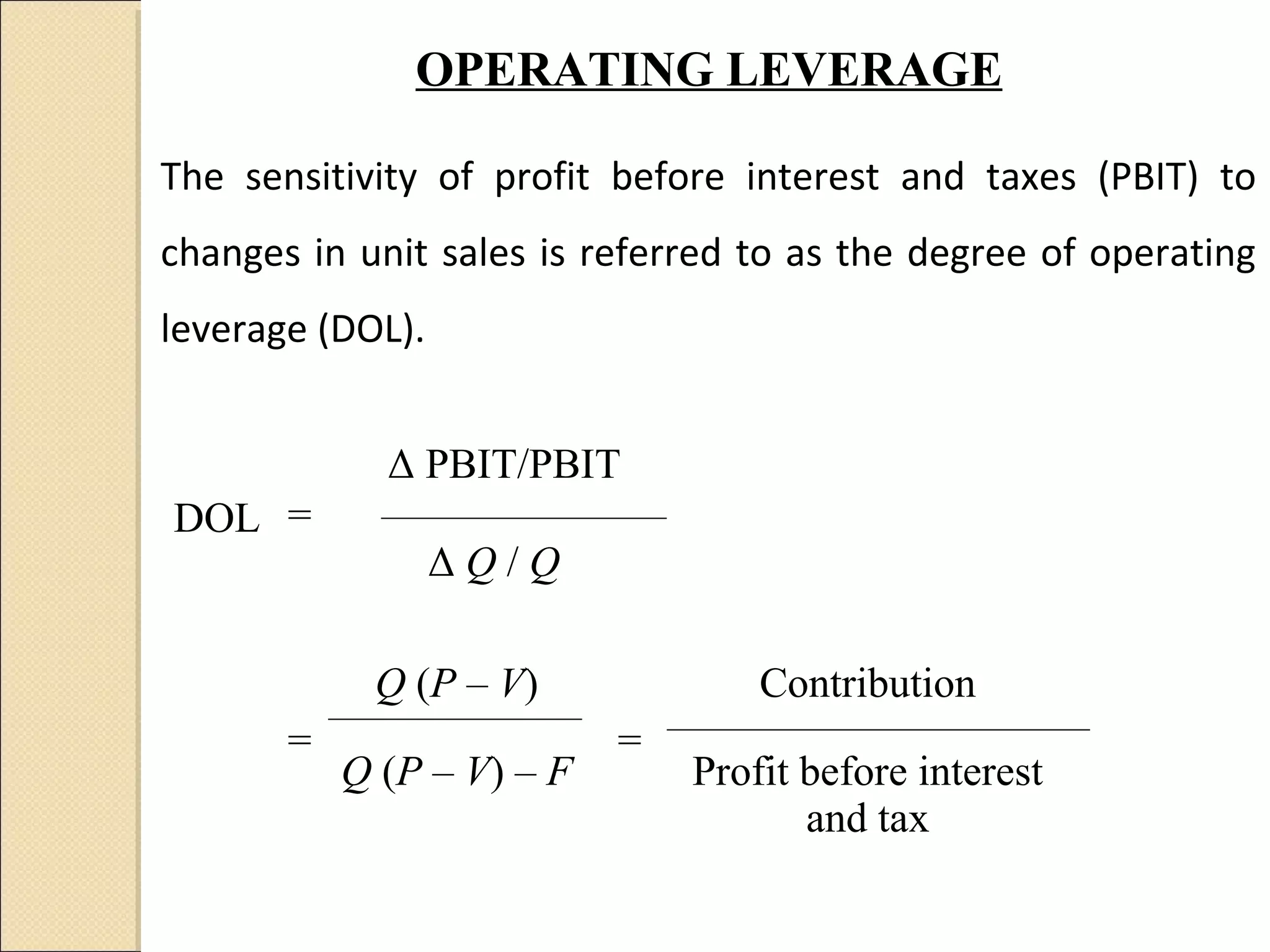
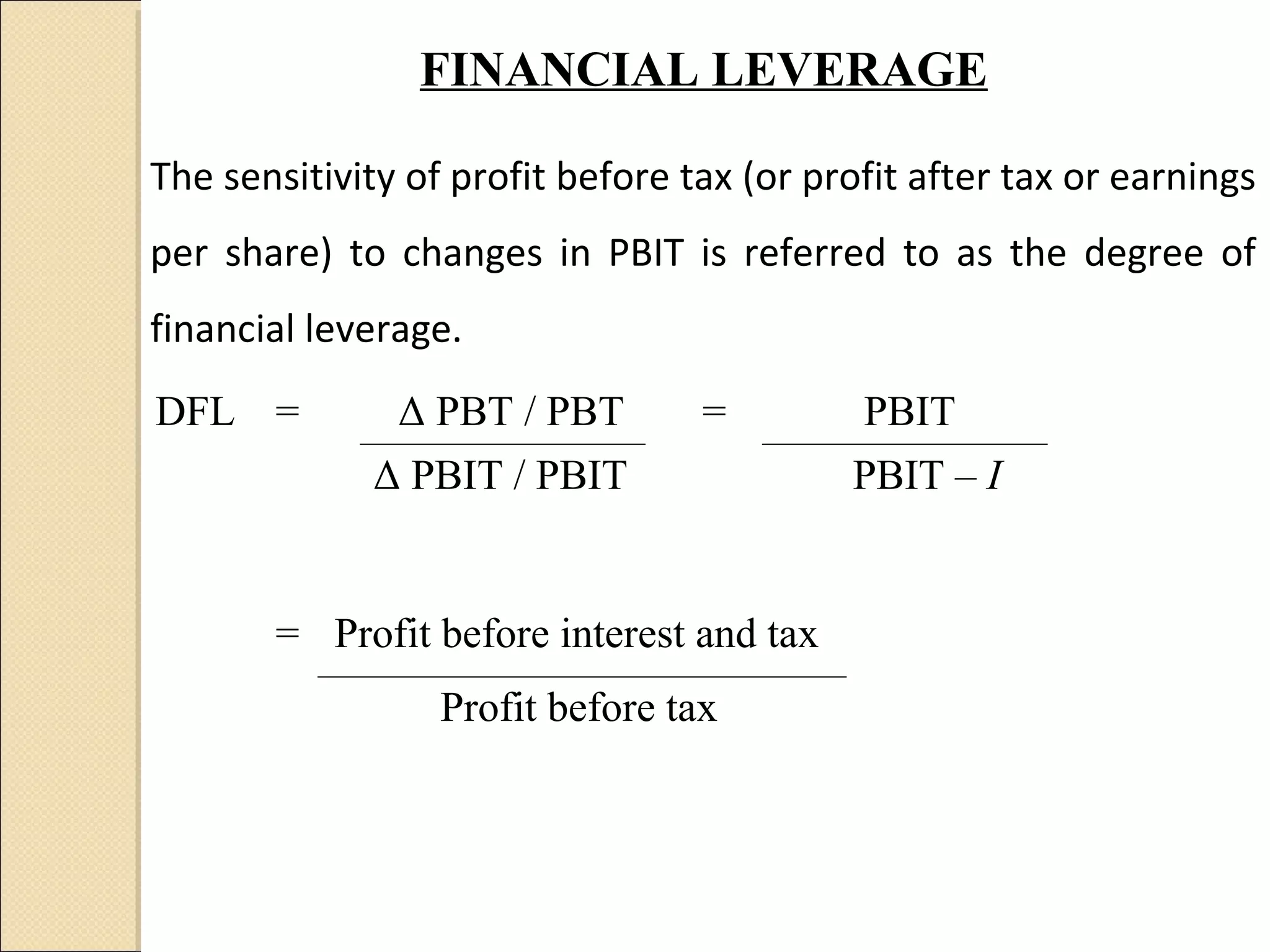
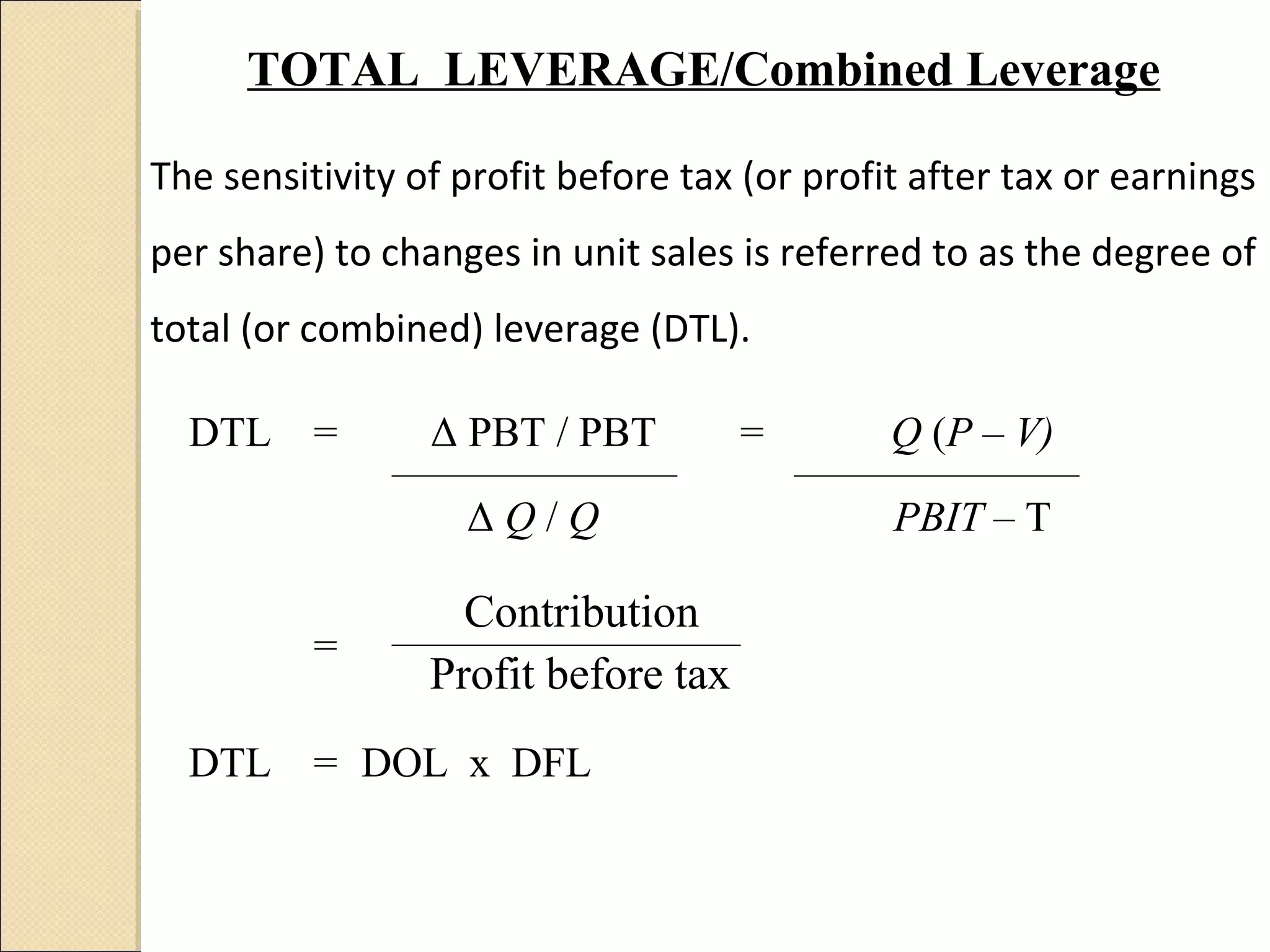
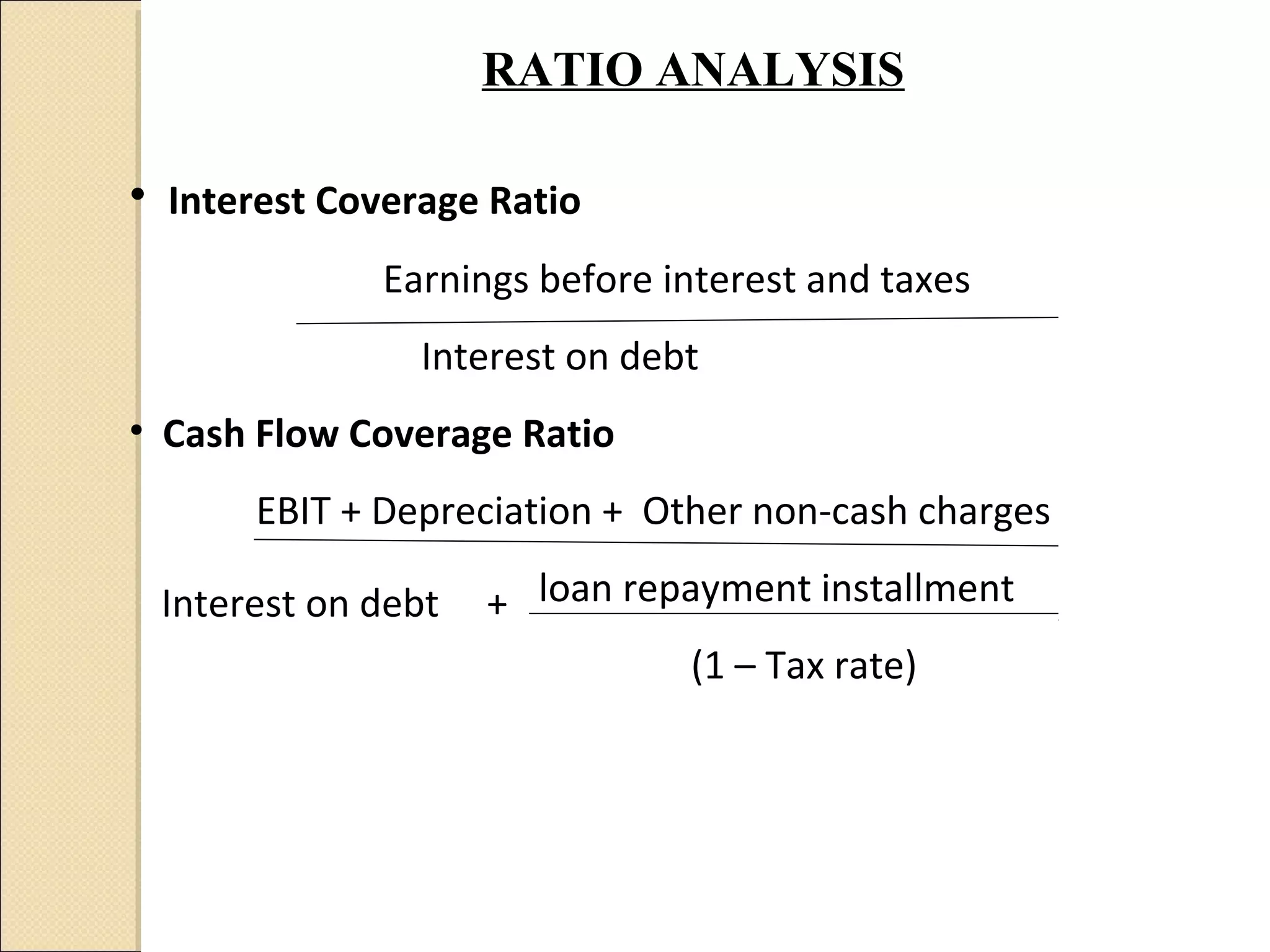
This document discusses capital structure decision making. It summarizes that business risk exists prior to financing decisions, while financial risk is added through the use of debt. Together these risks determine total corporate risk. It then outlines various analytical tools for evaluating capital structures, including EBIT-EPS analysis, leverage analysis, cash flow analysis, and comparative analysis against industry averages. Guidelines are provided for capital structure planning and common policies used in practice.




![ROI – ROE ANALYSIS
ROE = [ROI + (ROI – r) D/E] (1 – t)
where ROE = return on equity
ROI = return on investment
r = cost of debt
D/E = debt-equity ratio
t = tax rate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capitalstructuredecision-130416044928-phpapp02/75/Capital-structure-decision-6-2048.jpg)

![CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS
PBIT = Q (P – V) – F
PAT = (PBIT – I) ( 1 – T)
(PBIT – I) (1 – T) – Dp
EPS =
N
= [Q (P – V) – F – I] (1 – T) – Dp
N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capitalstructuredecision-130416044928-phpapp02/75/Capital-structure-decision-9-2048.jpg)