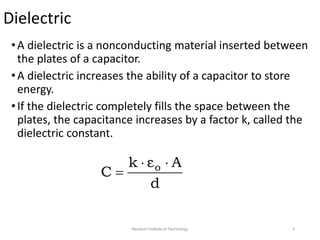
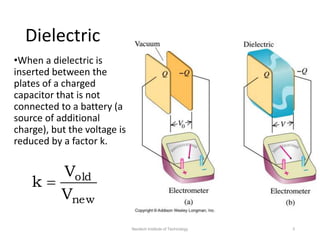
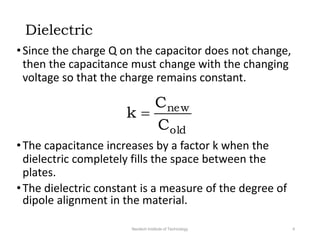
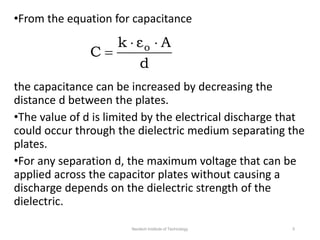
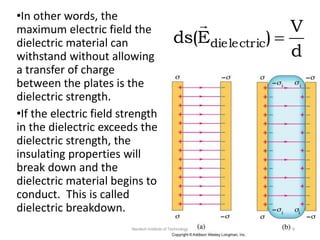
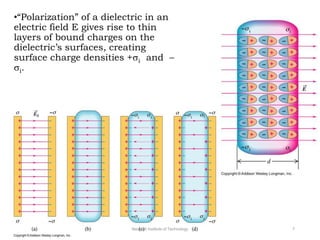
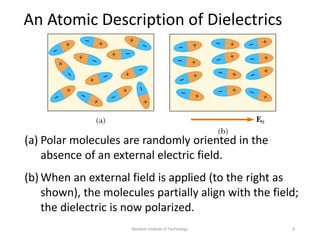
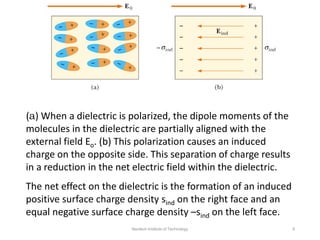
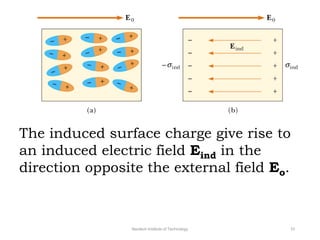
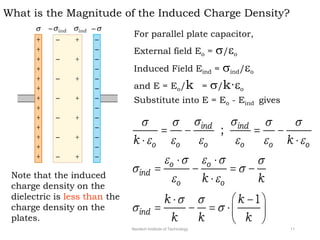
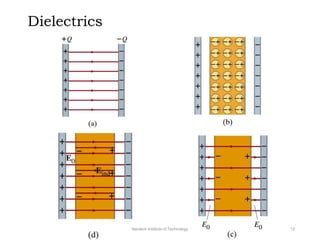
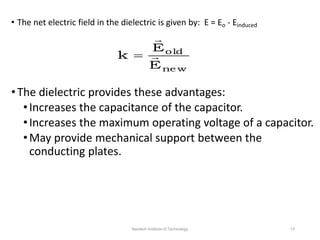
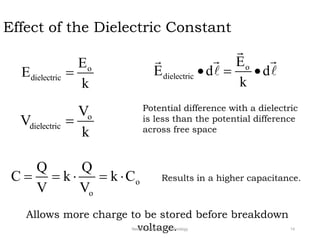
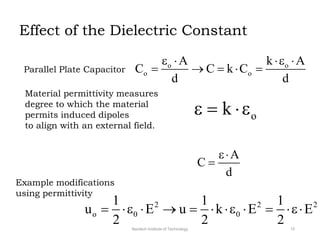
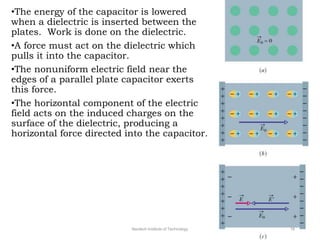
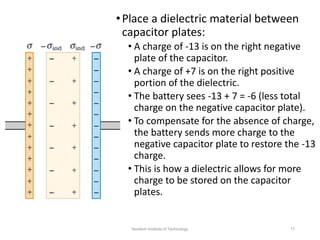
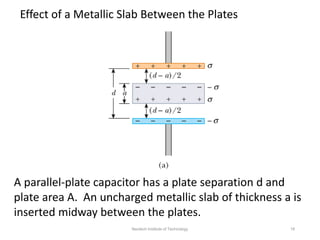
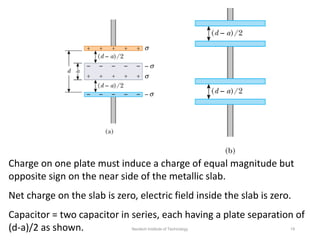
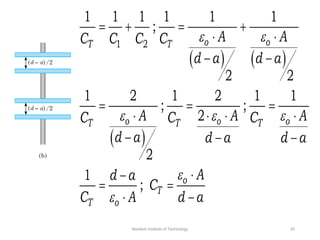
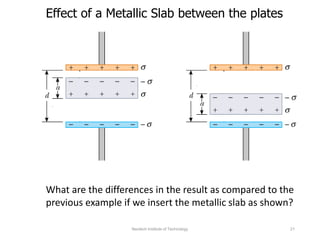
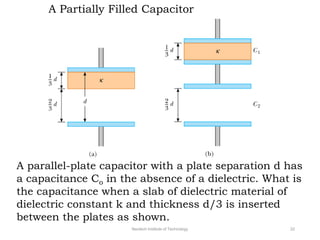
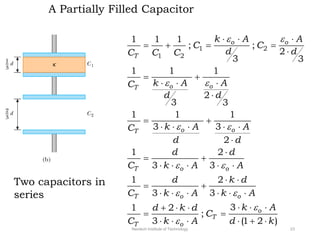
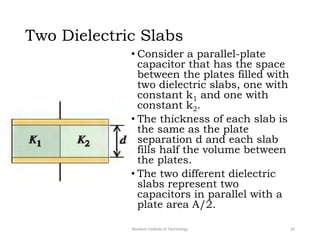
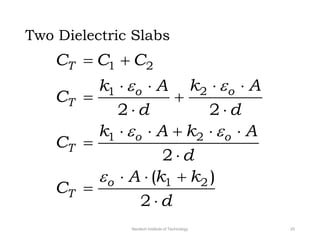
The document discusses capacitors with dielectrics, detailing the properties and effects of inserting dielectrics between capacitor plates, including how they increase capacitance and the maximum operating voltage. It explains concepts such as dielectric constant, polarization, and dielectric strength, alongside the implications of using metallic slabs and partially filled capacitors. The analysis is supported by equations describing capacitance changes and the behavior of electric fields in the presence of dielectrics.