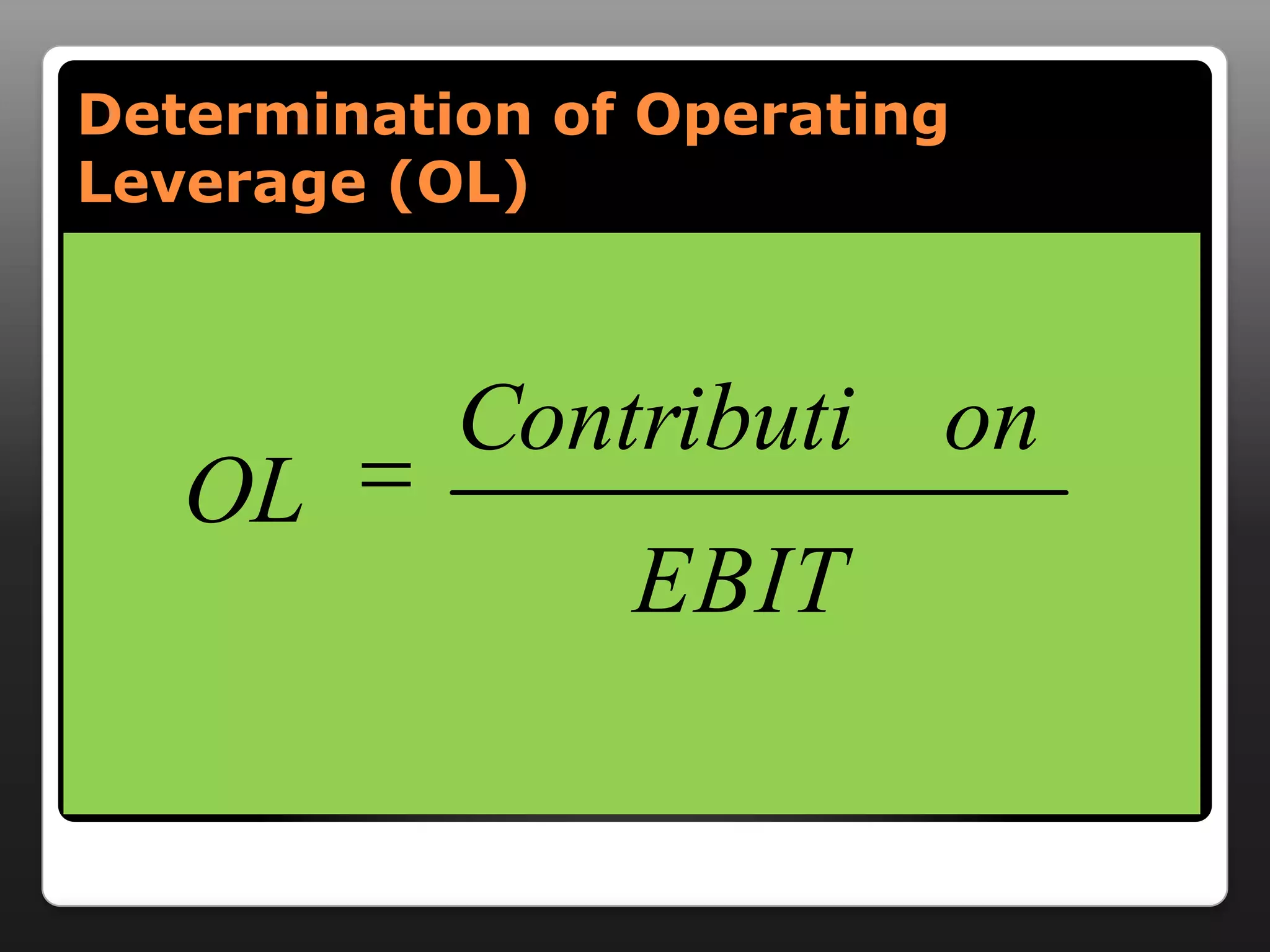
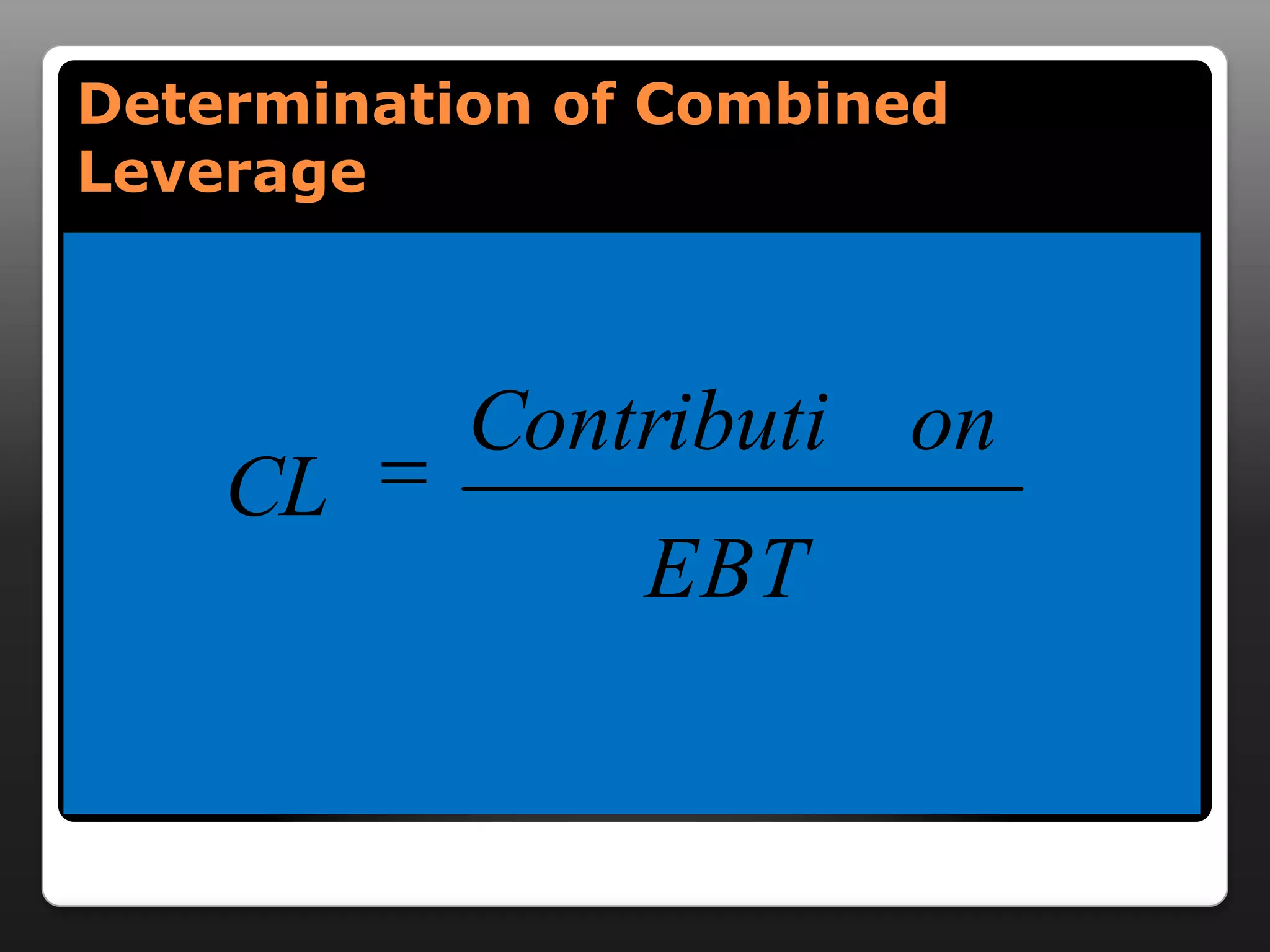
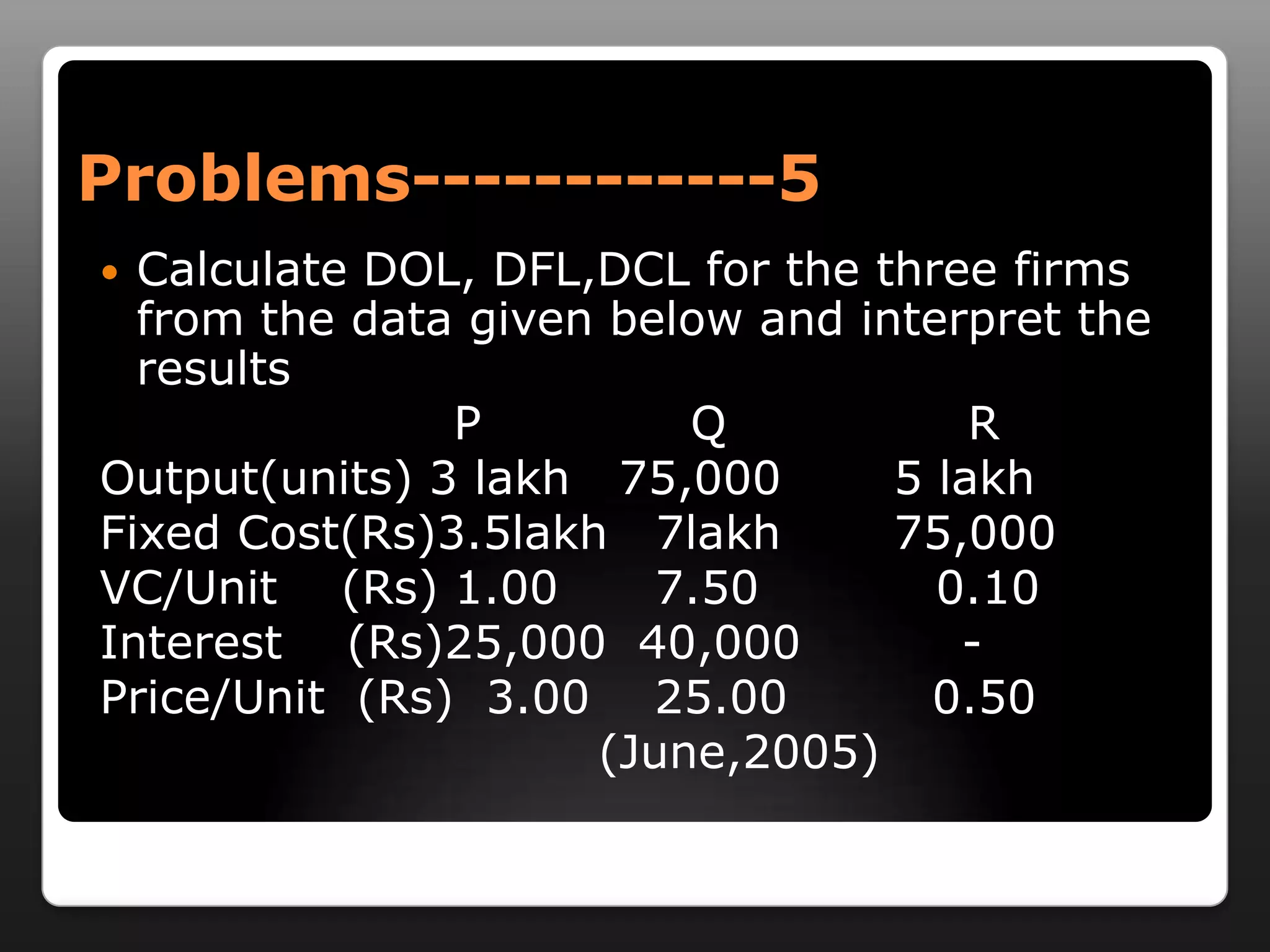
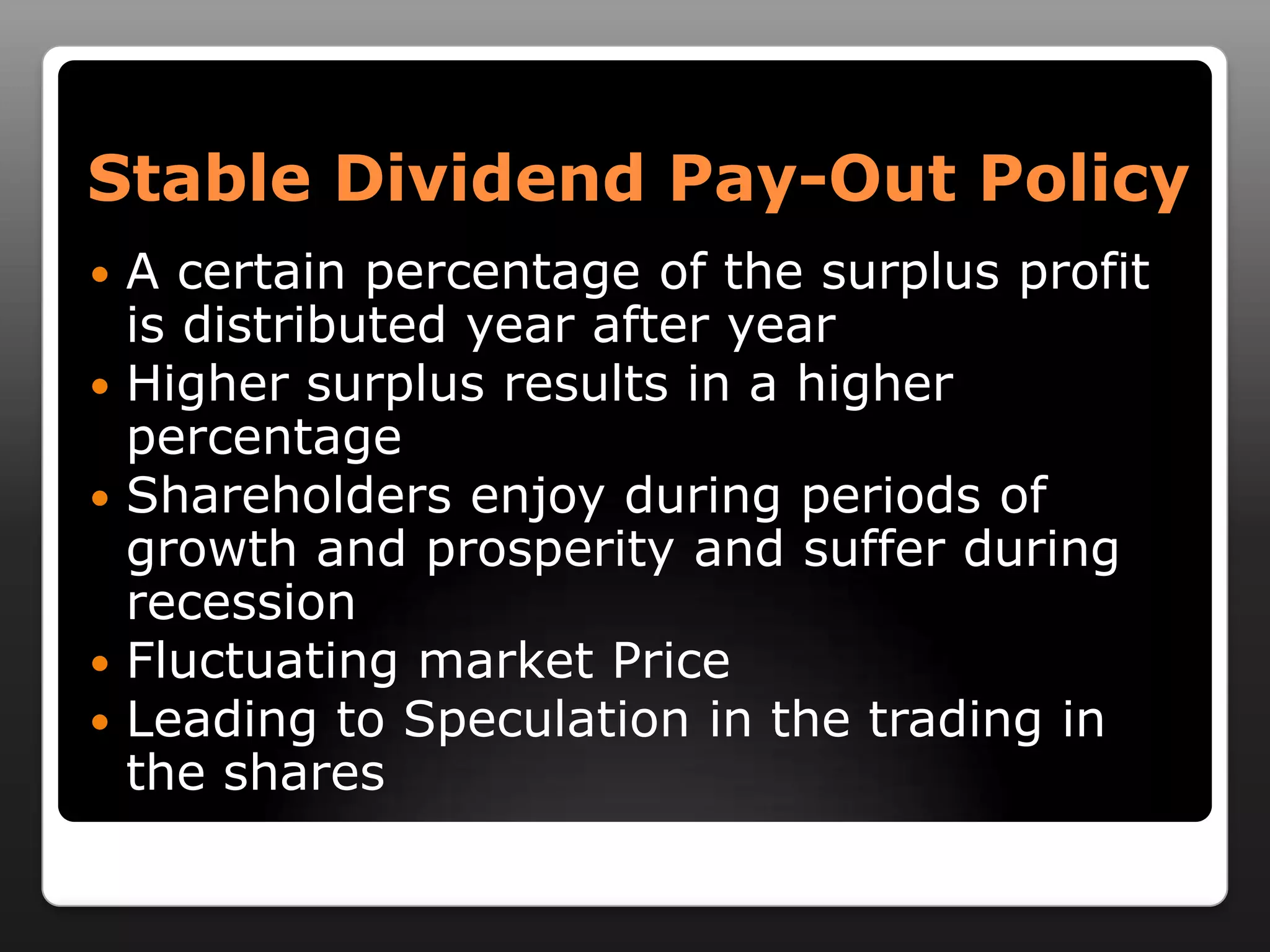
This document discusses capital structure and dividend policies. It defines capital structure as the permanent financing of a firm through long-term debt, preferred stock, and equity. It lists factors to consider when planning capital structure and describes the features, benefits, and drawbacks of debt and equity. It also discusses leverage, types of leverage including operating, financial, and combined leverage. Finally, it covers different dividend policies like stable dividend policy and stable dividend payout policy.