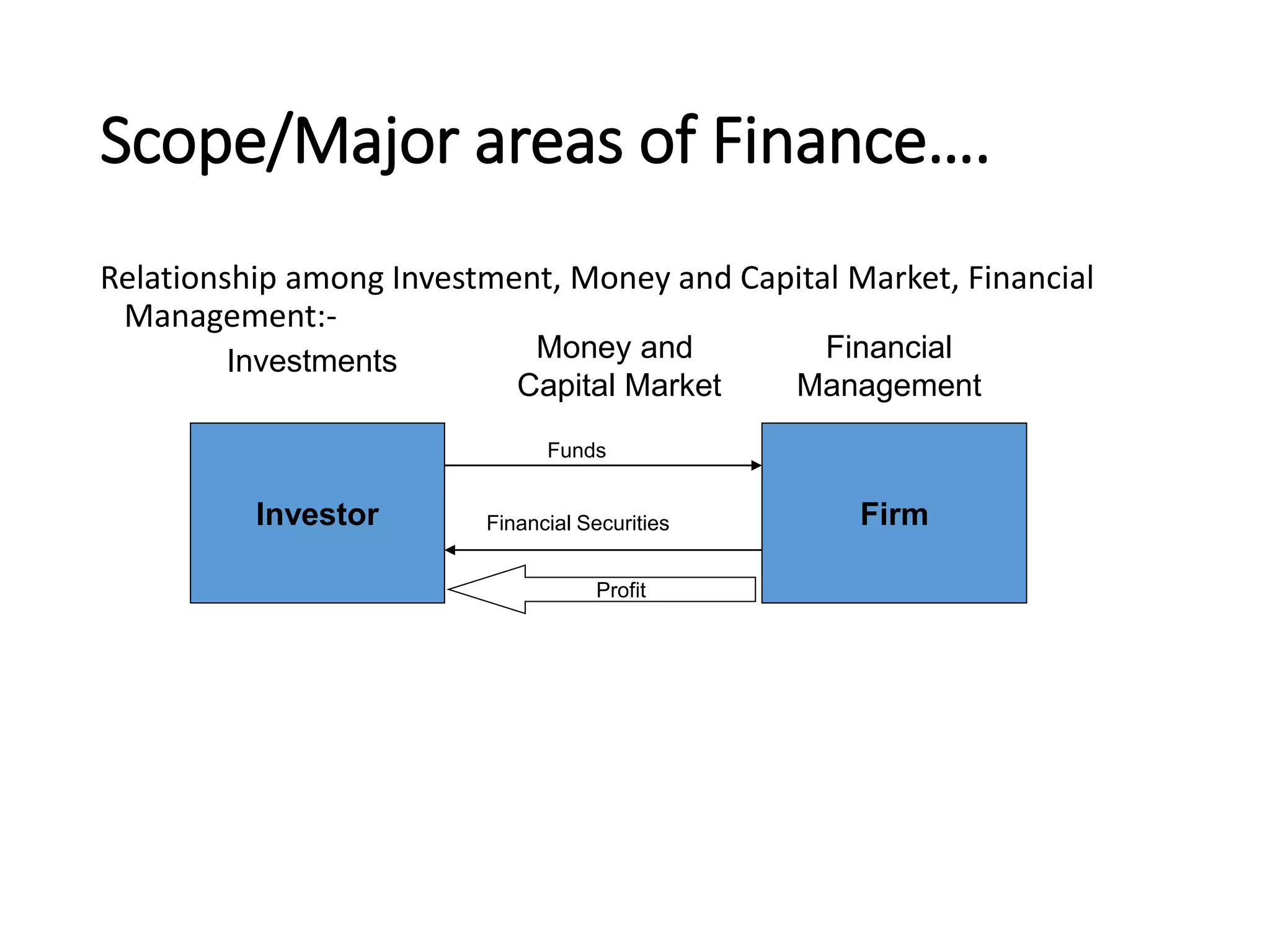
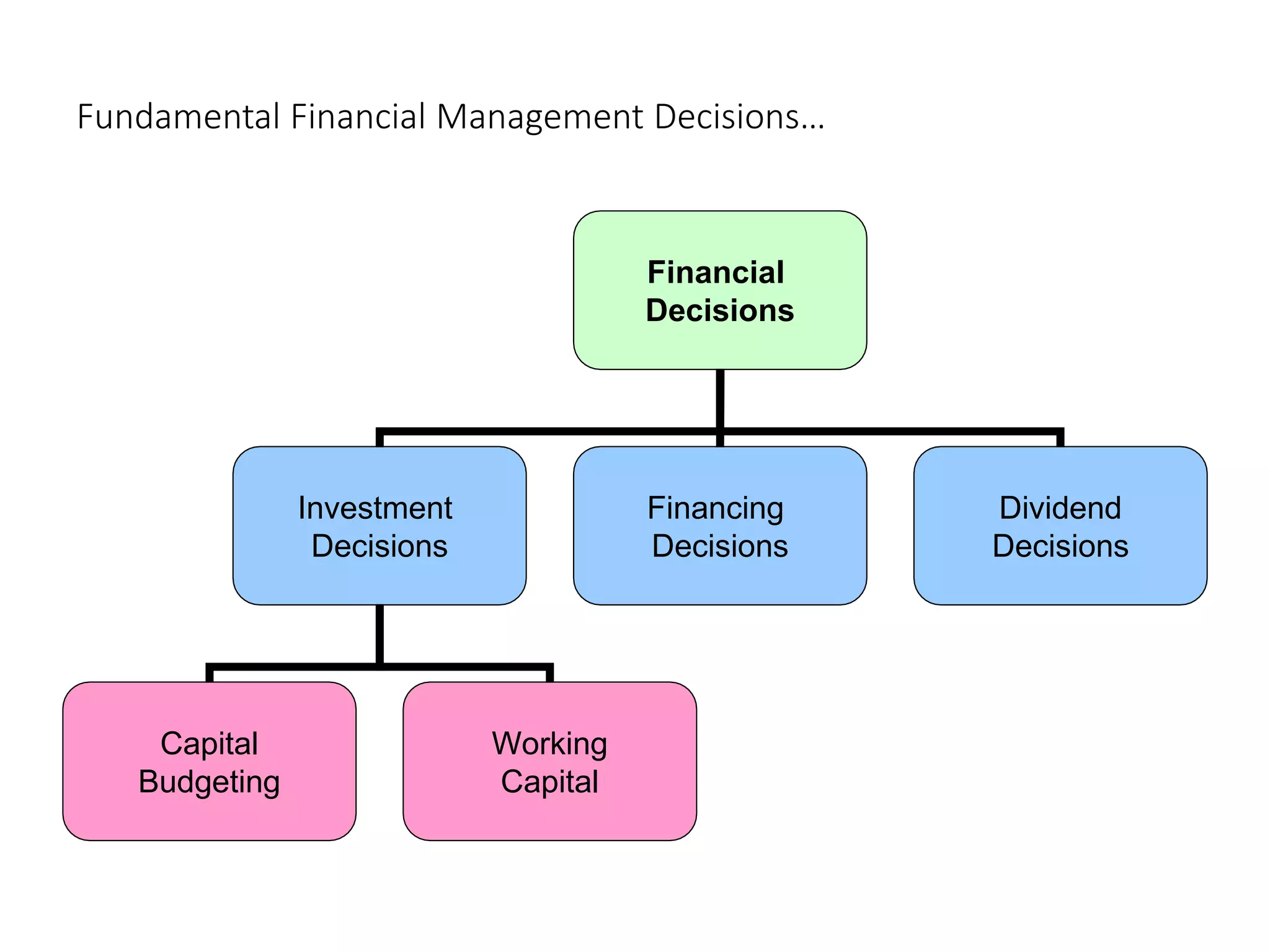
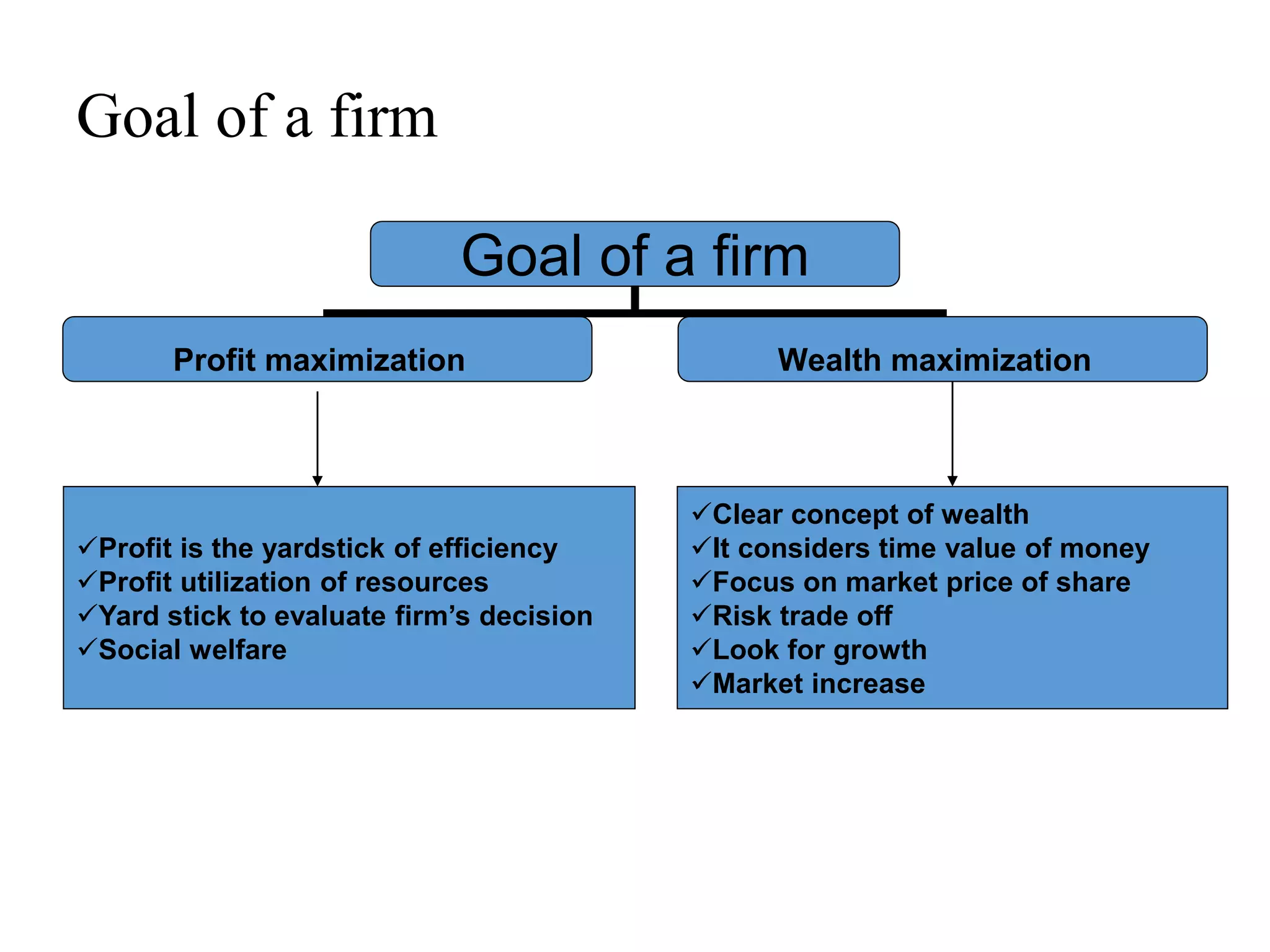
The document provides a comprehensive overview of finance, including its definition, major areas such as money markets, capital markets, and financial management. It covers the different categories of business finance, principles of finance, and the roles and goals of financial managers, while also addressing various business structures like sole proprietorships and corporations. Additionally, it discusses the agency theory and conflicts that may arise between shareholders and management.